[Illinois] PHYS466 2013 Lecture 11: Constant Pressure and Temp
[Illinois] Phys 466 Lecture 14: Constant Pressure and Temp
-
 1. Temperature and Pressure Contr…
0
00:00/00:00
1. Temperature and Pressure Contr…
0
00:00/00:00 -
 2. Constant Temperature MD
155.03513008256738
00:00/00:00
2. Constant Temperature MD
155.03513008256738
00:00/00:00 -
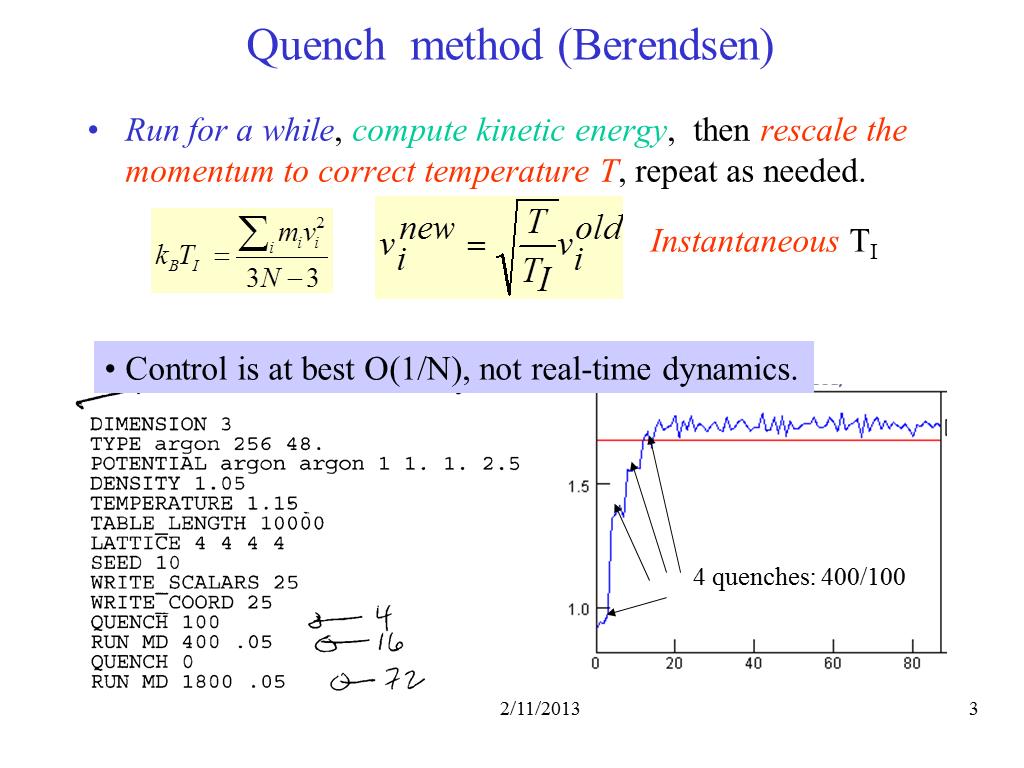 3. Quench method (Berendsen)
213.9143741812552
00:00/00:00
3. Quench method (Berendsen)
213.9143741812552
00:00/00:00 -
 4. Constant Temperature MD
515.17553888293435
00:00/00:00
4. Constant Temperature MD
515.17553888293435
00:00/00:00 -
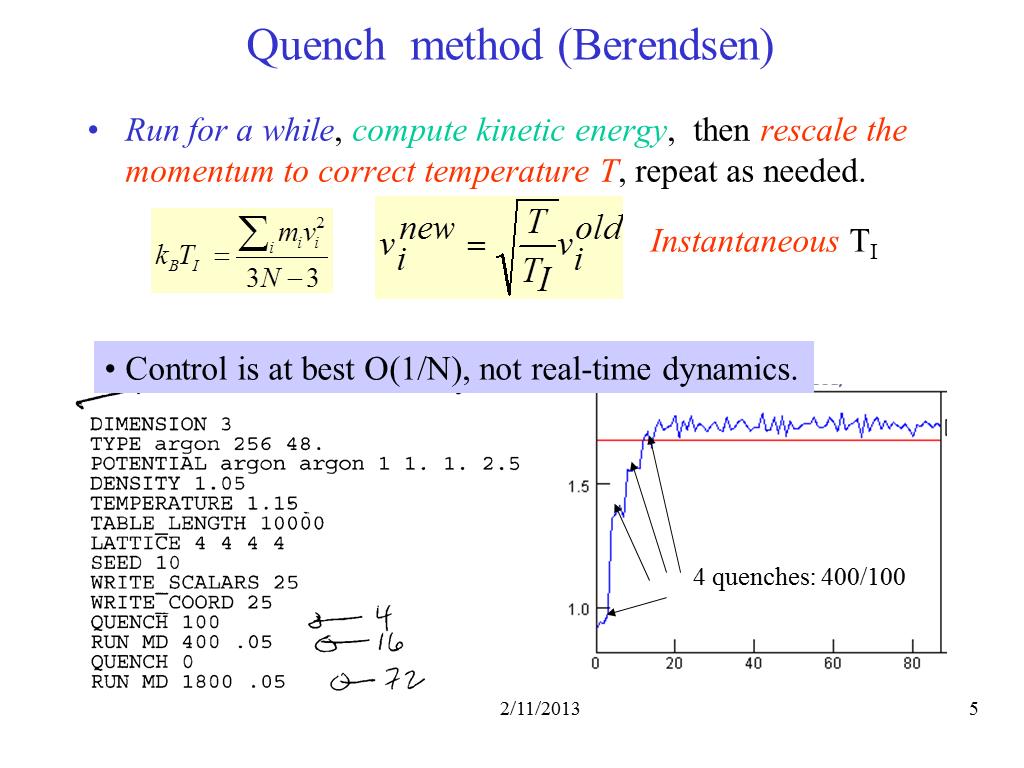 5. Quench method (Berendsen)
539.49116748044935
00:00/00:00
5. Quench method (Berendsen)
539.49116748044935
00:00/00:00 -
 6. Brownian dynamics/Andersen the…
689.30070263189236
00:00/00:00
6. Brownian dynamics/Andersen the…
689.30070263189236
00:00/00:00 -
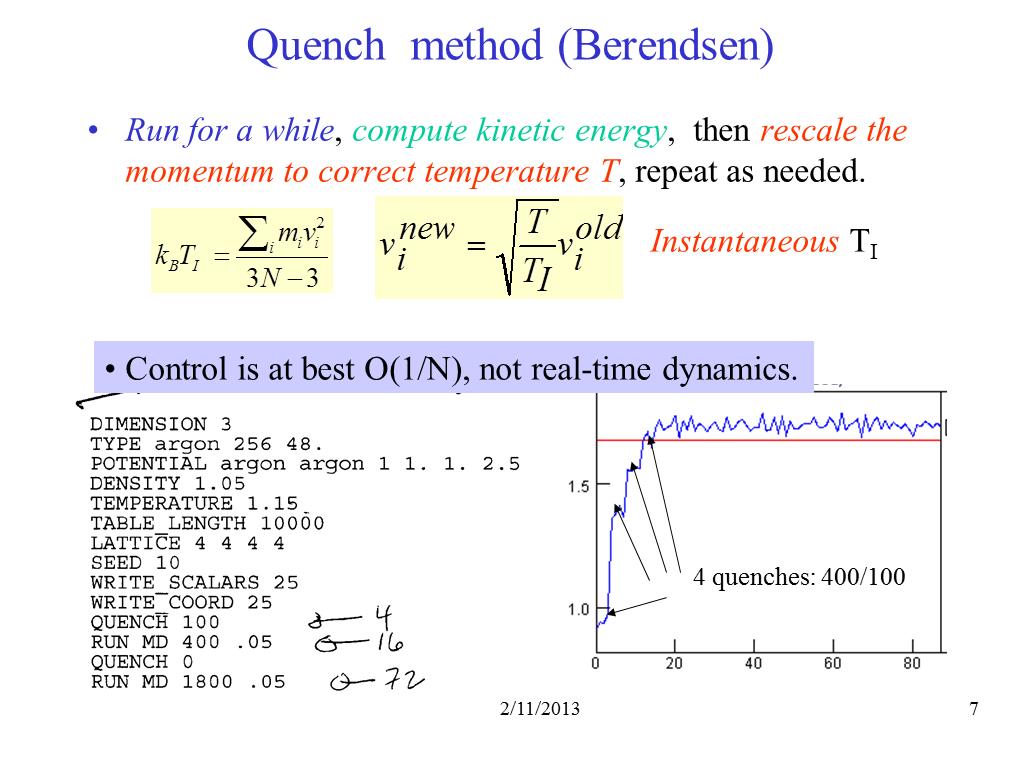 7. Quench method (Berendsen)
773.99487912349639
00:00/00:00
7. Quench method (Berendsen)
773.99487912349639
00:00/00:00 -
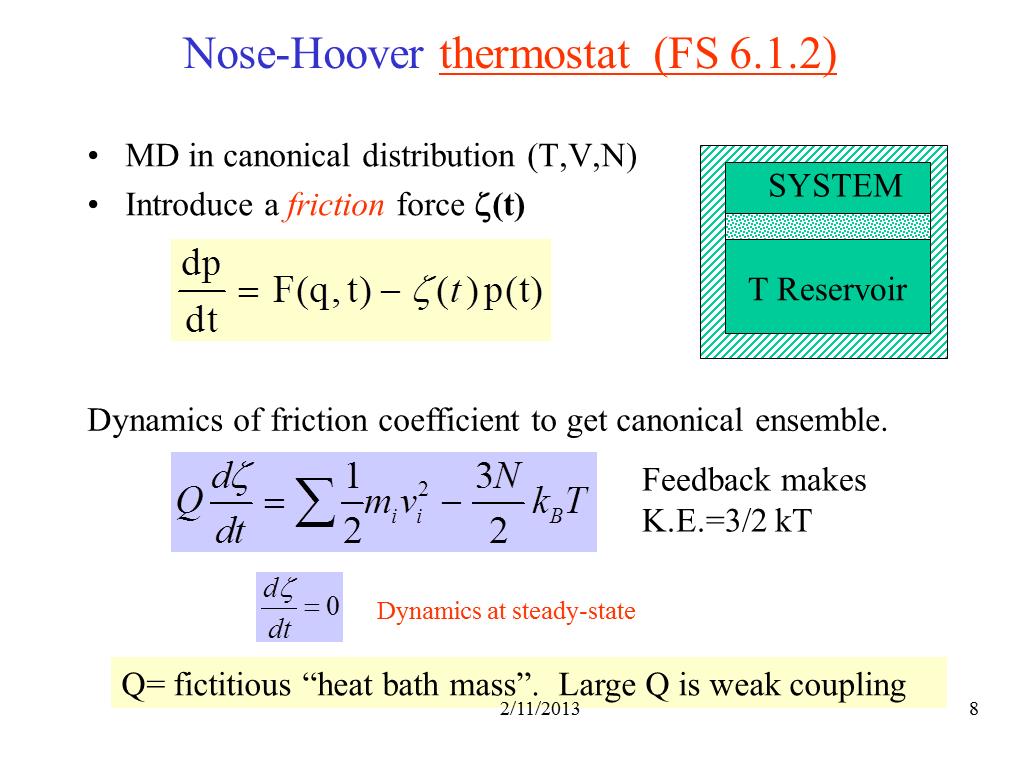 8. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
840.0575999364853
00:00/00:00
8. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
840.0575999364853
00:00/00:00 -
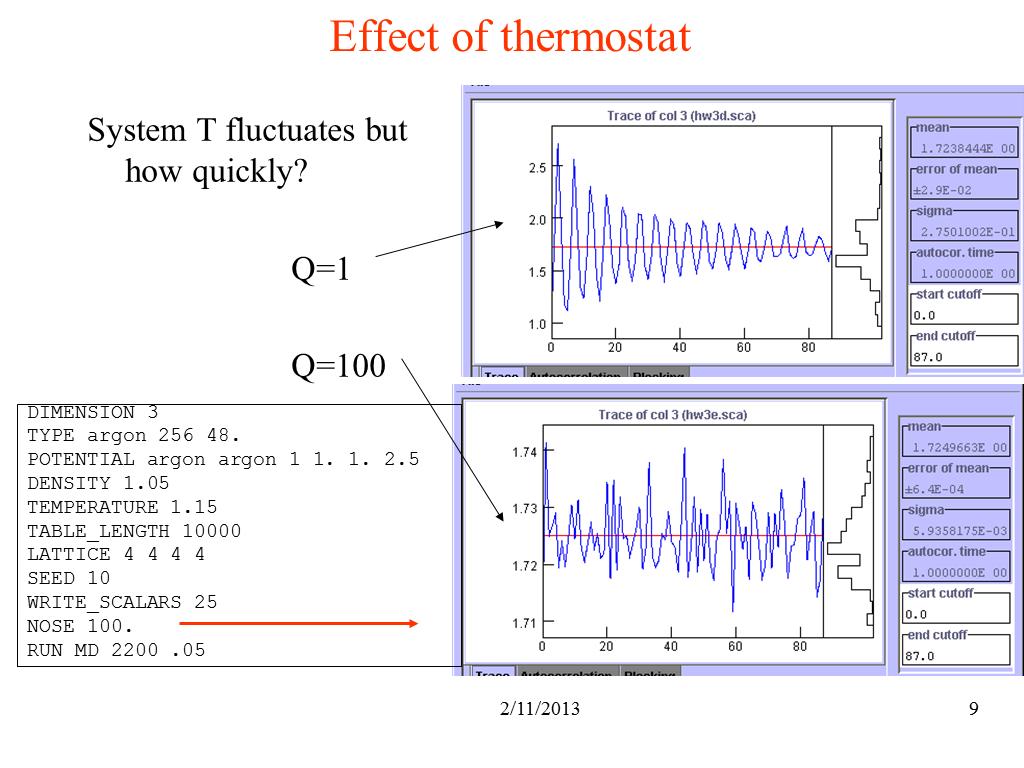 9. Effect of thermostat
994.28815846929467
00:00/00:00
9. Effect of thermostat
994.28815846929467
00:00/00:00 -
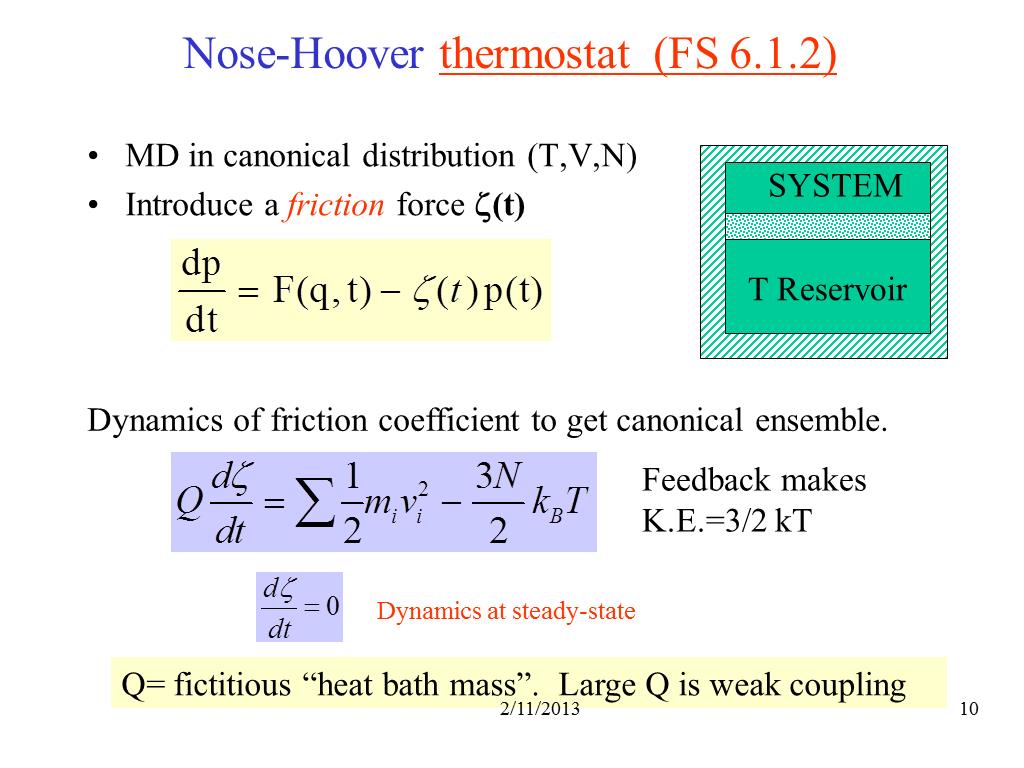 10. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
1067.1718867849629
00:00/00:00
10. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
1067.1718867849629
00:00/00:00 -
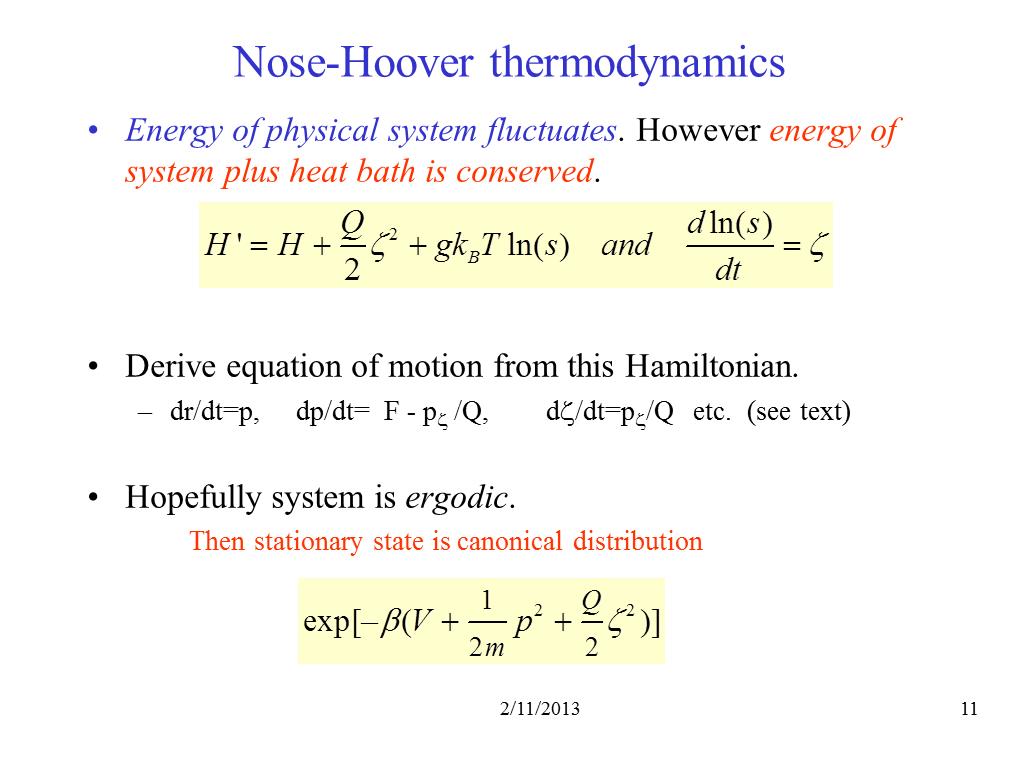 11. Nose-Hoover thermodynamics
1153.4450001984835
00:00/00:00
11. Nose-Hoover thermodynamics
1153.4450001984835
00:00/00:00 -
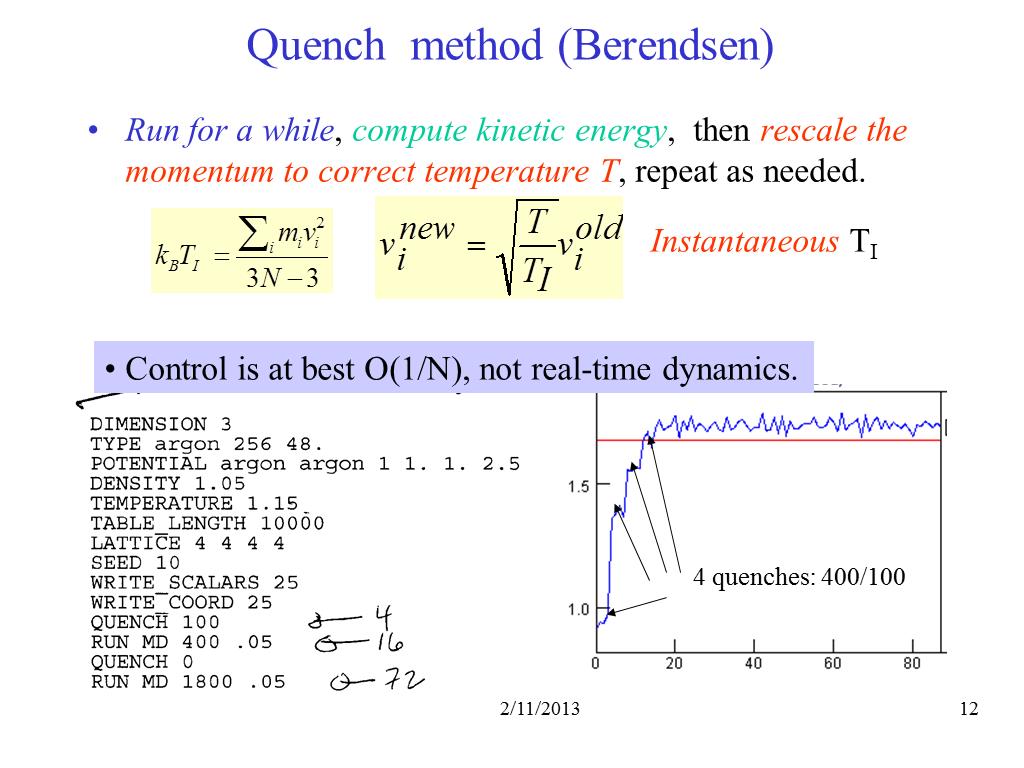 12. Quench method (Berendsen)
1332.5596046206979
00:00/00:00
12. Quench method (Berendsen)
1332.5596046206979
00:00/00:00 -
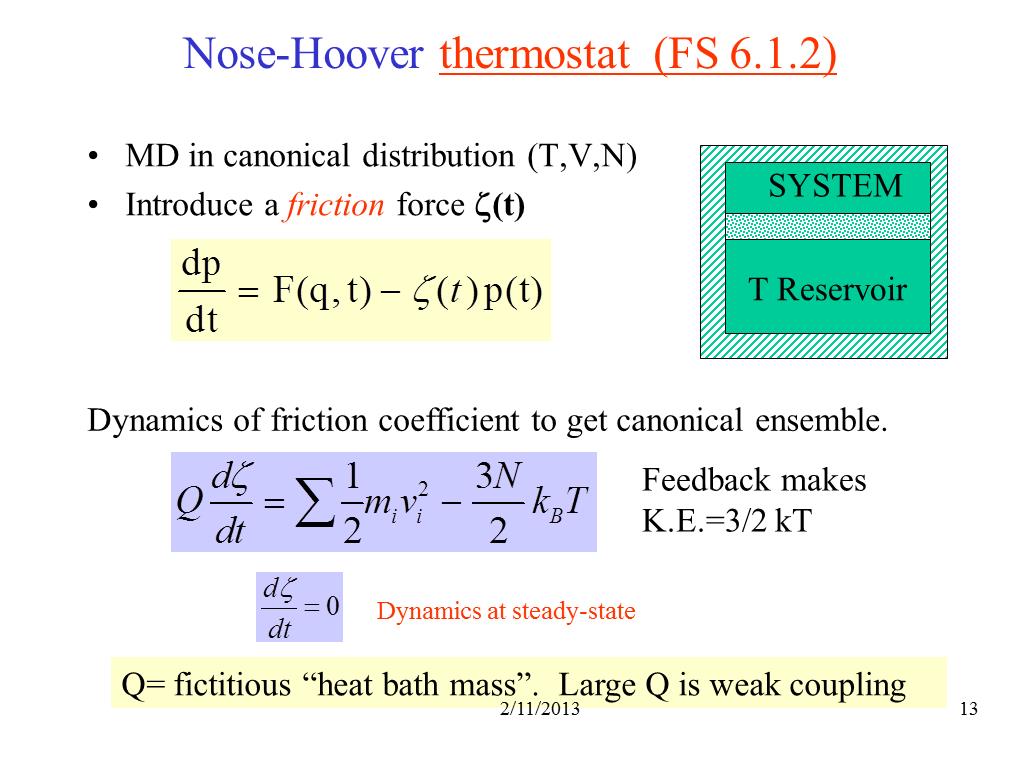 13. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
1350.6226430074234
00:00/00:00
13. Nose-Hoover thermostat (FS 6.1…
1350.6226430074234
00:00/00:00 -
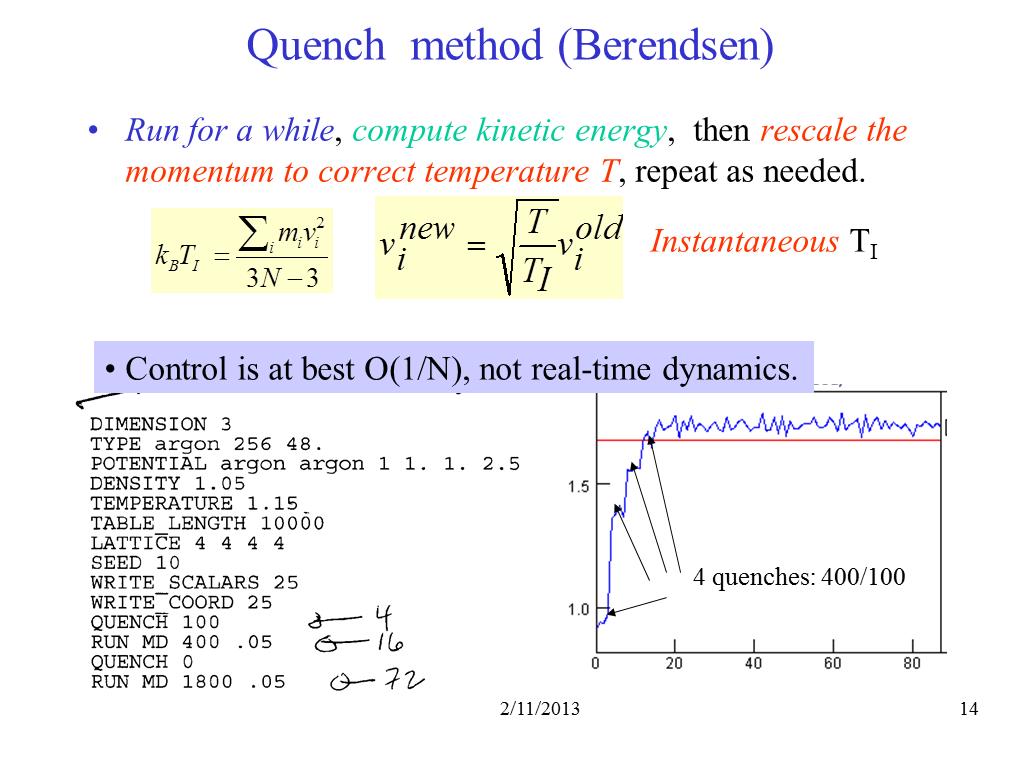 14. Quench method (Berendsen)
1357.5699654638561
00:00/00:00
14. Quench method (Berendsen)
1357.5699654638561
00:00/00:00 -
 15. Thermostats
1373.8645944980349
00:00/00:00
15. Thermostats
1373.8645944980349
00:00/00:00 -
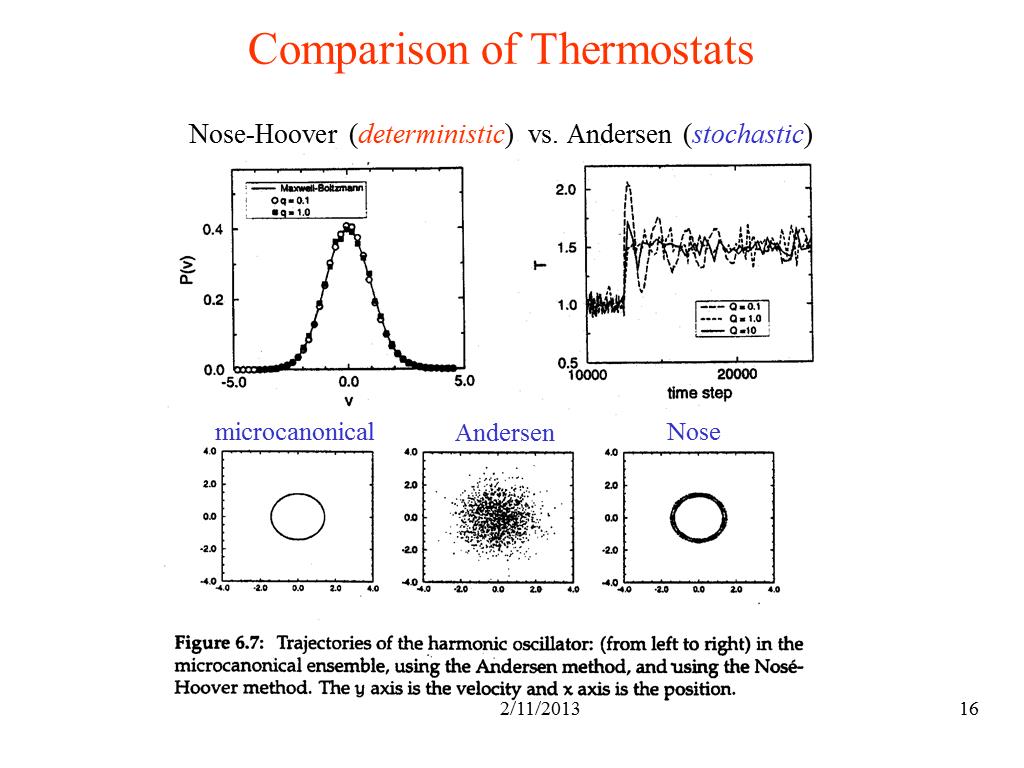 16. Comparison of Thermostats
1805.7985788575286
00:00/00:00
16. Comparison of Thermostats
1805.7985788575286
00:00/00:00 -
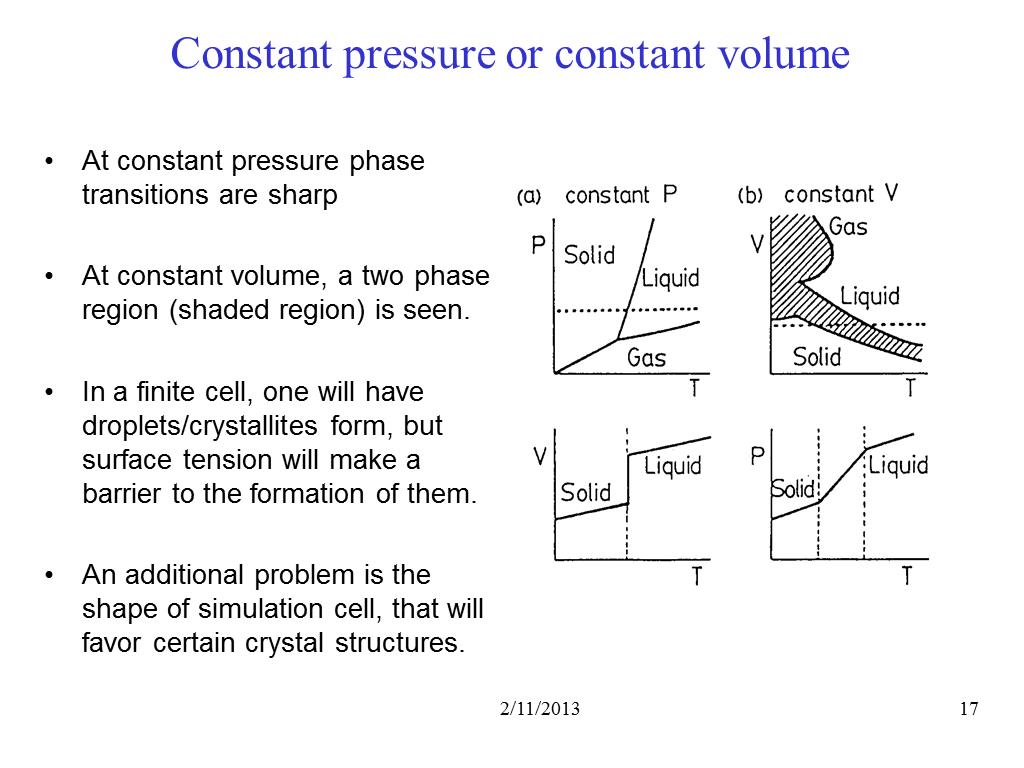 17. Constant pressure or constant …
1927.9451391369935
00:00/00:00
17. Constant pressure or constant …
1927.9451391369935
00:00/00:00 -
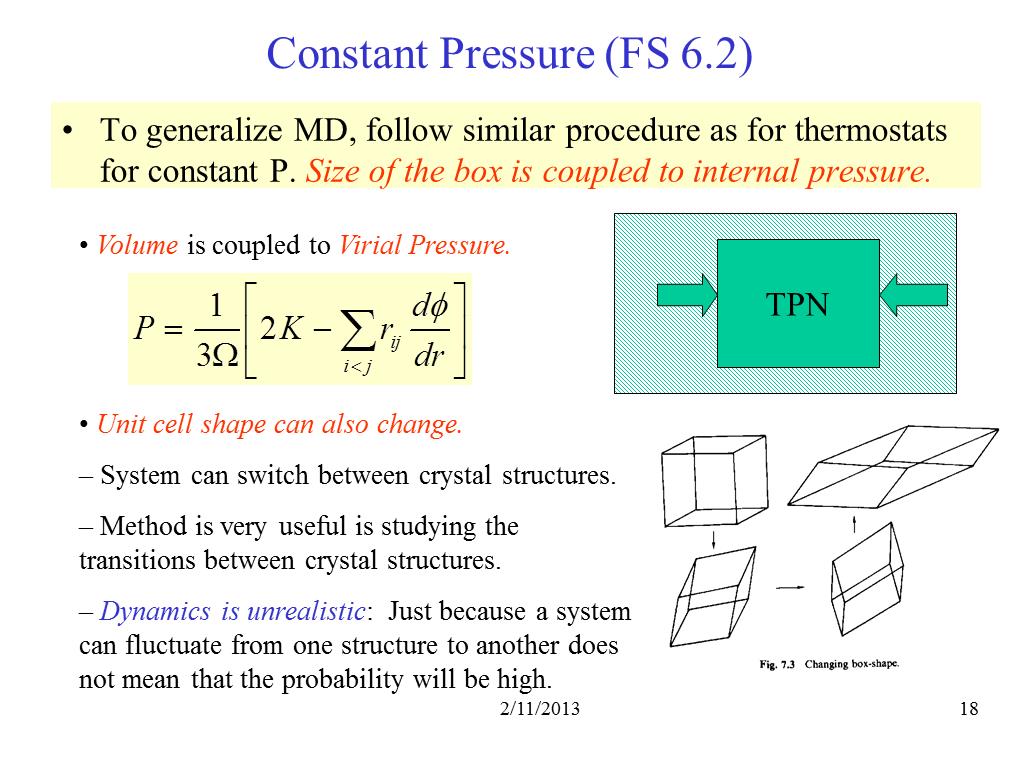 18. Constant Pressure (FS 6.2)
2147.0692475463466
00:00/00:00
18. Constant Pressure (FS 6.2)
2147.0692475463466
00:00/00:00 -
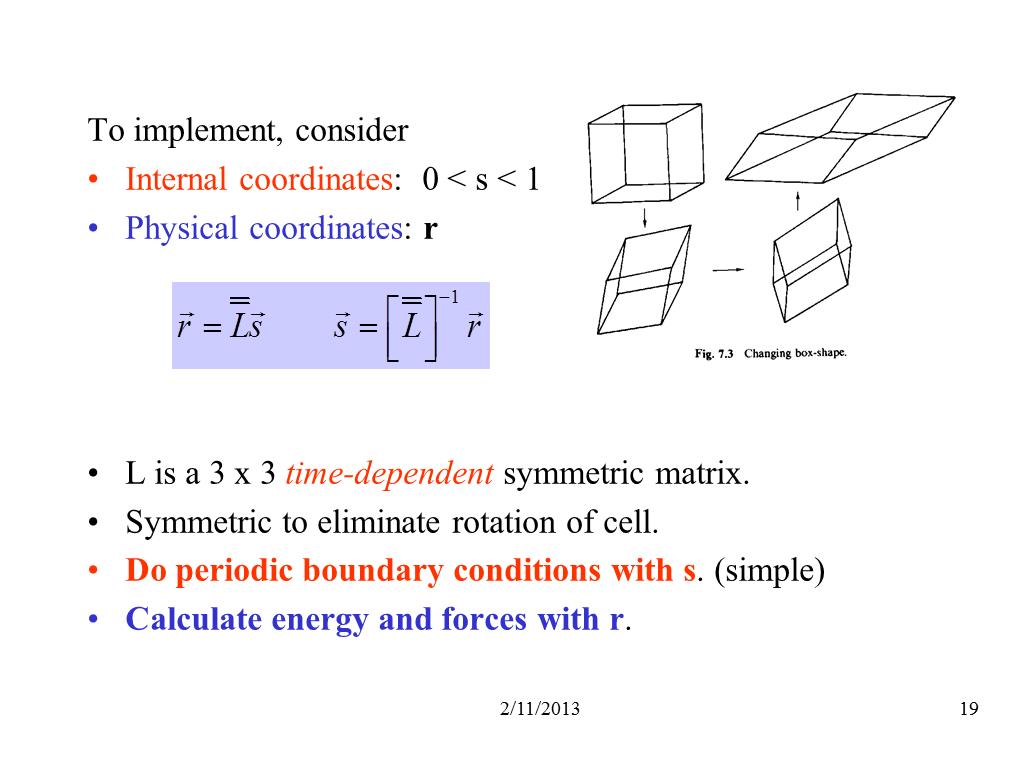 19. To implement
2559.1868474364969
00:00/00:00
19. To implement
2559.1868474364969
00:00/00:00 -
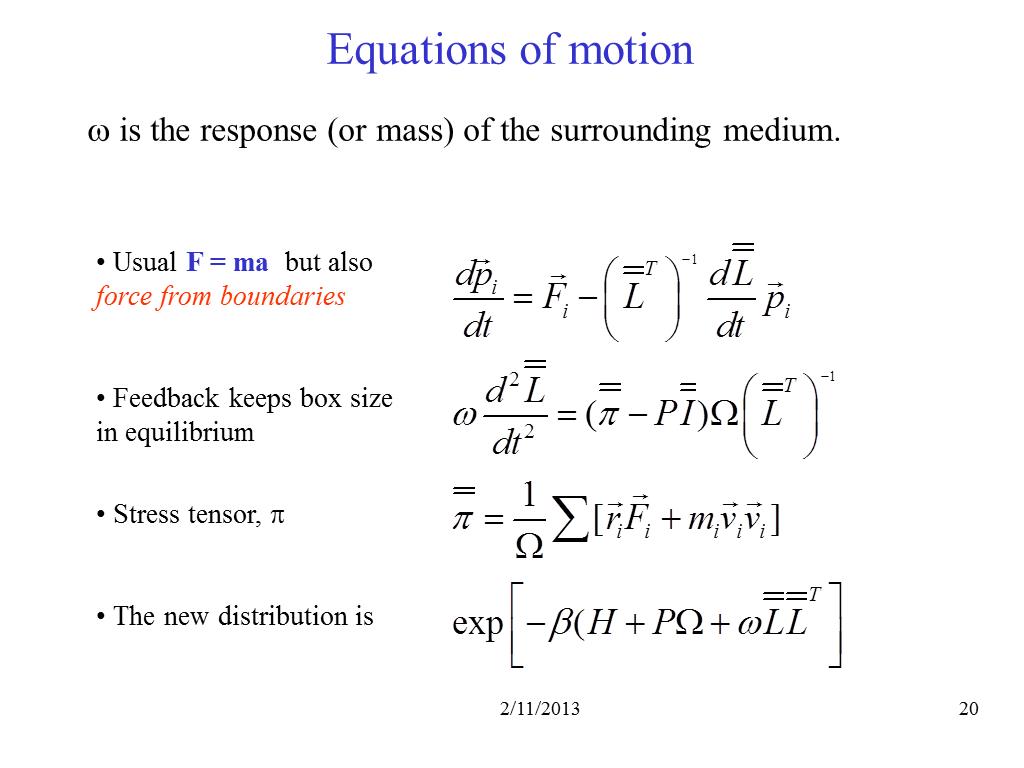 20. Equations of motion
2649.5592177029766
00:00/00:00
20. Equations of motion
2649.5592177029766
00:00/00:00 -
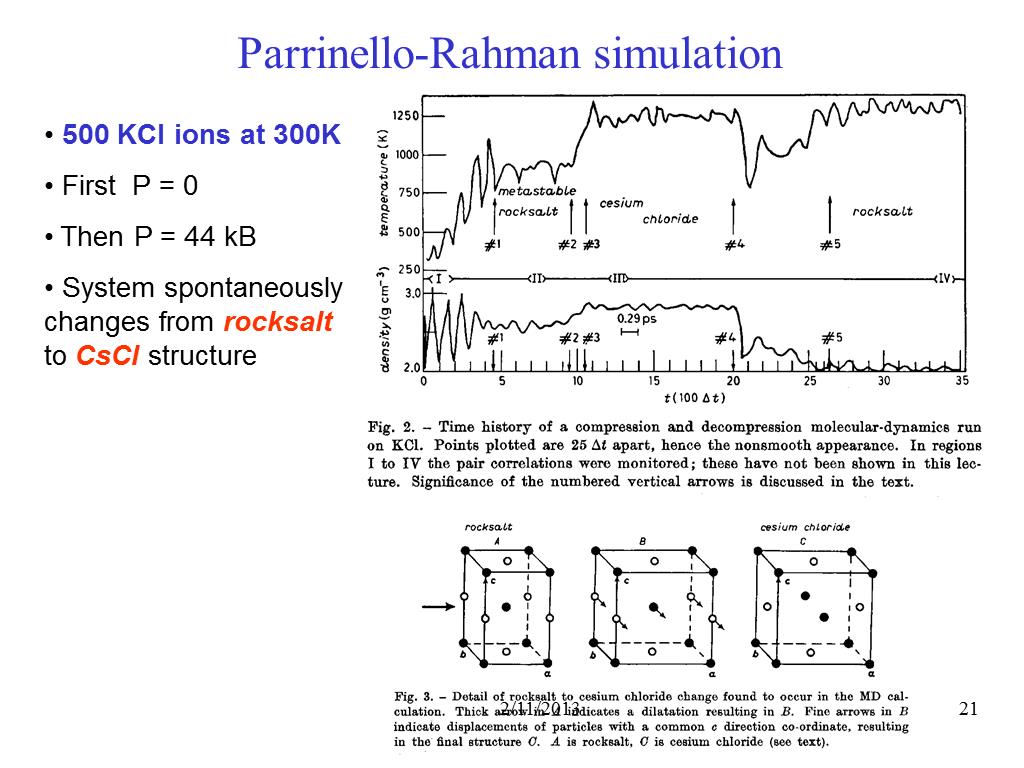 21. Parrinello-Rahman simulation
2926.0069347046906
00:00/00:00
21. Parrinello-Rahman simulation
2926.0069347046906
00:00/00:00 -
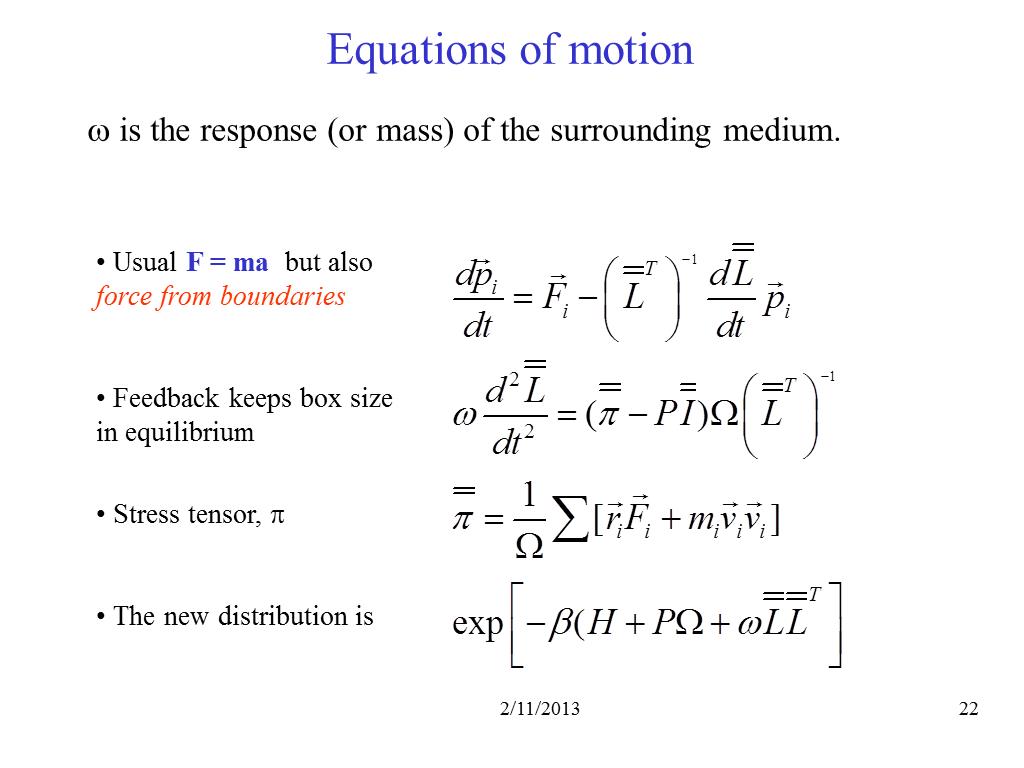 22. Equations of motion
3019.8503973819543
00:00/00:00
22. Equations of motion
3019.8503973819543
00:00/00:00 -
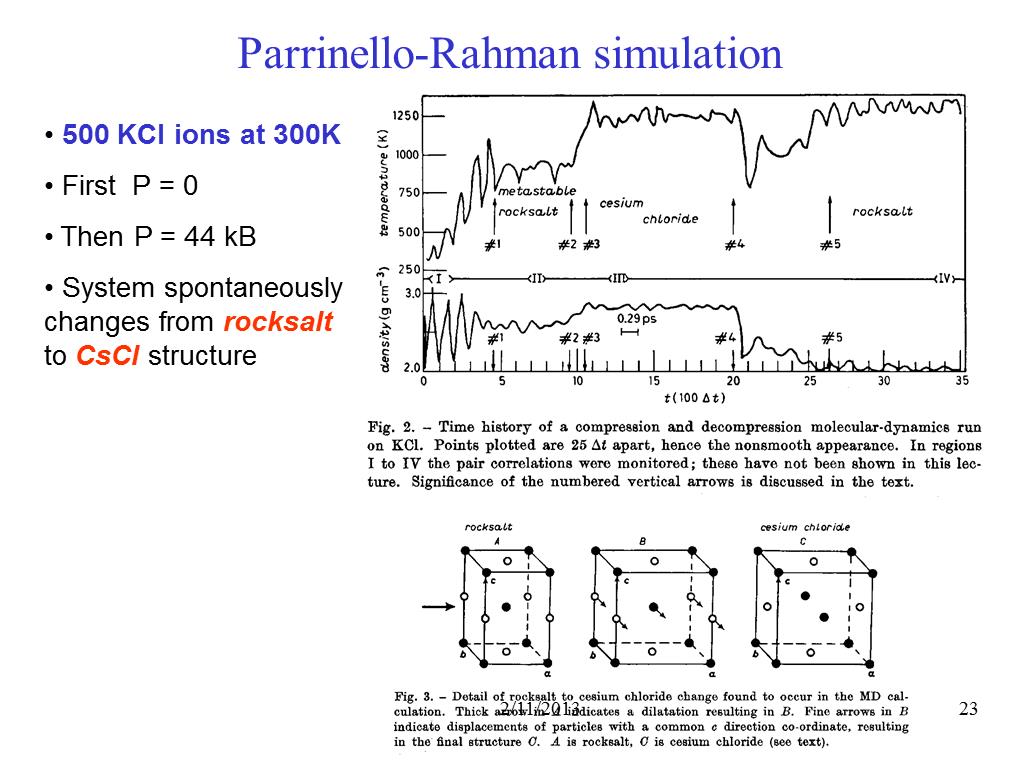 23. Parrinello-Rahman simulation
3027.5363877201185
00:00/00:00
23. Parrinello-Rahman simulation
3027.5363877201185
00:00/00:00 -
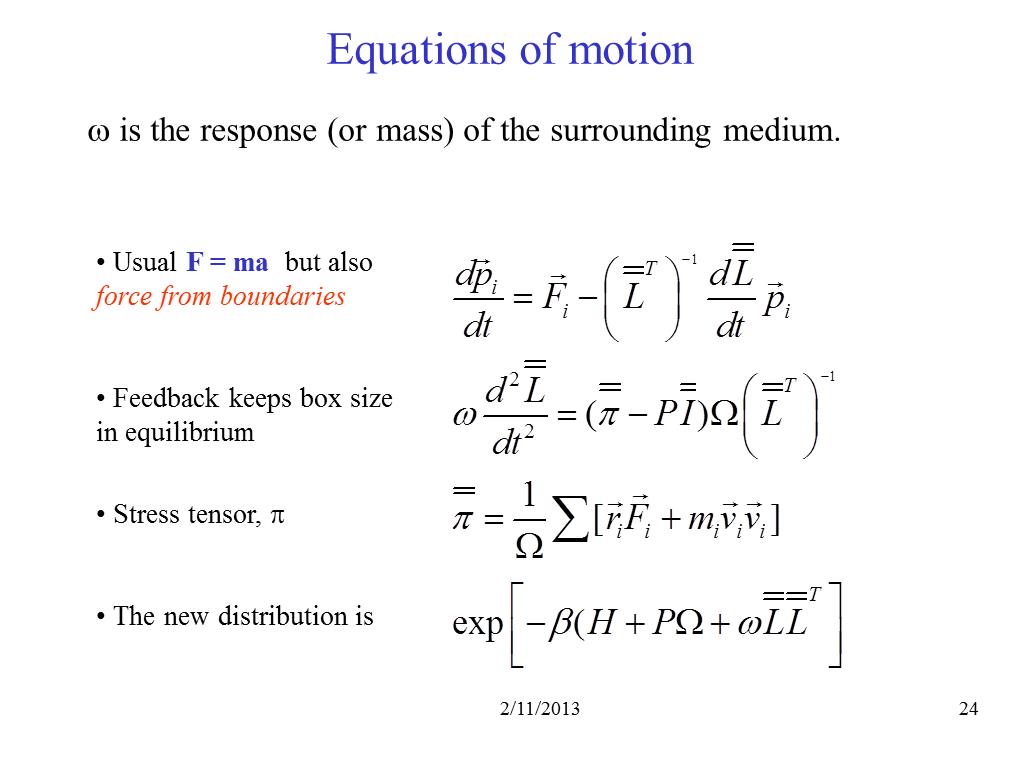 24. Equations of motion
3102.7847124824684
00:00/00:00
24. Equations of motion
3102.7847124824684
00:00/00:00 -
 25. Features of Constant Pressure/…
3114.9335359202123
00:00/00:00
25. Features of Constant Pressure/…
3114.9335359202123
00:00/00:00