Mathematics of Ions in Channels and Solutions: Stochastic Derivations, Direct, Variational and Inverse Solutions that fit Data
Mathematics of Molecular Biology
-
 1. Mathematics of Molecular Biolo…
0
00:00/00:00
1. Mathematics of Molecular Biolo…
0
00:00/00:00 -
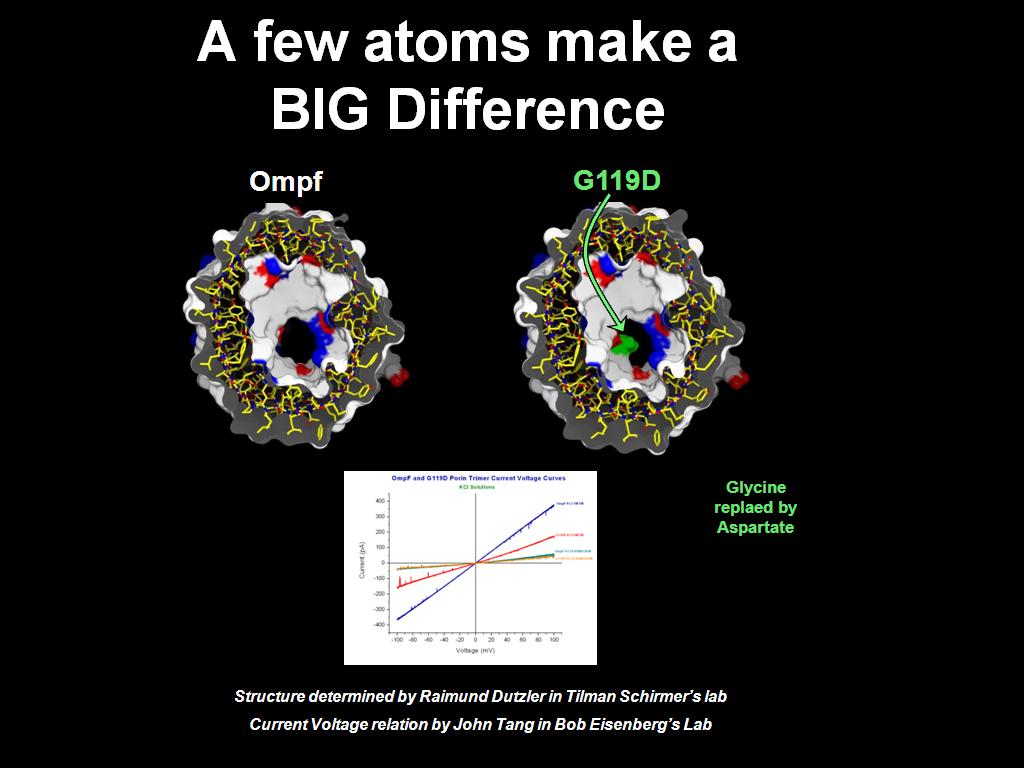 2. A few atoms make a BIG Differe…
199.83316649983317
00:00/00:00
2. A few atoms make a BIG Differe…
199.83316649983317
00:00/00:00 -
 3. General Theme Mathematics of M…
375.67567567567568
00:00/00:00
3. General Theme Mathematics of M…
375.67567567567568
00:00/00:00 -
 4. How does it work?
481.51484818151488
00:00/00:00
4. How does it work?
481.51484818151488
00:00/00:00 -
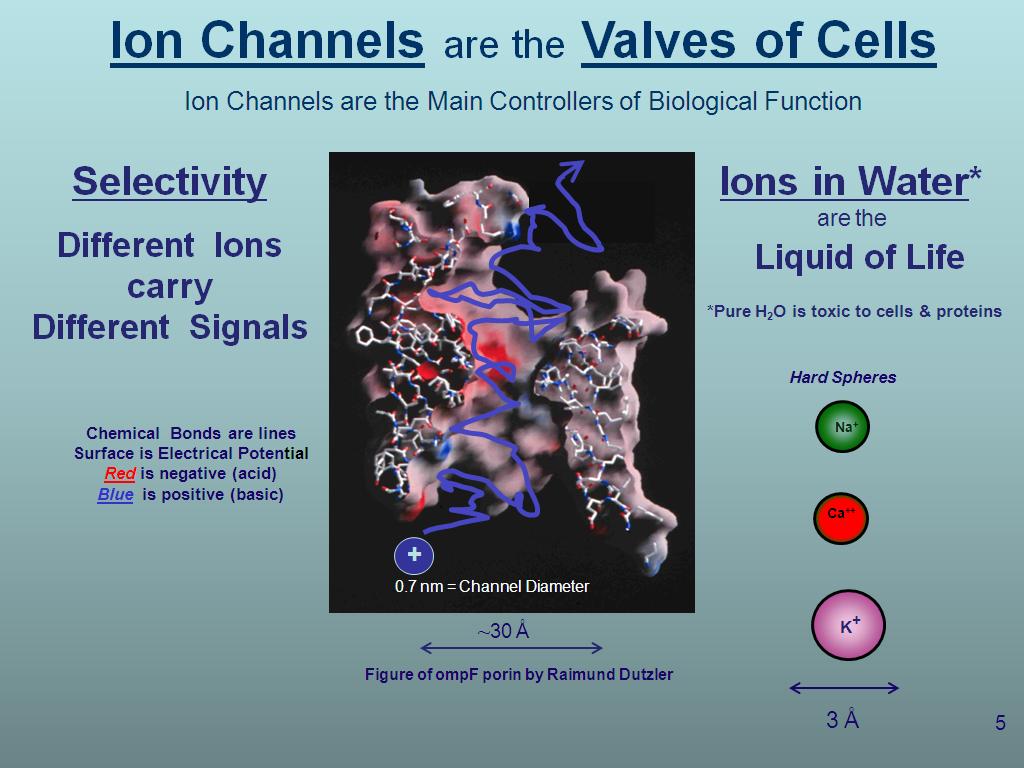 5. Ion Channels are the Valves of…
488.98898898898904
00:00/00:00
5. Ion Channels are the Valves of…
488.98898898898904
00:00/00:00 -
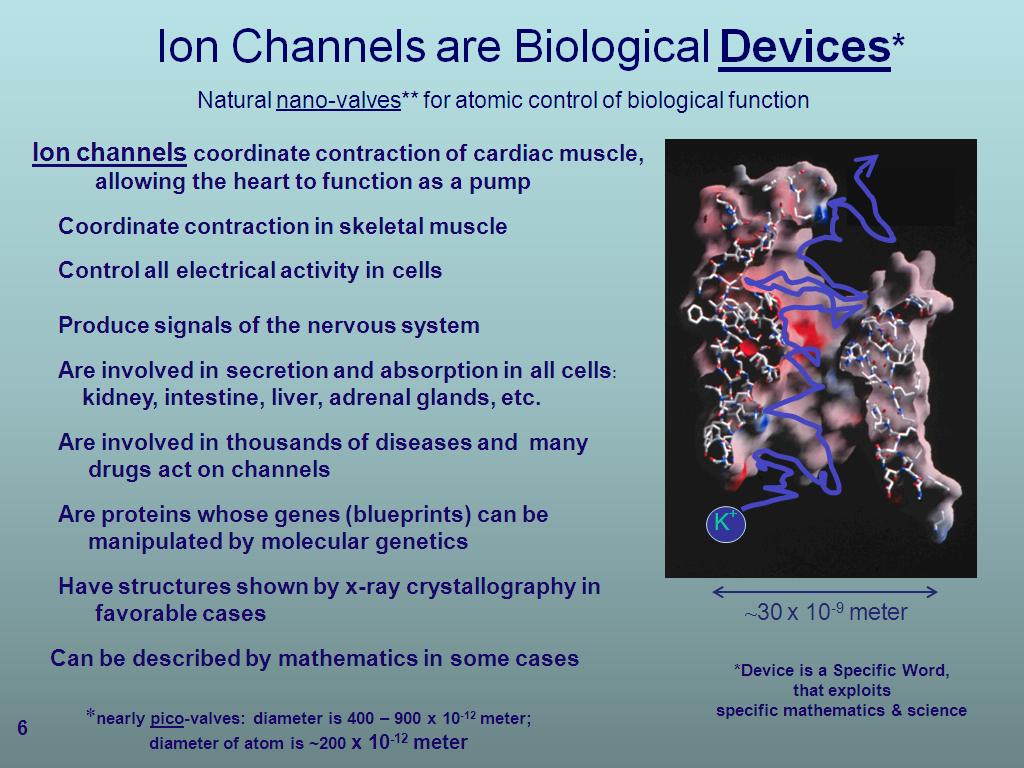 6. Ion Channels are Biological De…
714.18084751418087
00:00/00:00
6. Ion Channels are Biological De…
714.18084751418087
00:00/00:00 -
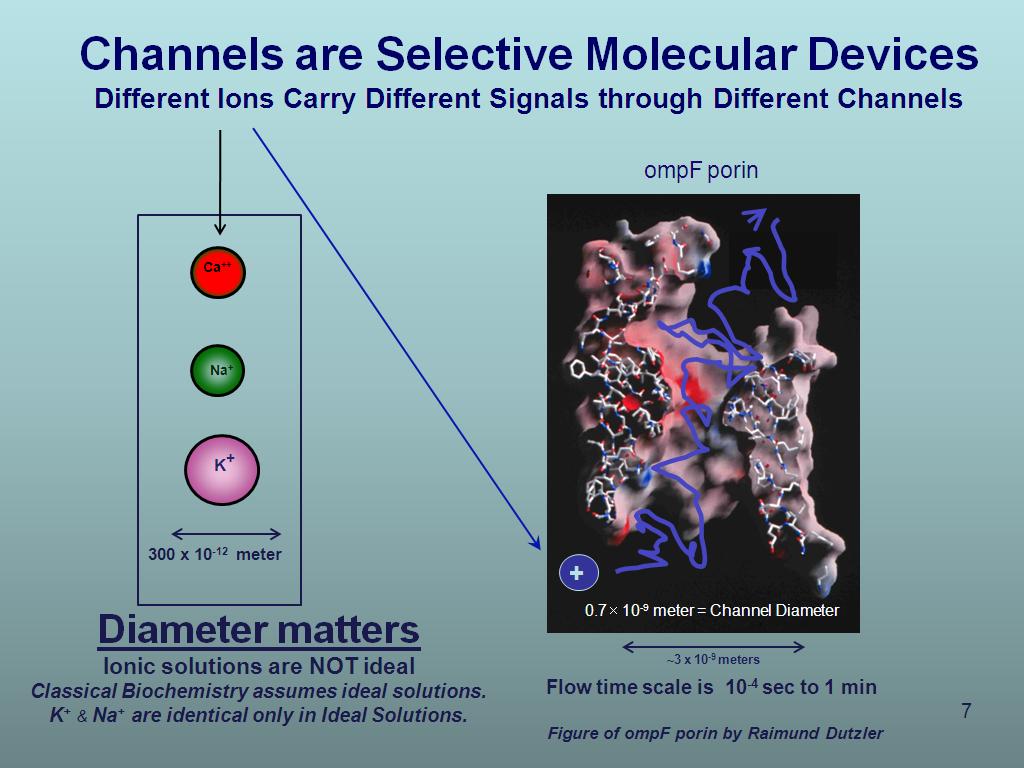 7. Channels are Selective Molecul…
1273.8071404738073
00:00/00:00
7. Channels are Selective Molecul…
1273.8071404738073
00:00/00:00 -
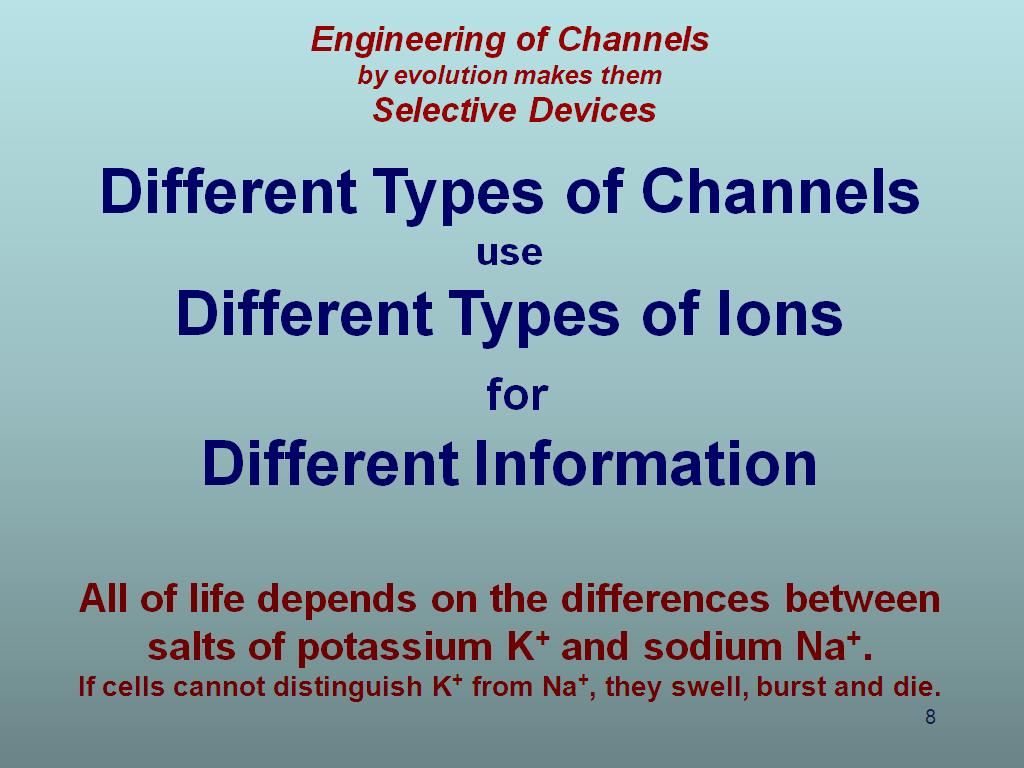 8. Different Types of Channels us…
1275.342008675342
00:00/00:00
8. Different Types of Channels us…
1275.342008675342
00:00/00:00 -
 9. Multi-Scale Issues are Always …
1298.4651317984651
00:00/00:00
9. Multi-Scale Issues are Always …
1298.4651317984651
00:00/00:00 -
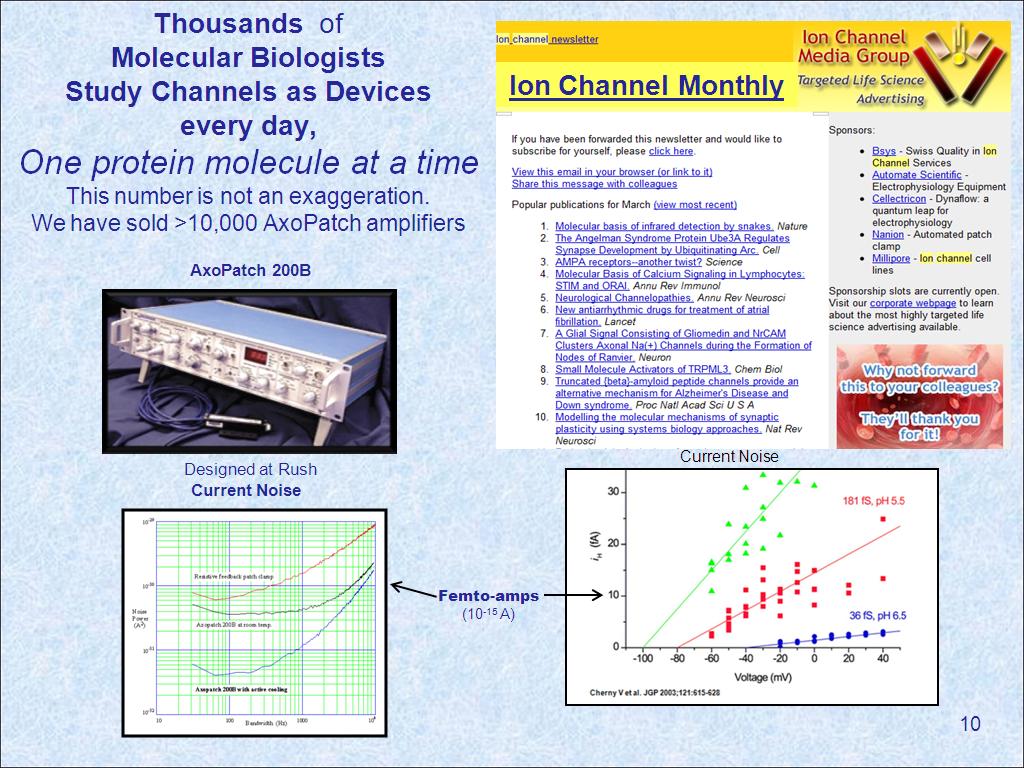 10. Thousands of Molecular Biologi…
1312.2455789122457
00:00/00:00
10. Thousands of Molecular Biologi…
1312.2455789122457
00:00/00:00 -
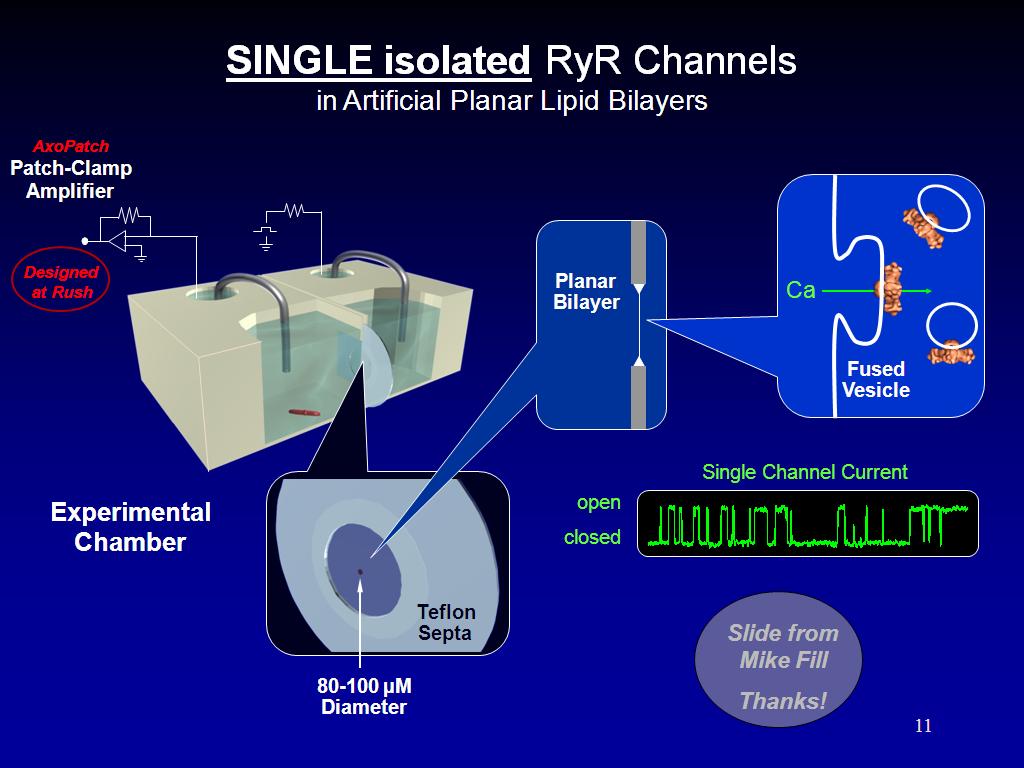 11. SINGLE isolated RyR Channels
1421.5882549215883
00:00/00:00
11. SINGLE isolated RyR Channels
1421.5882549215883
00:00/00:00 -
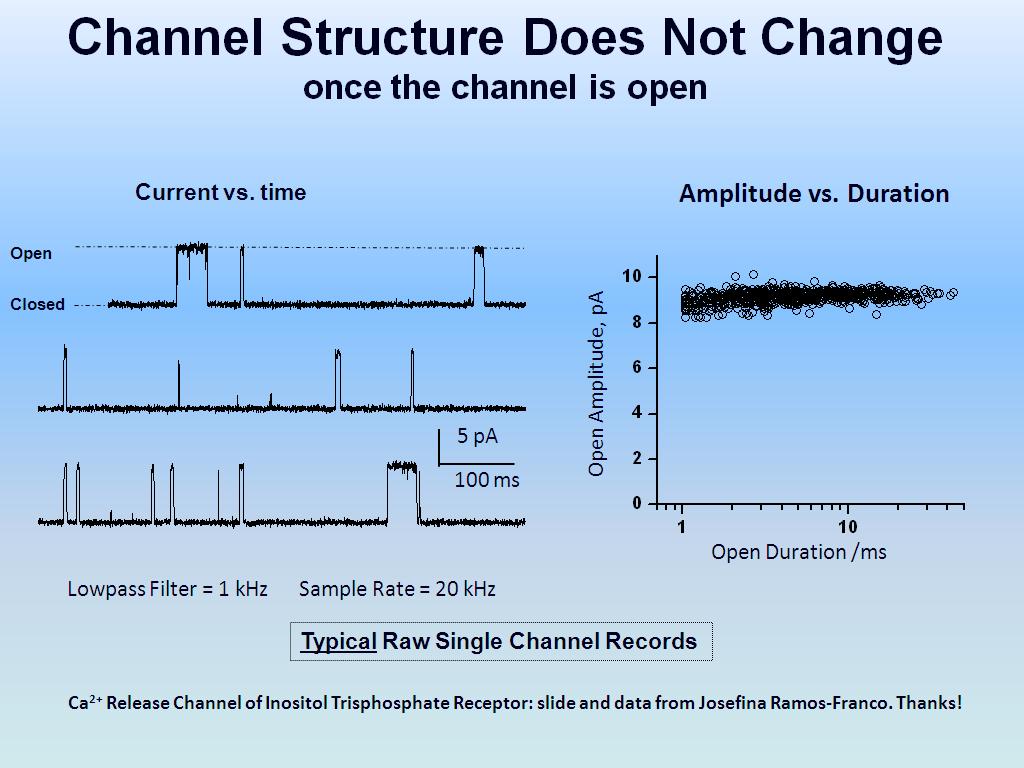 12. Channel Structure Does Not Cha…
1429.0290290290291
00:00/00:00
12. Channel Structure Does Not Cha…
1429.0290290290291
00:00/00:00 -
 13. Where to start?
1515.2485819152487
00:00/00:00
13. Where to start?
1515.2485819152487
00:00/00:00 -
 14. Atomic Scale Engineering
1521.0543877210544
00:00/00:00
14. Atomic Scale Engineering
1521.0543877210544
00:00/00:00 -
 15. Uncalibrated Simulations will …
1604.8715382048715
00:00/00:00
15. Uncalibrated Simulations will …
1604.8715382048715
00:00/00:00 -
 16. Where to start?
1647.8812145478812
00:00/00:00
16. Where to start?
1647.8812145478812
00:00/00:00 -
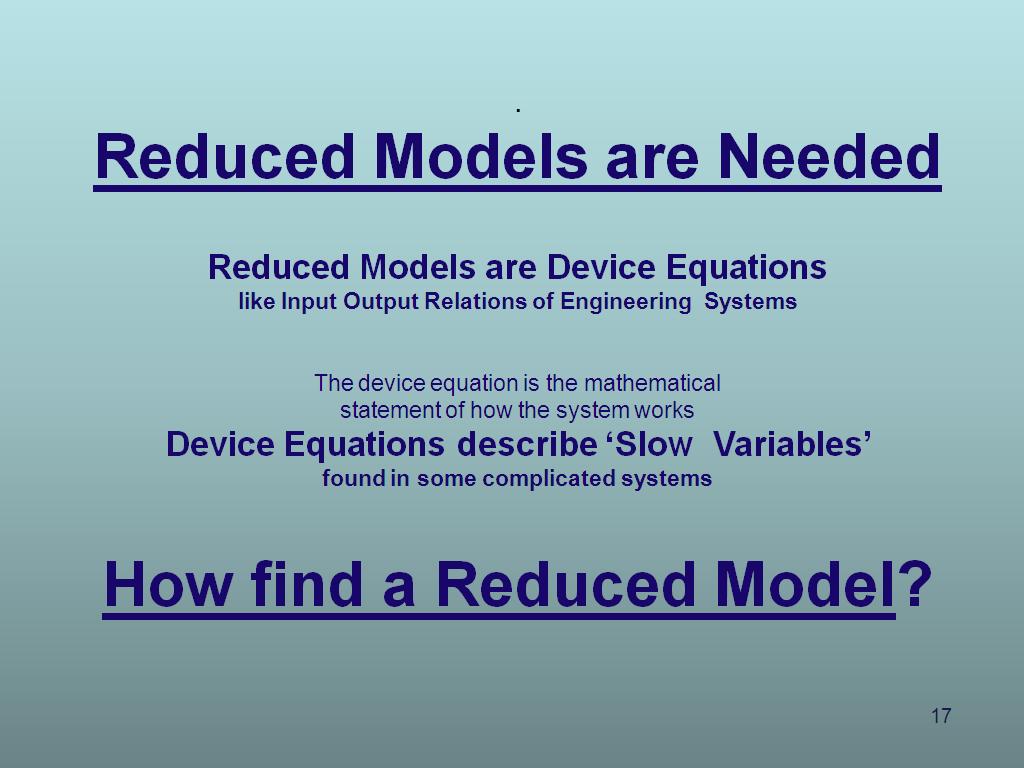 17. Reduced Models are Needed
1675.6423089756424
00:00/00:00
17. Reduced Models are Needed
1675.6423089756424
00:00/00:00 -
 18. Biology is Easier than Physics
1691.4247580914248
00:00/00:00
18. Biology is Easier than Physics
1691.4247580914248
00:00/00:00 -
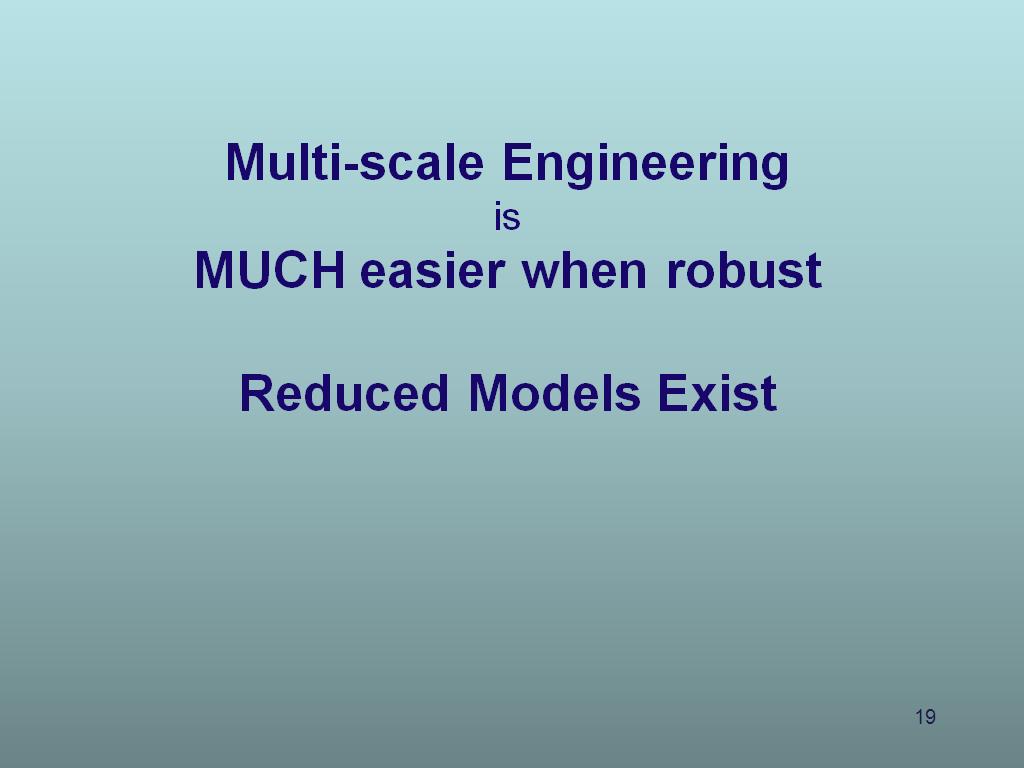 19. Multi-scale Engineering is MUC…
1746.8802135468802
00:00/00:00
19. Multi-scale Engineering is MUC…
1746.8802135468802
00:00/00:00 -
 20. Reduced models exist
1750.0166833500168
00:00/00:00
20. Reduced models exist
1750.0166833500168
00:00/00:00 -
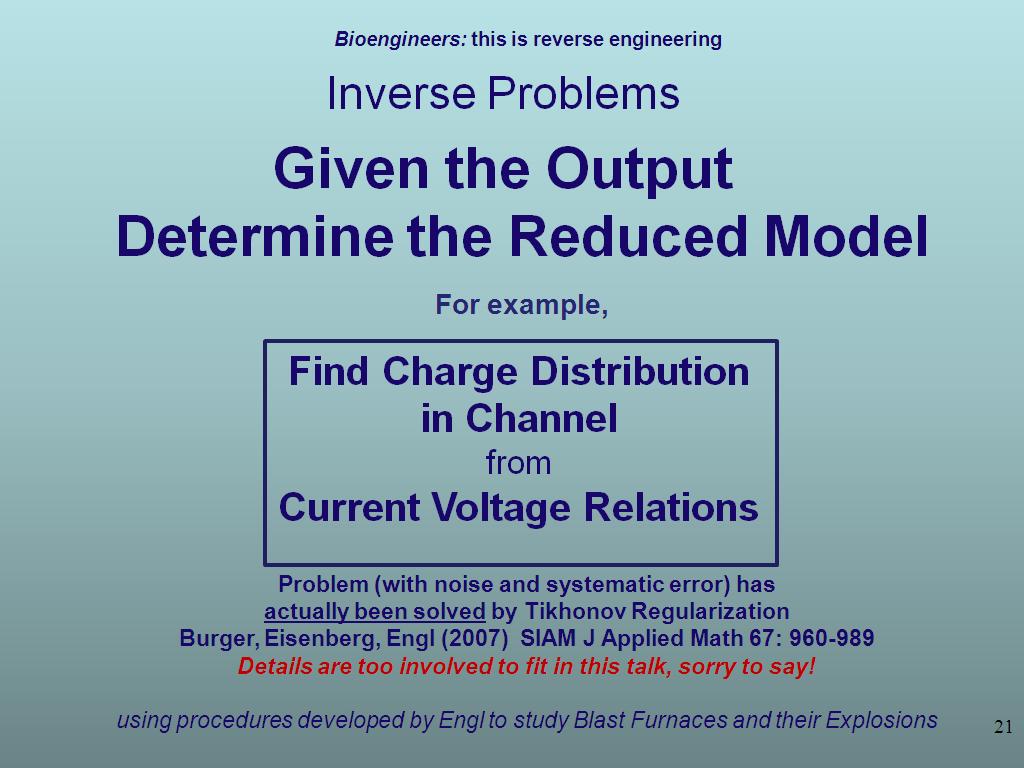 21. Inverse Problems
1754.9883216549883
00:00/00:00
21. Inverse Problems
1754.9883216549883
00:00/00:00 -
 22. Bioengineers: this is reverse …
1796.3630296963631
00:00/00:00
22. Bioengineers: this is reverse …
1796.3630296963631
00:00/00:00 -
 23. Ill posed problems
1851.5515515515517
00:00/00:00
23. Ill posed problems
1851.5515515515517
00:00/00:00 -
 24. Inverse Problems: many answers…
1853.31998665332
00:00/00:00
24. Inverse Problems: many answers…
1853.31998665332
00:00/00:00 -
 25. Molecular Dynamics usually yie…
1917.017017017017
00:00/00:00
25. Molecular Dynamics usually yie…
1917.017017017017
00:00/00:00 -
 26. Crowded Ions and Side Chains
1918.3516850183517
00:00/00:00
26. Crowded Ions and Side Chains
1918.3516850183517
00:00/00:00 -
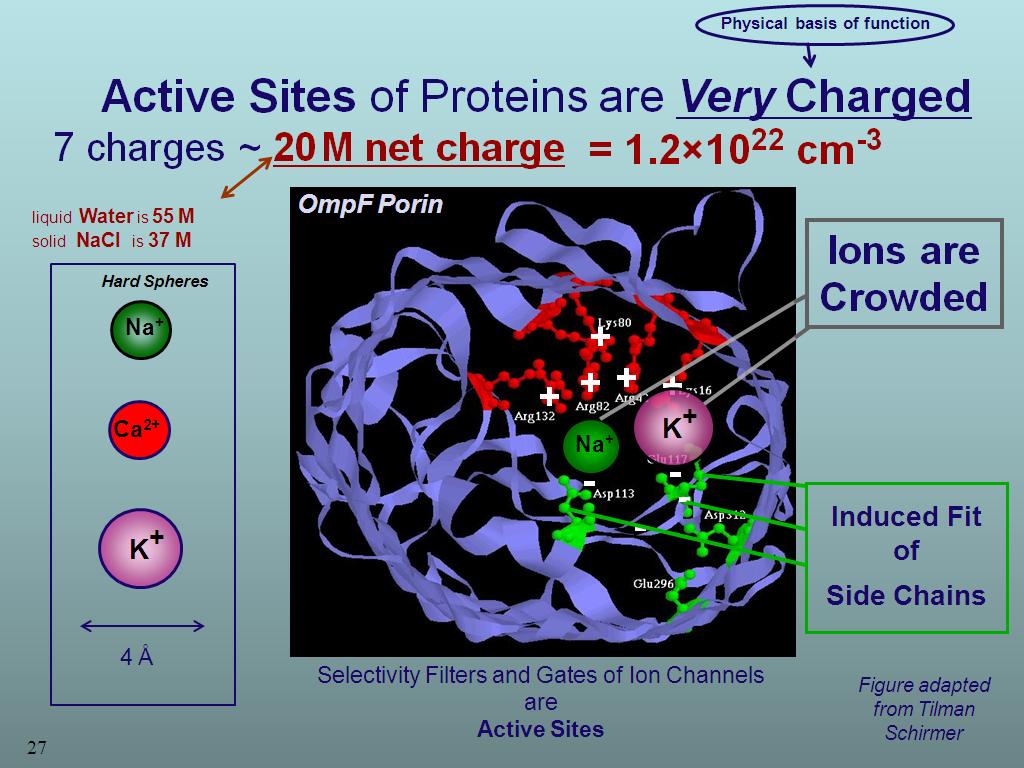 27. Ions are Crowded
1949.84984984985
00:00/00:00
27. Ions are Crowded
1949.84984984985
00:00/00:00 -
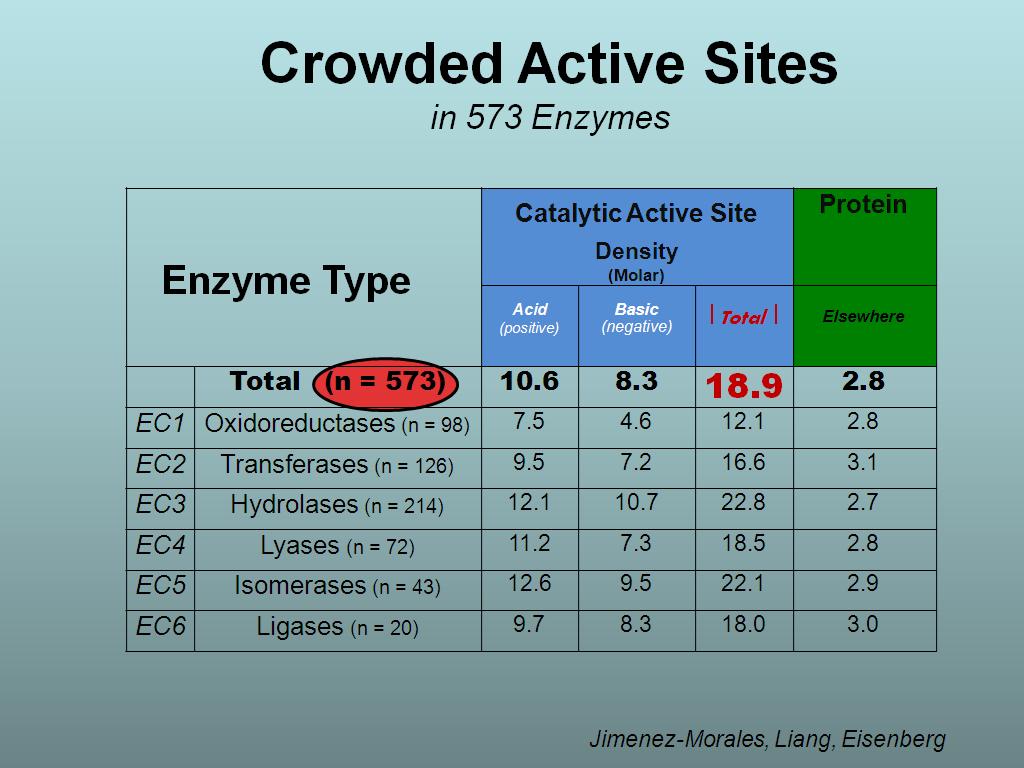 28. Crowded Active Sites in 573 En…
2045.6456456456458
00:00/00:00
28. Crowded Active Sites in 573 En…
2045.6456456456458
00:00/00:00 -
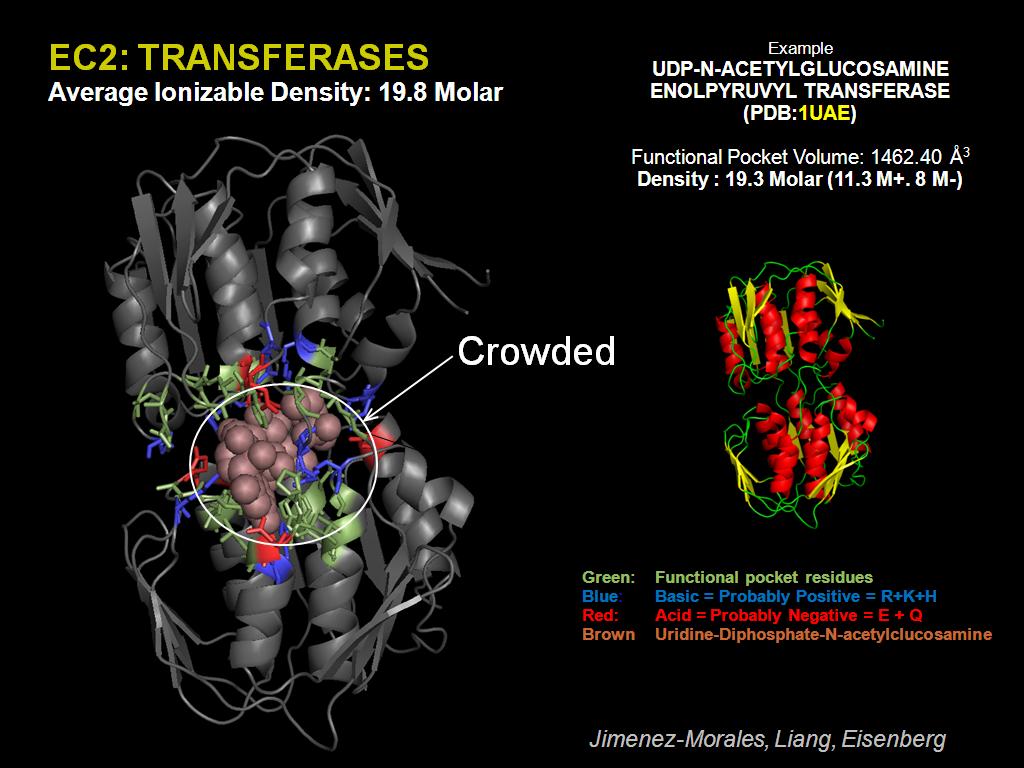 29. EC2: TRANSFERASES
2133.4668001334667
00:00/00:00
29. EC2: TRANSFERASES
2133.4668001334667
00:00/00:00 -
 30. Everything Interacts with Ever…
2150.1501501501502
00:00/00:00
30. Everything Interacts with Ever…
2150.1501501501502
00:00/00:00 -
 31. Stochastic PDE and Field Theor…
2199.9332665999332
00:00/00:00
31. Stochastic PDE and Field Theor…
2199.9332665999332
00:00/00:00 -
 32. Always start with Trajectories
2387.3206539873208
00:00/00:00
32. Always start with Trajectories
2387.3206539873208
00:00/00:00 -
 33. From Trajectories to Probabili…
2539.3393393393394
00:00/00:00
33. From Trajectories to Probabili…
2539.3393393393394
00:00/00:00 -
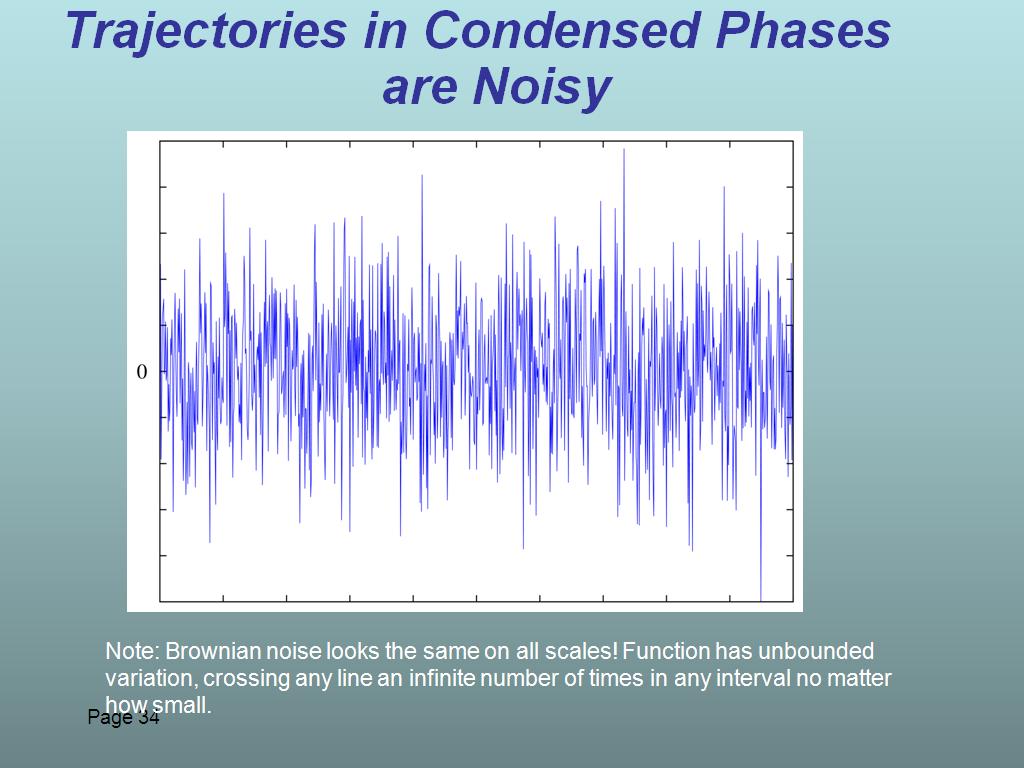 34. Trajectories in Condensed Phas…
2567.867867867868
00:00/00:00
34. Trajectories in Condensed Phas…
2567.867867867868
00:00/00:00 -
 35. Theory of Stochastic Processes
2627.3606940273608
00:00/00:00
35. Theory of Stochastic Processes
2627.3606940273608
00:00/00:00 -
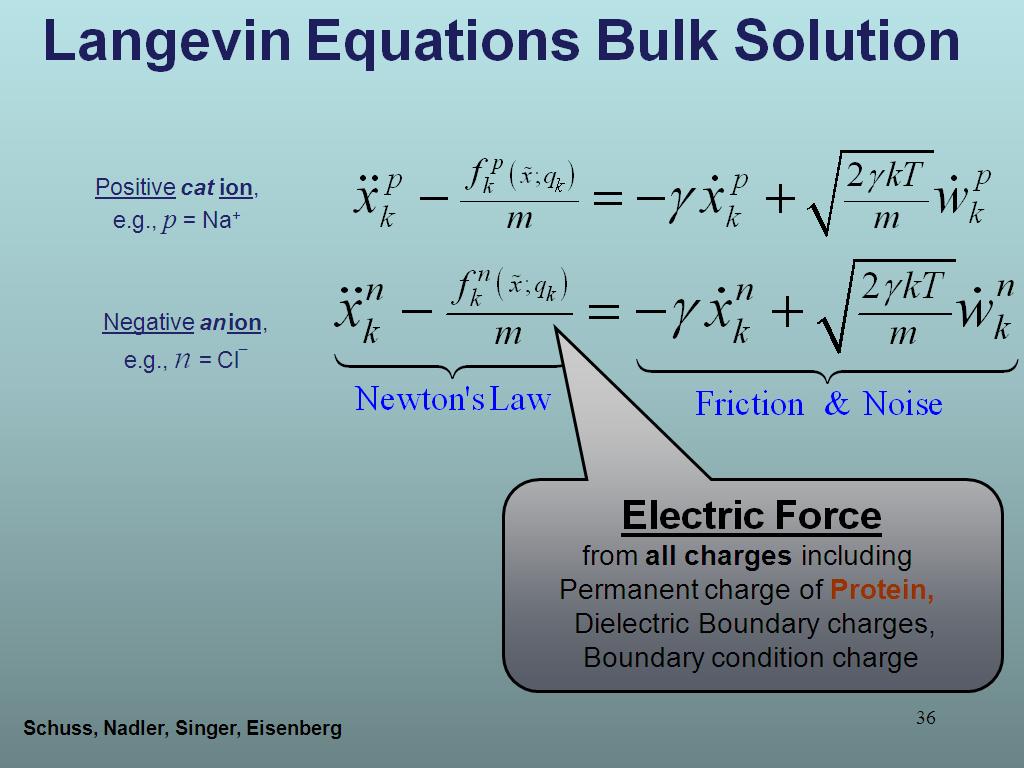 36. Langevin Equations Bulk Soluti…
2638.9723056389726
00:00/00:00
36. Langevin Equations Bulk Soluti…
2638.9723056389726
00:00/00:00 -
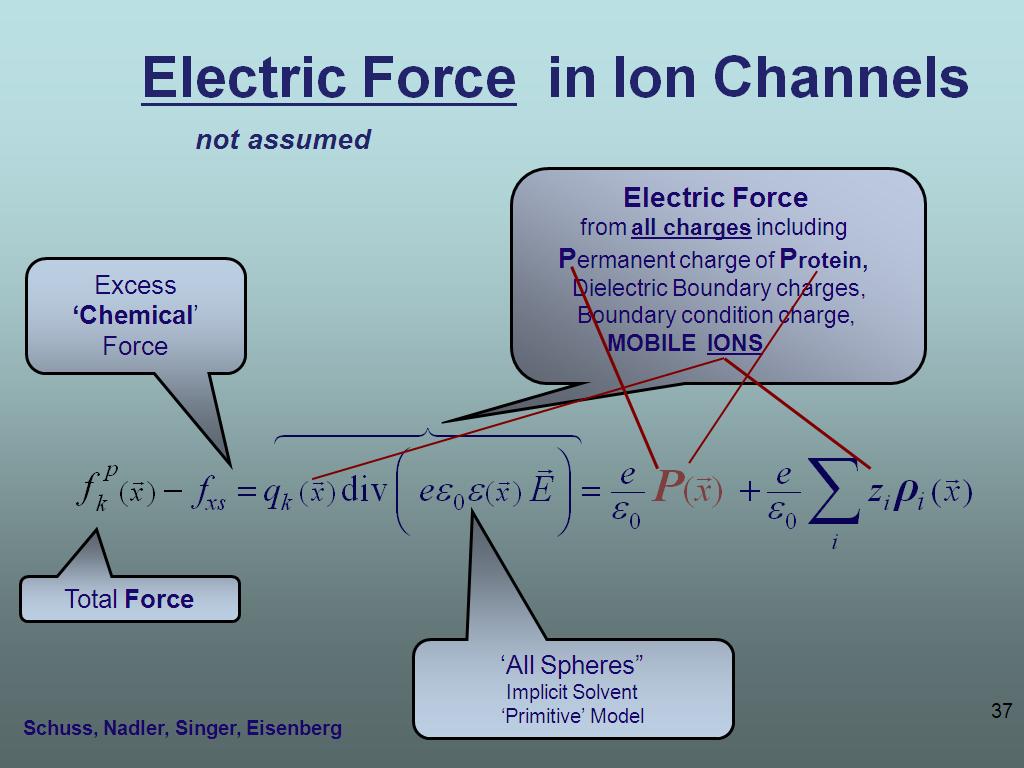 37. Electric Force
2797.4307640974307
00:00/00:00
37. Electric Force
2797.4307640974307
00:00/00:00 -
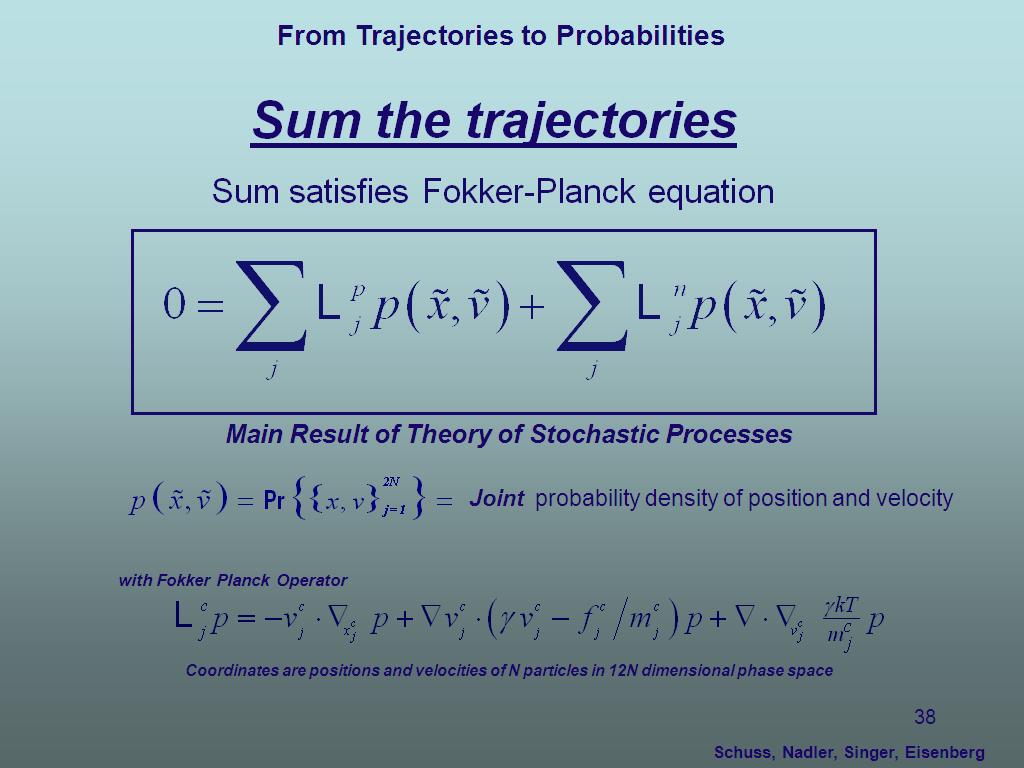 38. Sum the traqjectories
2810.2102102102103
00:00/00:00
38. Sum the traqjectories
2810.2102102102103
00:00/00:00 -
 39. More Math Many papers
2815.4821488154821
00:00/00:00
39. More Math Many papers
2815.4821488154821
00:00/00:00 -
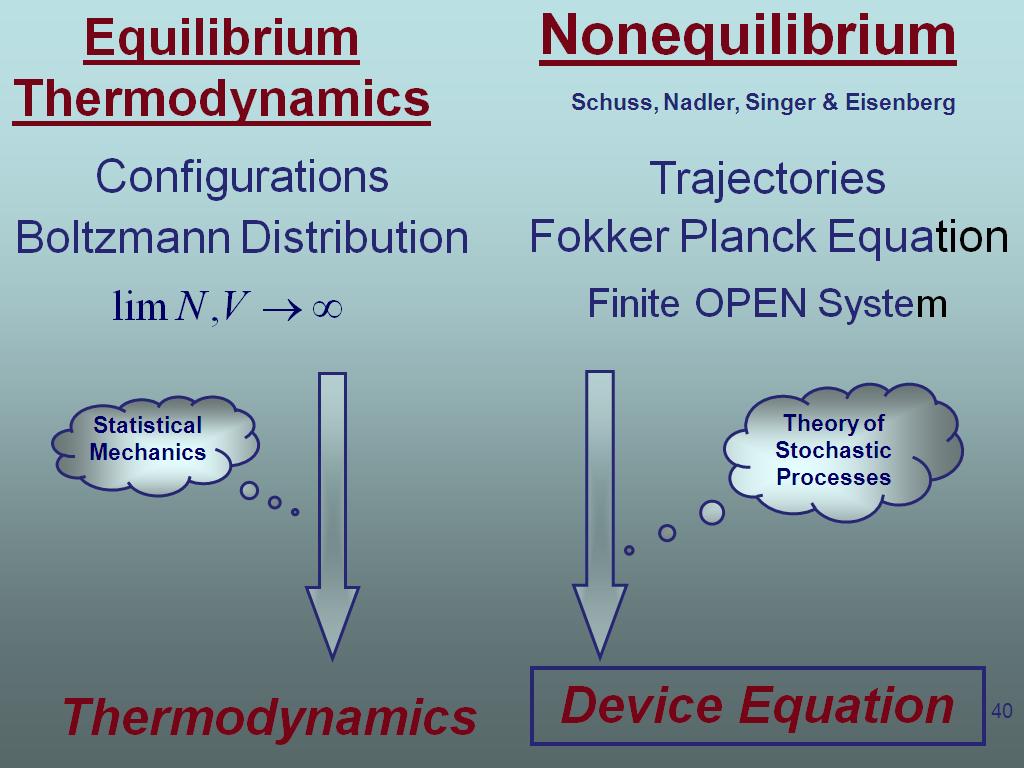 40. Device Equation
2877.5775775775778
00:00/00:00
40. Device Equation
2877.5775775775778
00:00/00:00 -
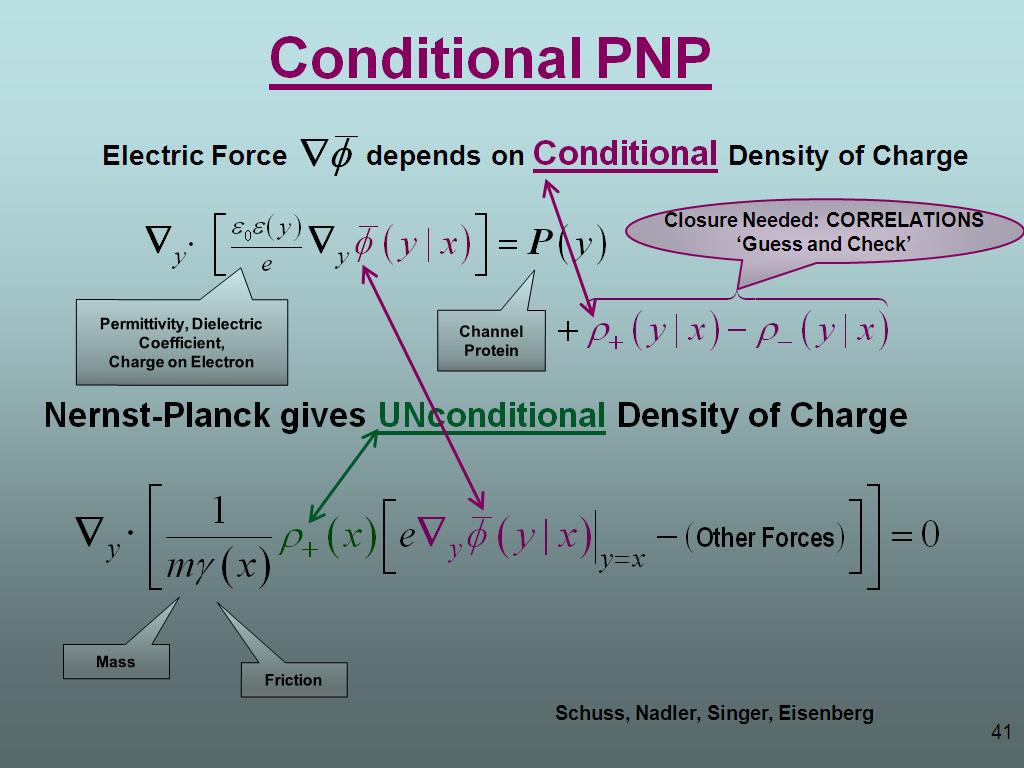 41. Conditional PNP
2897.3973973973975
00:00/00:00
41. Conditional PNP
2897.3973973973975
00:00/00:00 -
 42. Probability and Conditional Pr…
3047.4474474474478
00:00/00:00
42. Probability and Conditional Pr…
3047.4474474474478
00:00/00:00 -
 43. Conditioning and Correlations
3067.0337003670338
00:00/00:00
43. Conditioning and Correlations
3067.0337003670338
00:00/00:00 -
 44. Kirchoff's Current Law
3077.8778778778778
00:00/00:00
44. Kirchoff's Current Law
3077.8778778778778
00:00/00:00 -
 45. Science, not Mathematics
3185.3186519853189
00:00/00:00
45. Science, not Mathematics
3185.3186519853189
00:00/00:00 -
 46. Everything Interacts
3189.5895895895897
00:00/00:00
46. Everything Interacts
3189.5895895895897
00:00/00:00 -
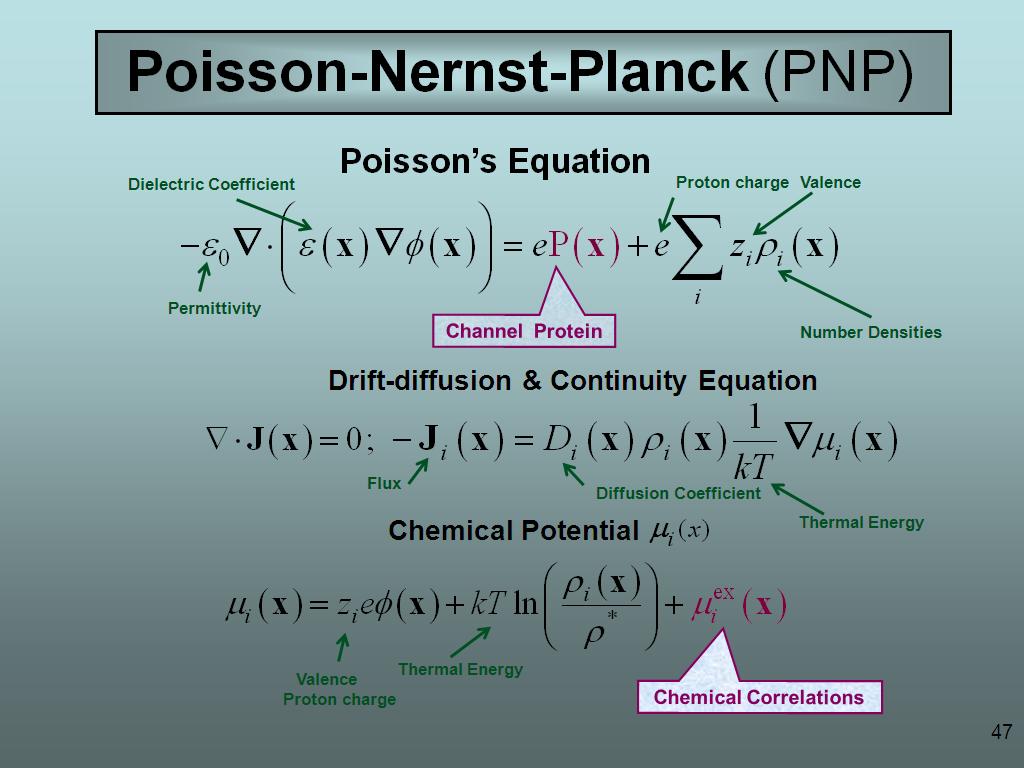 47. Poisson-Nernst-Planck
3191.9586252919589
00:00/00:00
47. Poisson-Nernst-Planck
3191.9586252919589
00:00/00:00 -
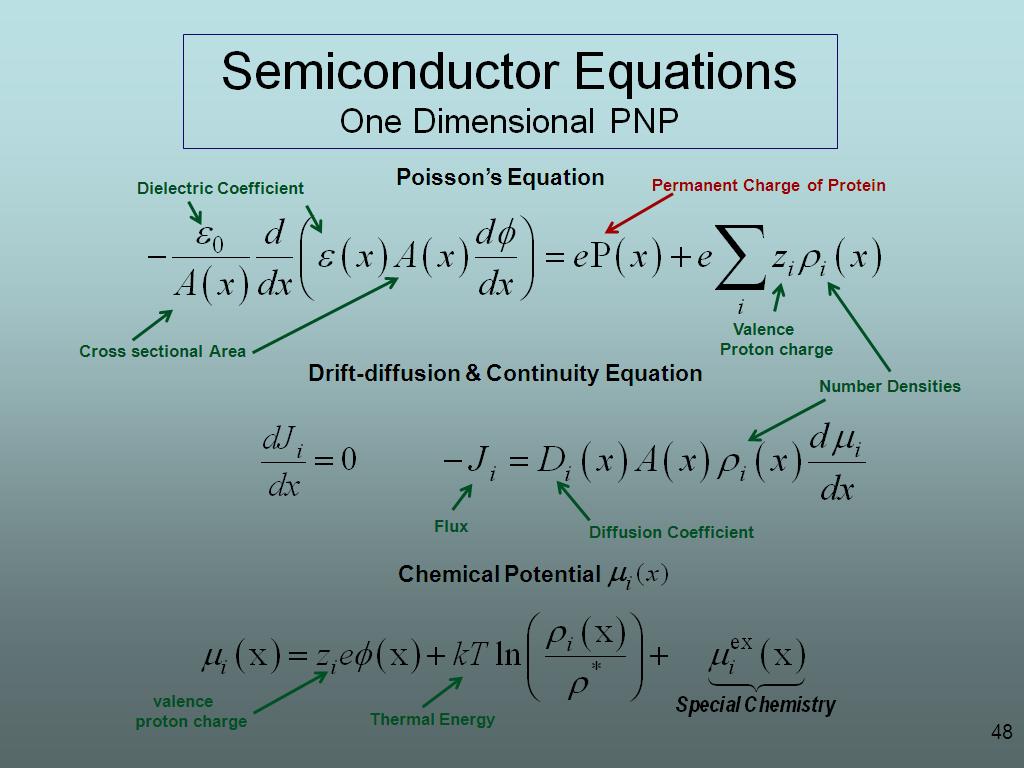 48. Semiconductor Equations
3215.2152152152153
00:00/00:00
48. Semiconductor Equations
3215.2152152152153
00:00/00:00 -
 49. Counting at low resolution giv…
3237.4374374374374
00:00/00:00
49. Counting at low resolution giv…
3237.4374374374374
00:00/00:00 -
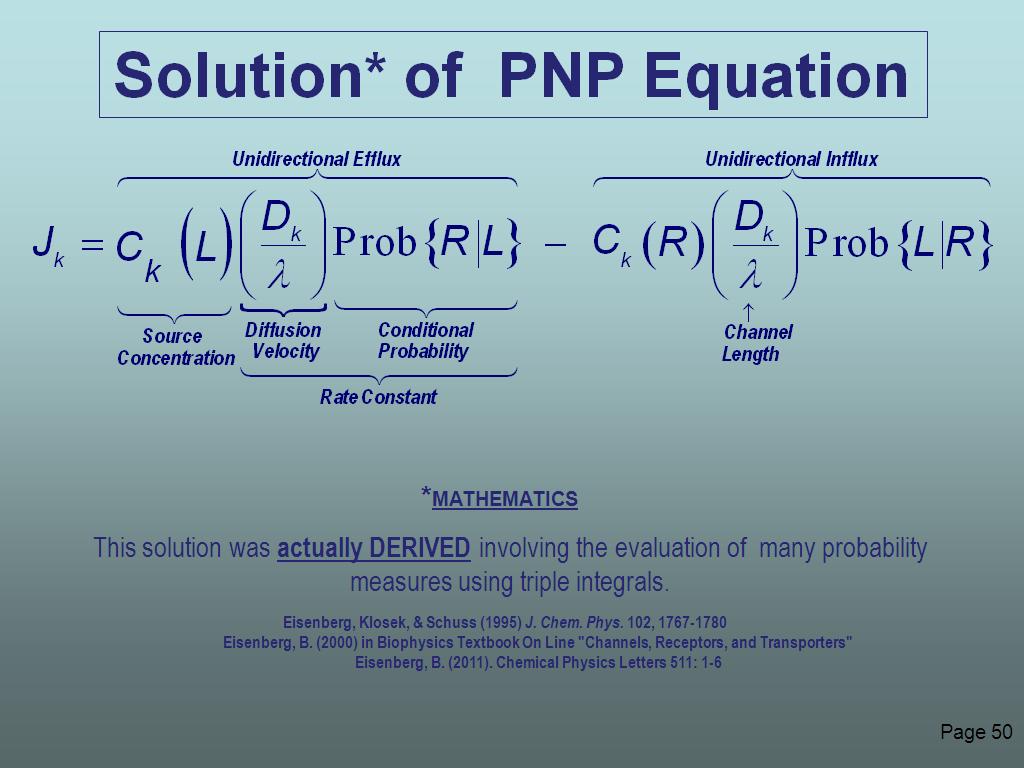 50. Solution of PNP Equation
3248.0146813480146
00:00/00:00
50. Solution of PNP Equation
3248.0146813480146
00:00/00:00 -
 51. Solution was actually DERIVED
3275.8425091758427
00:00/00:00
51. Solution was actually DERIVED
3275.8425091758427
00:00/00:00 -
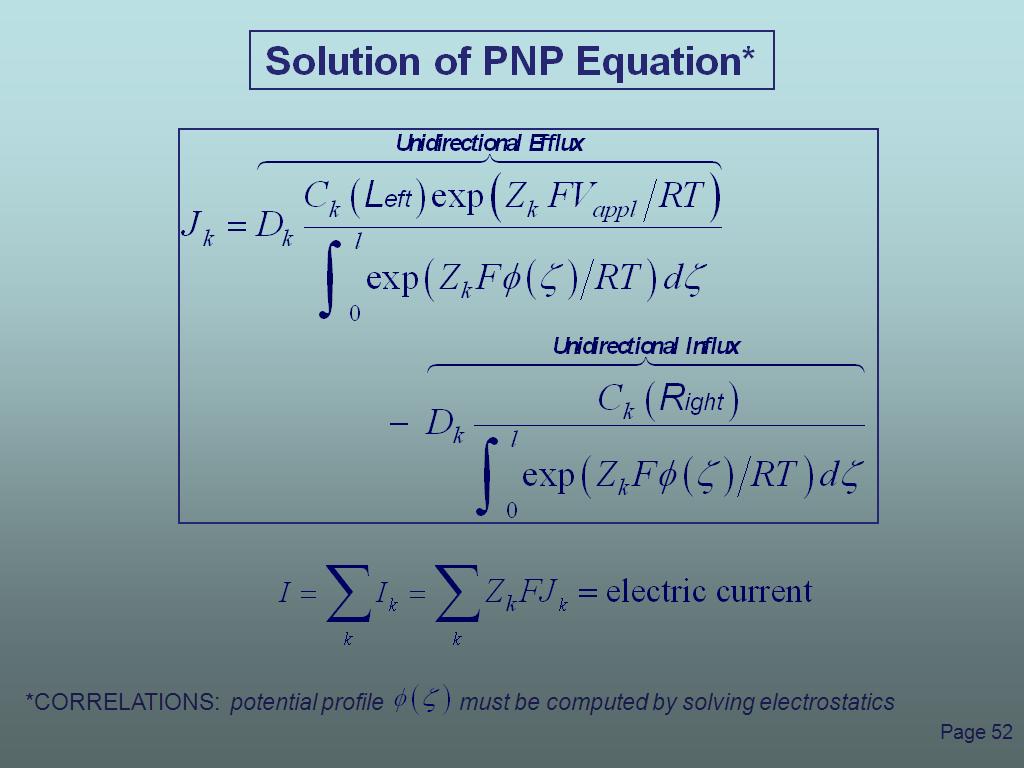 52. Solution of PNP Equation
3299.5995995995995
00:00/00:00
52. Solution of PNP Equation
3299.5995995995995
00:00/00:00 -
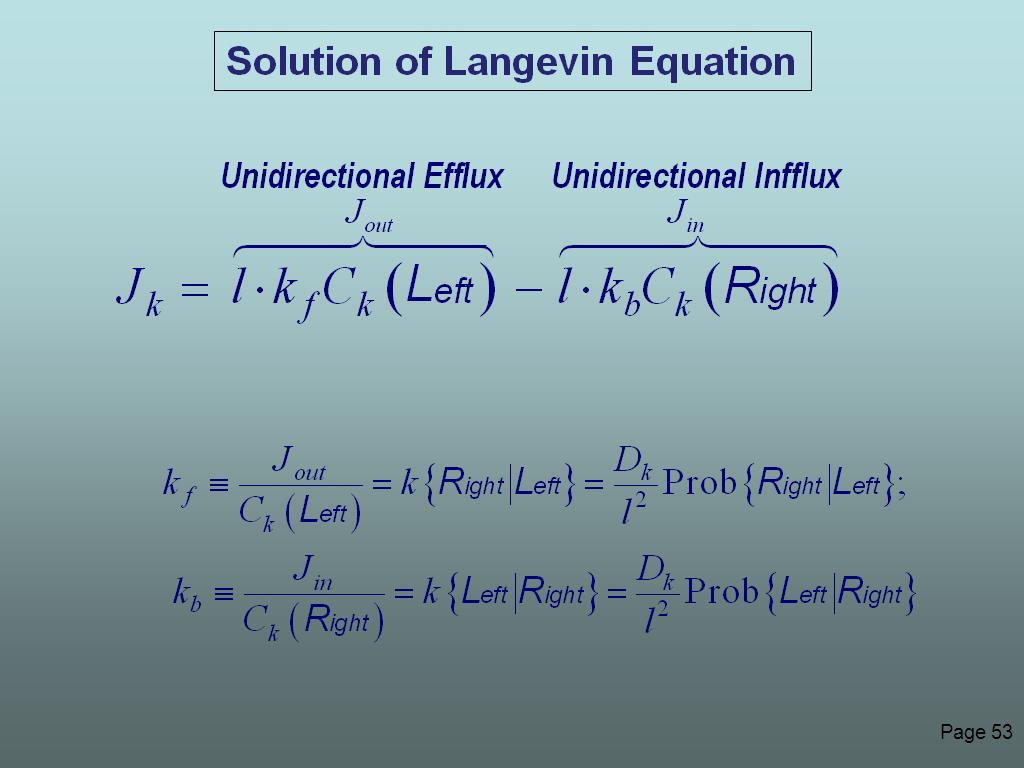 53. Solution of Langevin Equation
3303.16983650317
00:00/00:00
53. Solution of Langevin Equation
3303.16983650317
00:00/00:00 -
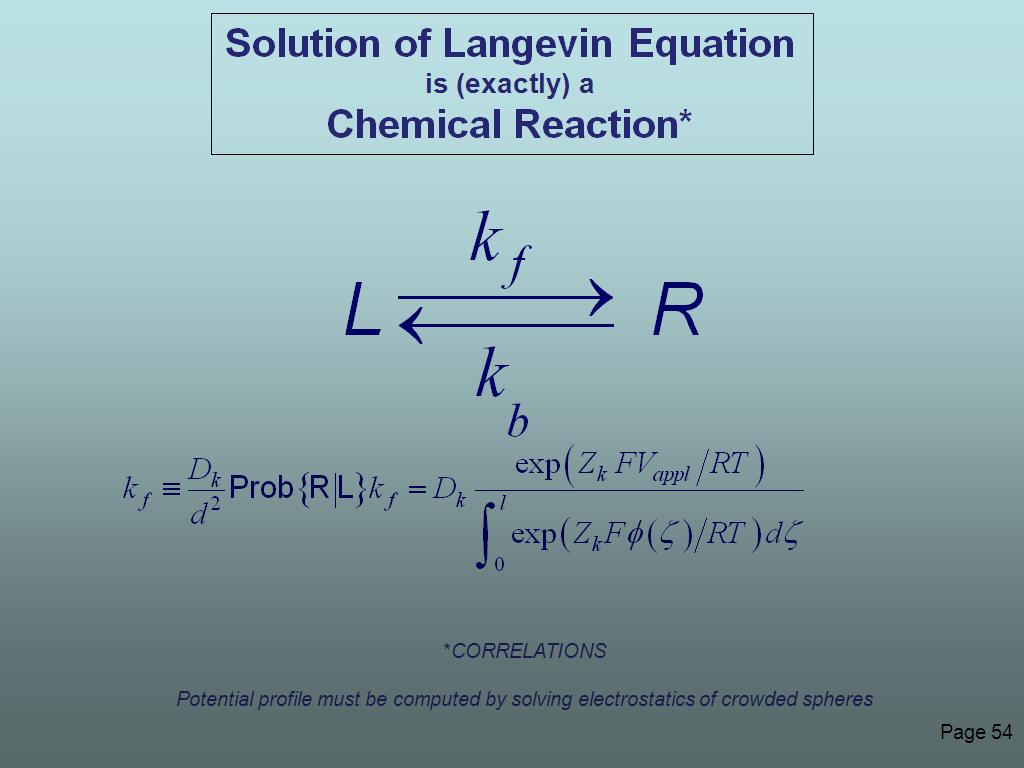 54. Solution of Langevin Equation
3306.63997330664
00:00/00:00
54. Solution of Langevin Equation
3306.63997330664
00:00/00:00 -
 55. Overwhelming effoect of Correl…
3343.677010343677
00:00/00:00
55. Overwhelming effoect of Correl…
3343.677010343677
00:00/00:00 -
 56. Classical Chemistry ignores Co…
3348.8822155488824
00:00/00:00
56. Classical Chemistry ignores Co…
3348.8822155488824
00:00/00:00 -
 57. Theory of Ideal Gases
3437.4040707374043
00:00/00:00
57. Theory of Ideal Gases
3437.4040707374043
00:00/00:00 -
 58. Generalization of 'Law' of Mas…
3439.2392392392394
00:00/00:00
58. Generalization of 'Law' of Mas…
3439.2392392392394
00:00/00:00 -
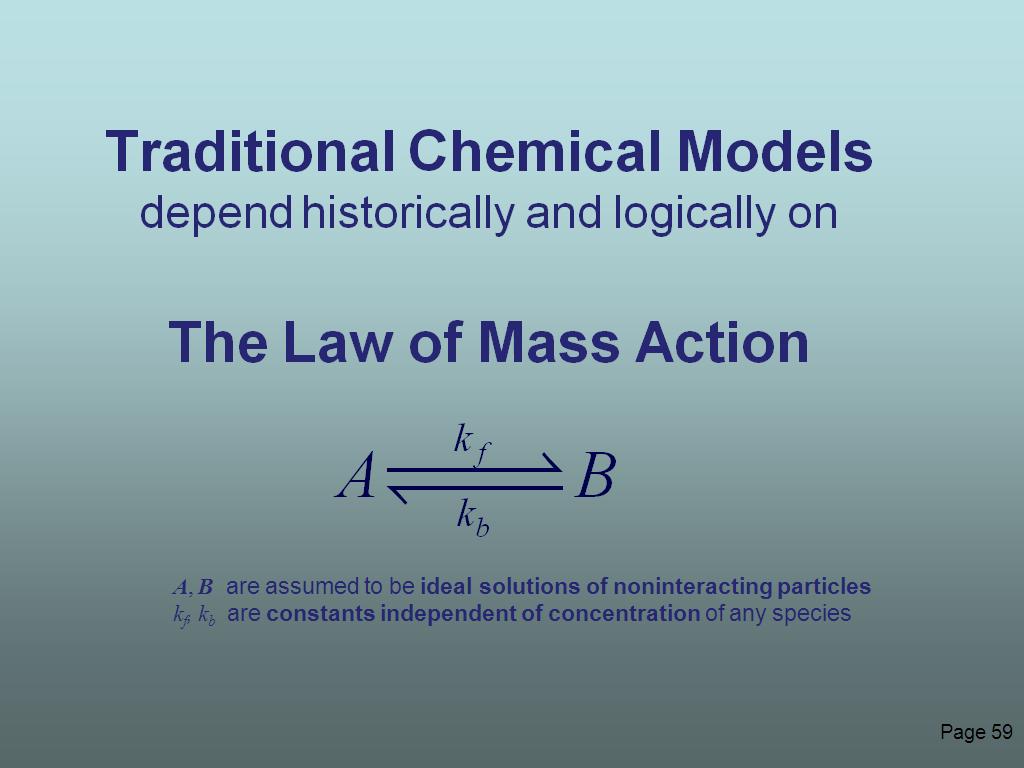 59. The Law of Mass Action
3539.3393393393394
00:00/00:00
59. The Law of Mass Action
3539.3393393393394
00:00/00:00 -
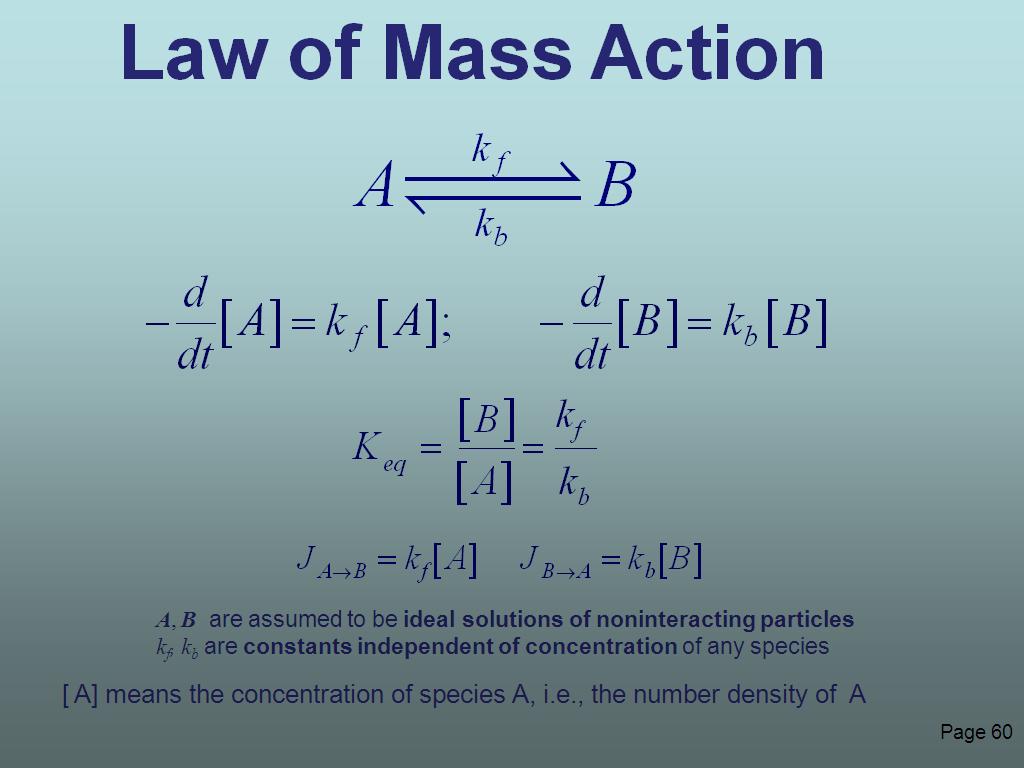 60. Law of Mass Action
3543.1097764431097
00:00/00:00
60. Law of Mass Action
3543.1097764431097
00:00/00:00 -
 61. Nothing is Ideal!
3544.4444444444448
00:00/00:00
61. Nothing is Ideal!
3544.4444444444448
00:00/00:00 -
 62. Highly Compressible Plasma
3547.8812145478814
00:00/00:00
62. Highly Compressible Plasma
3547.8812145478814
00:00/00:00 -
 63. Ionic Solutions are Complex Fl…
3623.0563897230563
00:00/00:00
63. Ionic Solutions are Complex Fl…
3623.0563897230563
00:00/00:00 -
 64. Everything is hidden
3652.2856189522859
00:00/00:00
64. Everything is hidden
3652.2856189522859
00:00/00:00 -
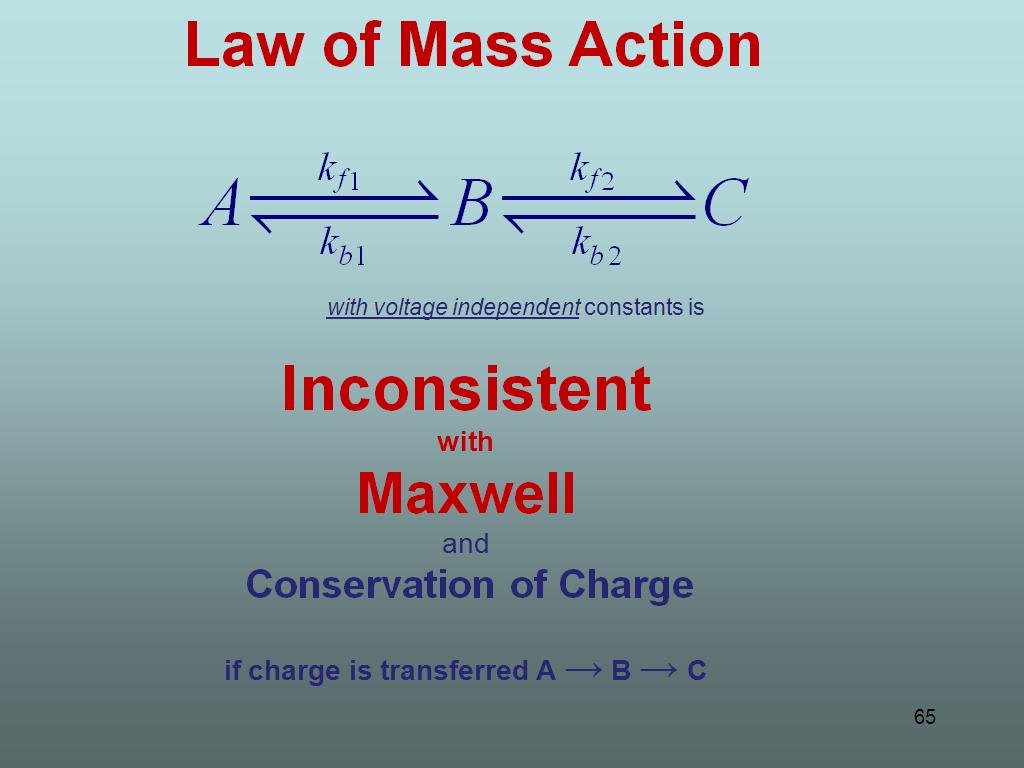 65. Law of Mass Action
3655.0884217550883
00:00/00:00
65. Law of Mass Action
3655.0884217550883
00:00/00:00 -
 66. Macroscopic Models are True IN…
3735.5355355355355
00:00/00:00
66. Macroscopic Models are True IN…
3735.5355355355355
00:00/00:00 -
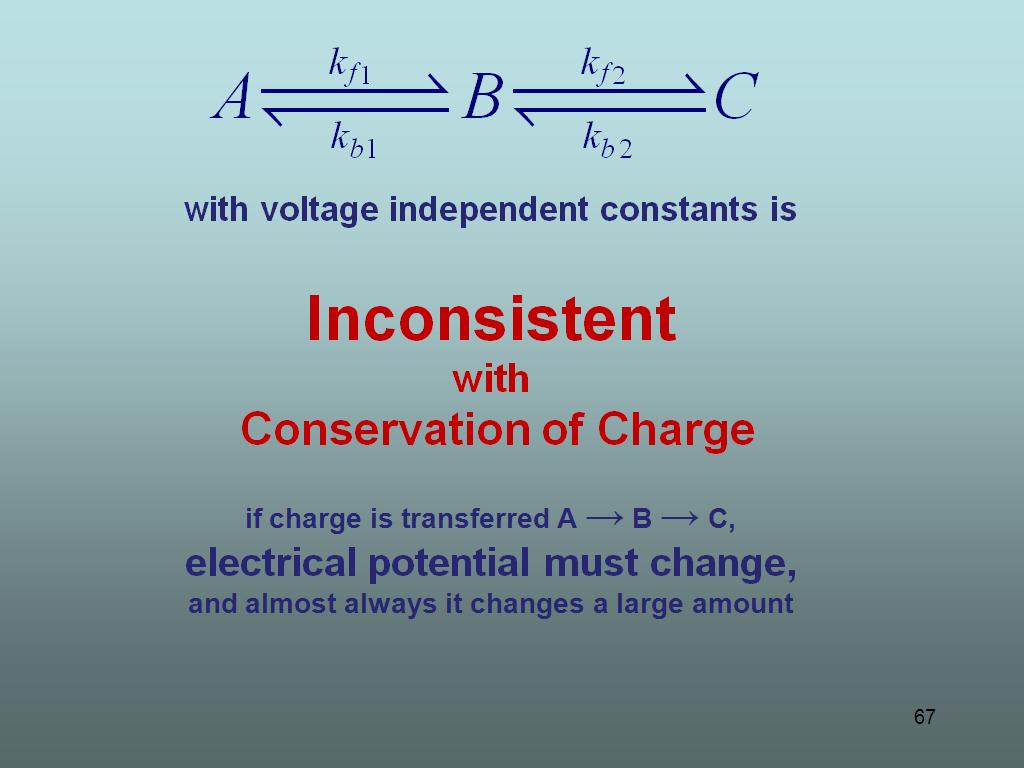 67. Inconsistent with Conservation…
3740.2736069402736
00:00/00:00
67. Inconsistent with Conservation…
3740.2736069402736
00:00/00:00 -
 68. All BIOLOGY OCCURS IN CHARGED …
3741.3079746413082
00:00/00:00
68. All BIOLOGY OCCURS IN CHARGED …
3741.3079746413082
00:00/00:00 -
 69. Inconsistent Treatments
3742.7093760427097
00:00/00:00
69. Inconsistent Treatments
3742.7093760427097
00:00/00:00