ECE 595Z Lecture 30: Low Power Design II
ECE 595Z Lecture 30: Low Power Design II
-
 1. ECE 595Z Digital Systems Desig…
0
00:00/00:00
1. ECE 595Z Digital Systems Desig…
0
00:00/00:00 -
 2. Lecture 29: Re-cap
16.683350016683352
00:00/00:00
2. Lecture 29: Re-cap
16.683350016683352
00:00/00:00 -
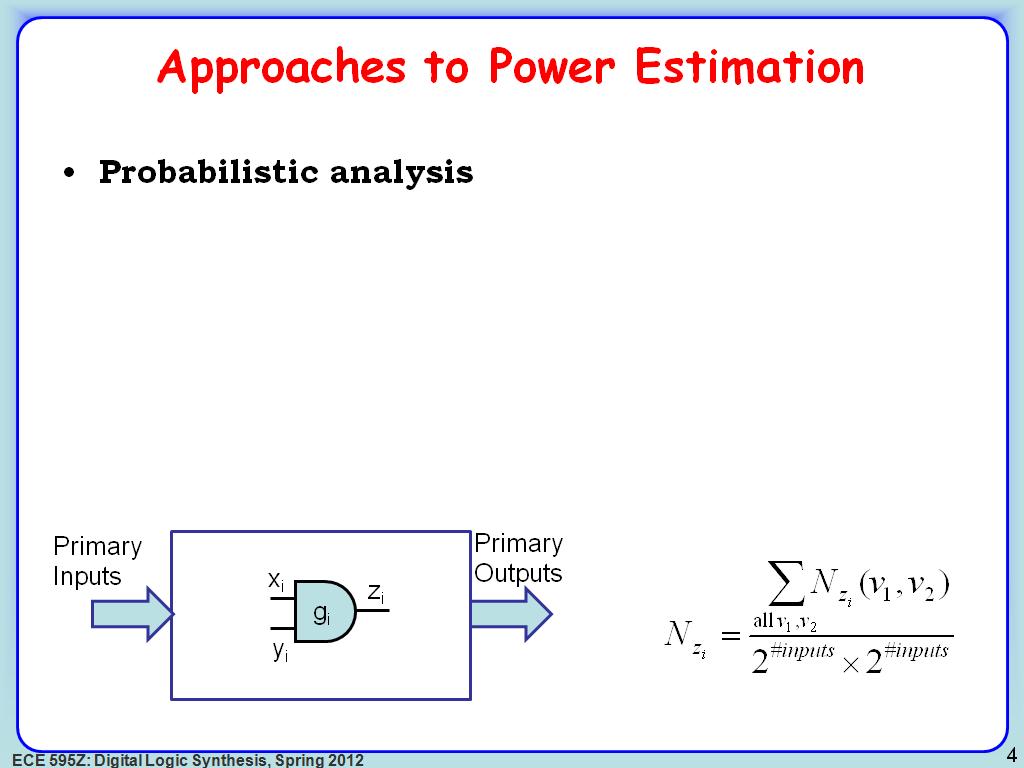
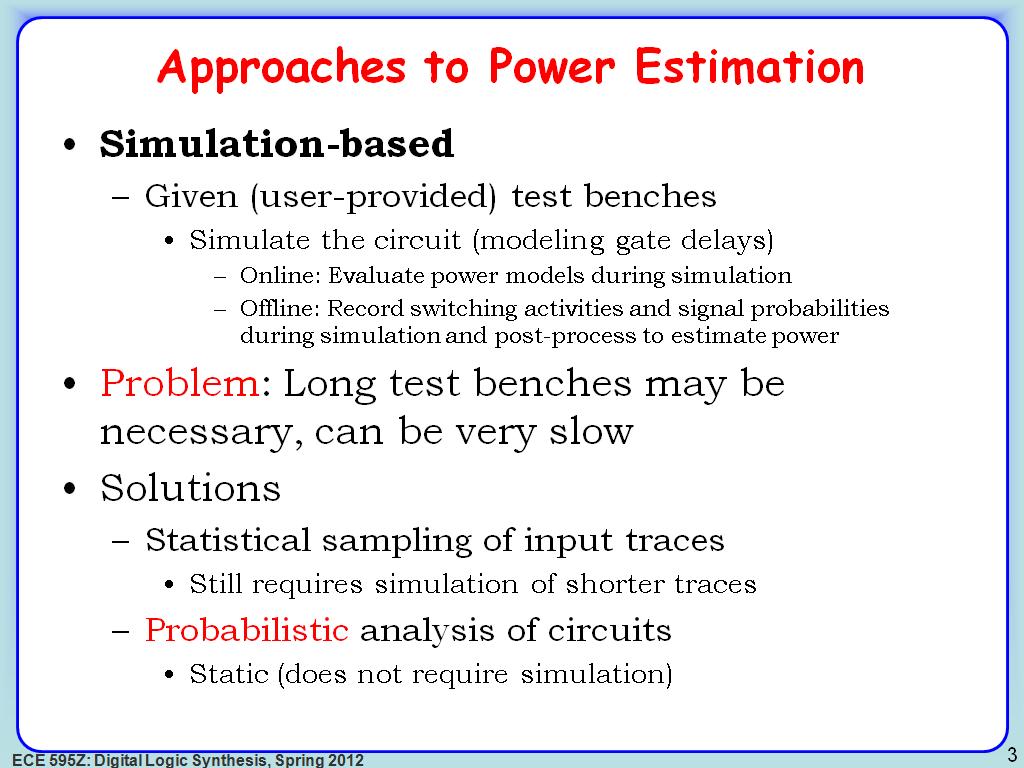 3. Approaches to Power Estimation
159.12579245912579
00:00/00:00
3. Approaches to Power Estimation
159.12579245912579
00:00/00:00 -
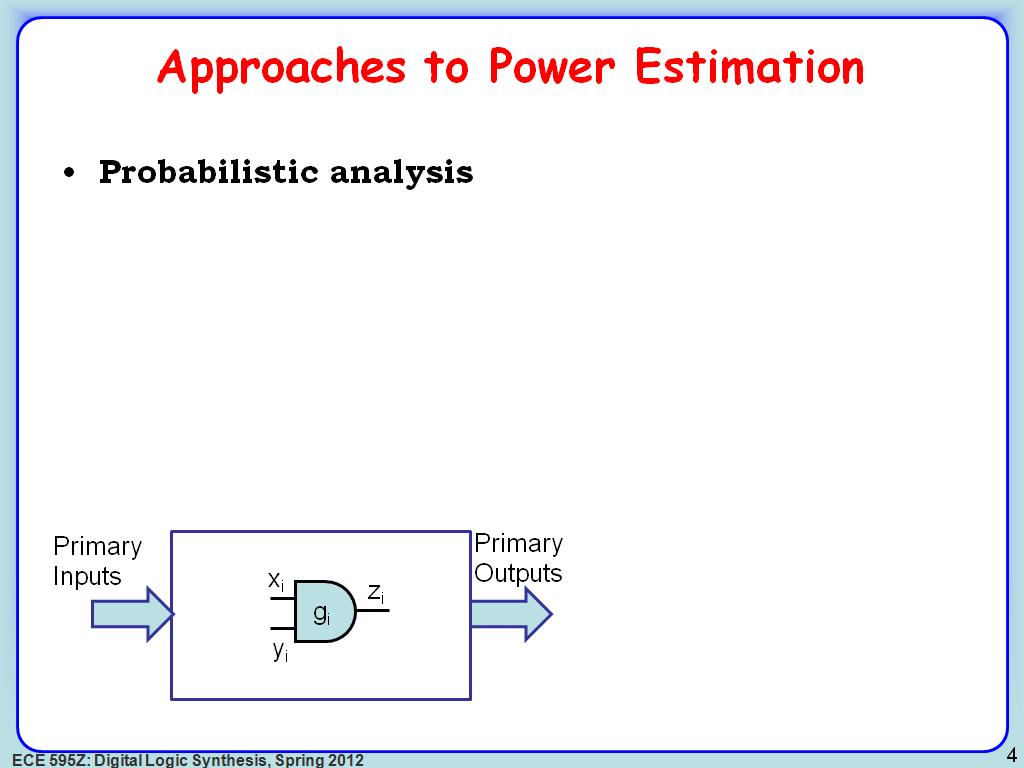
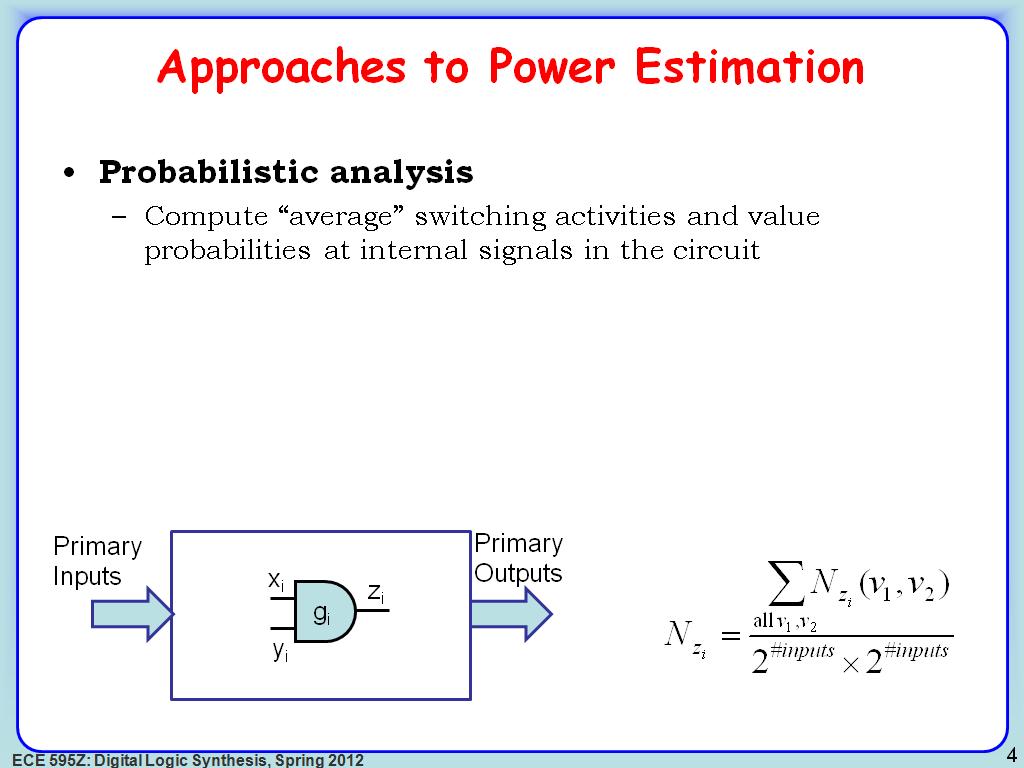
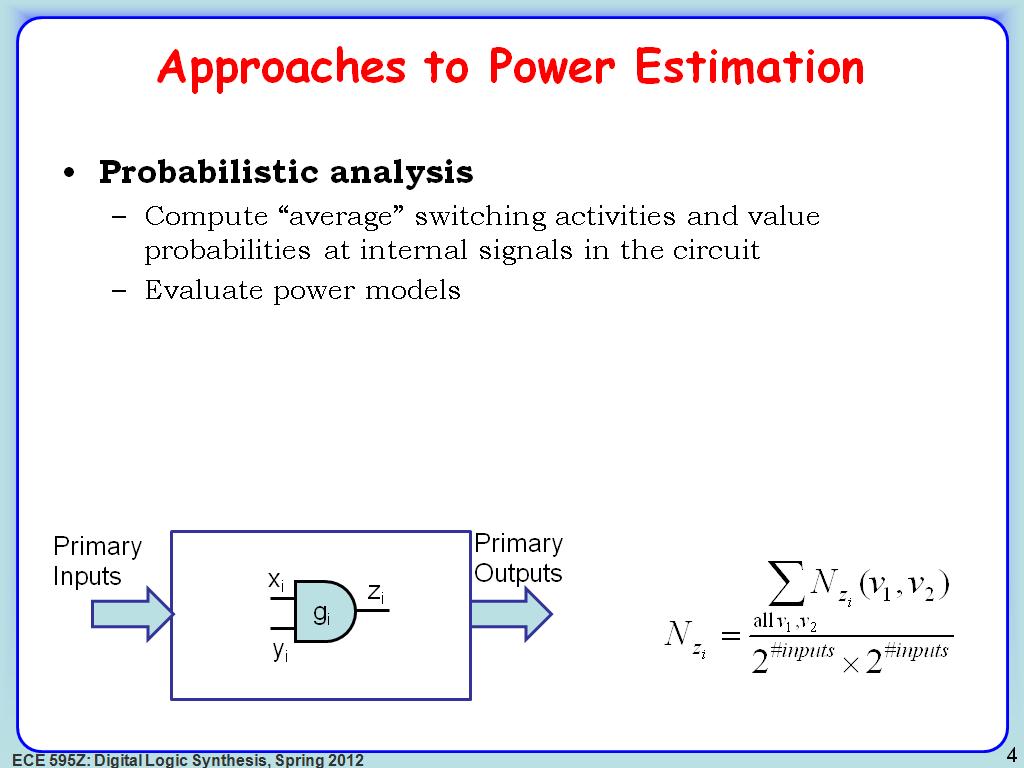
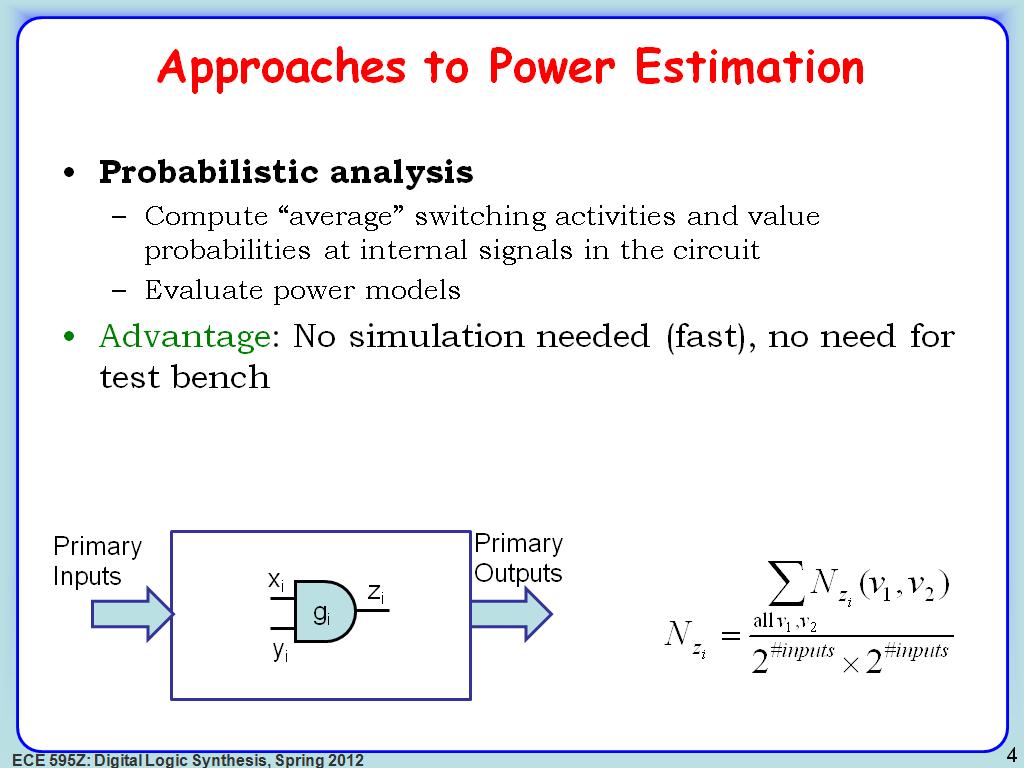 4. Approaches to Power Estimation
636.60326993660328
00:00/00:00
4. Approaches to Power Estimation
636.60326993660328
00:00/00:00 -
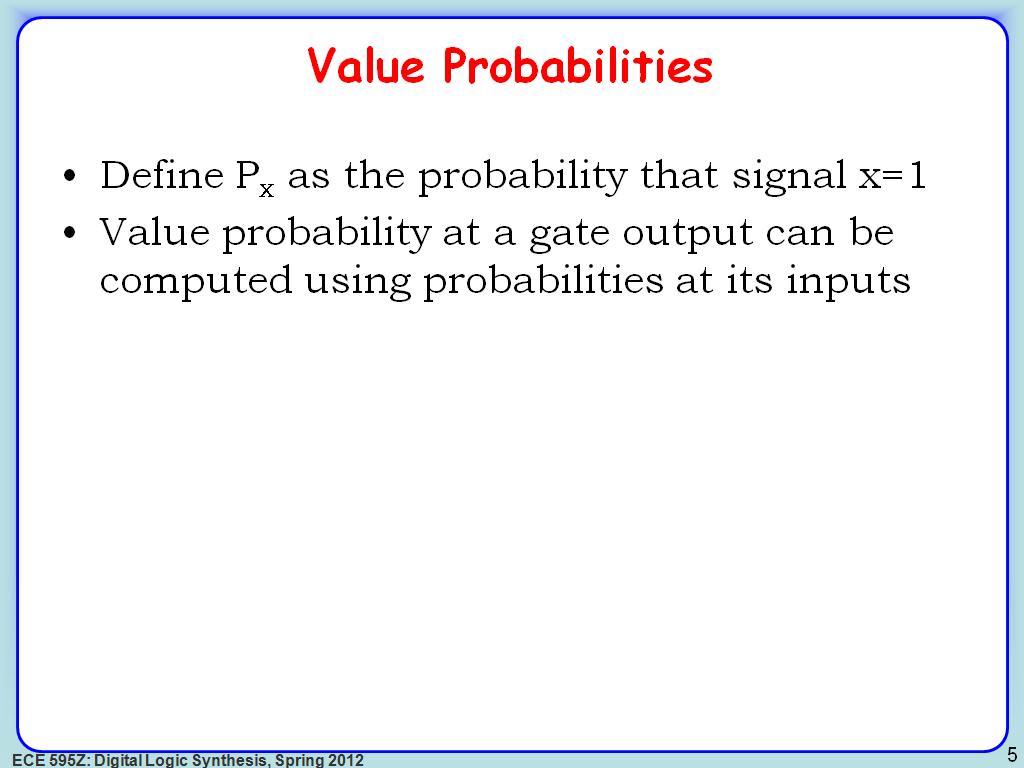
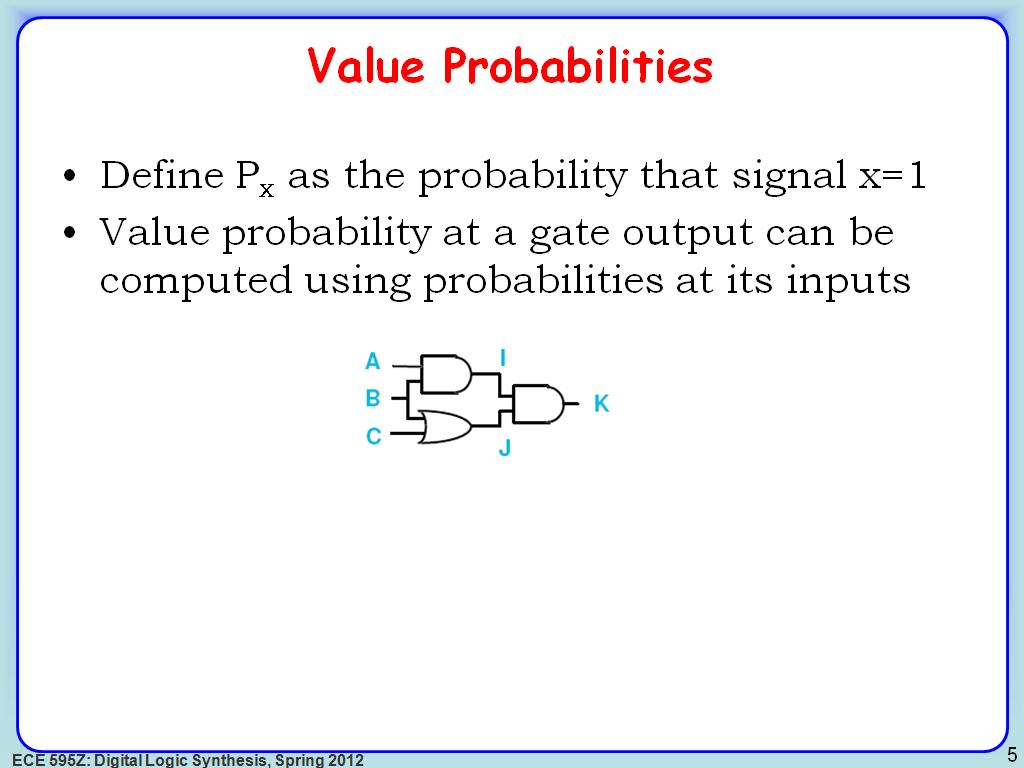
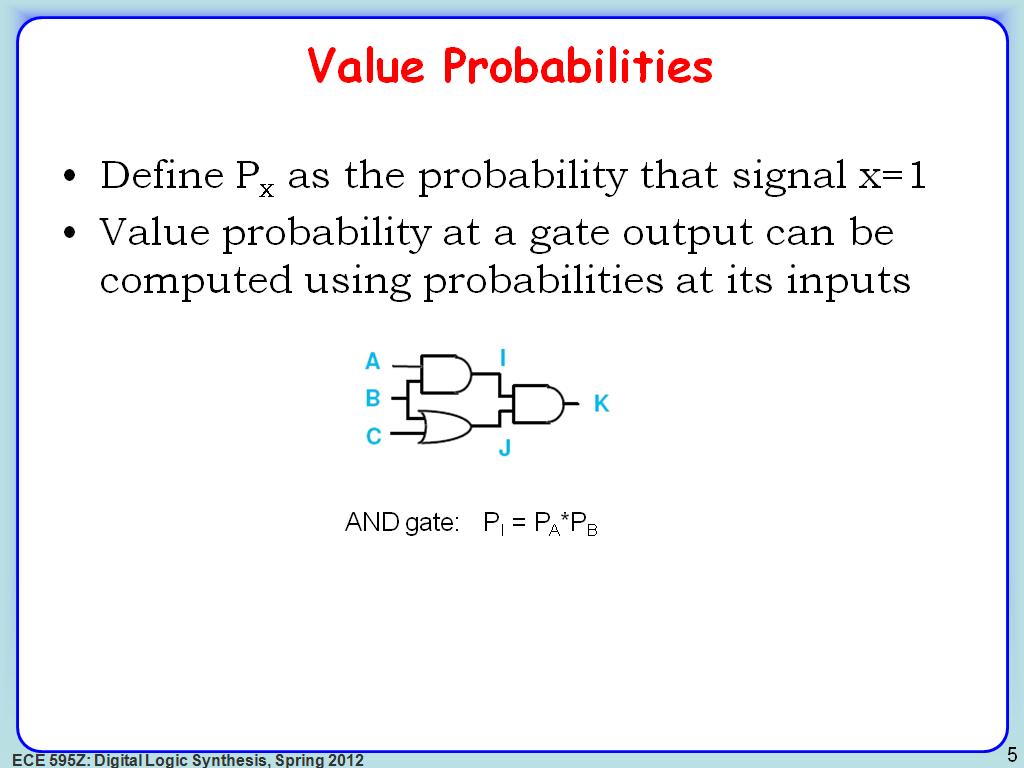
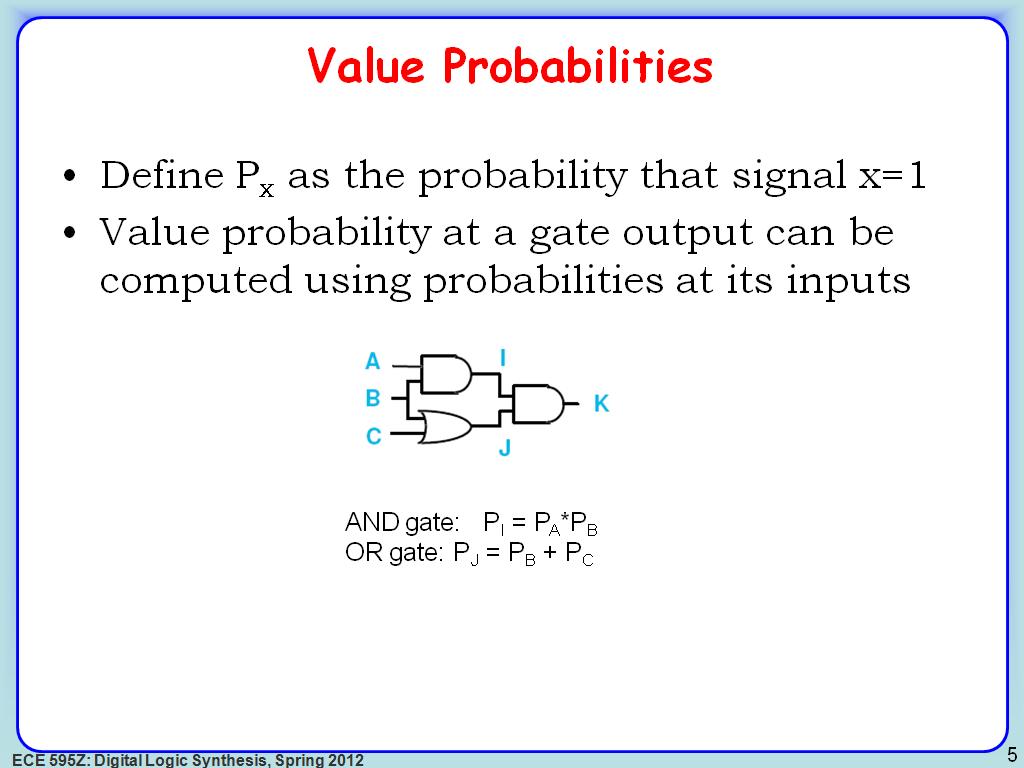
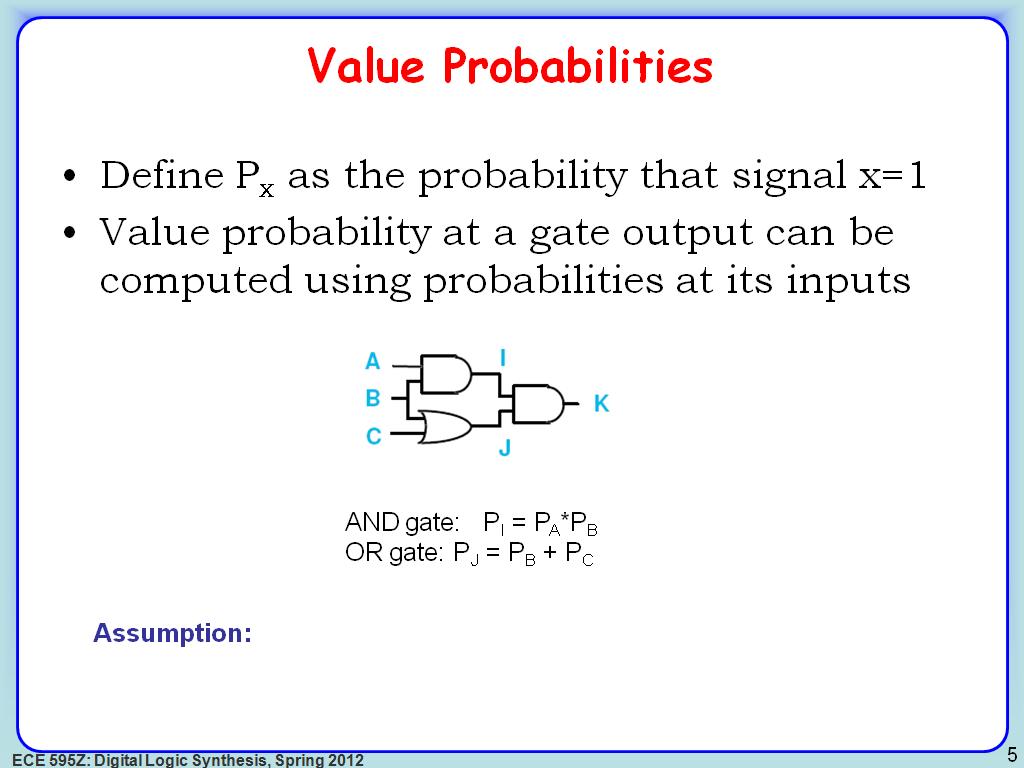
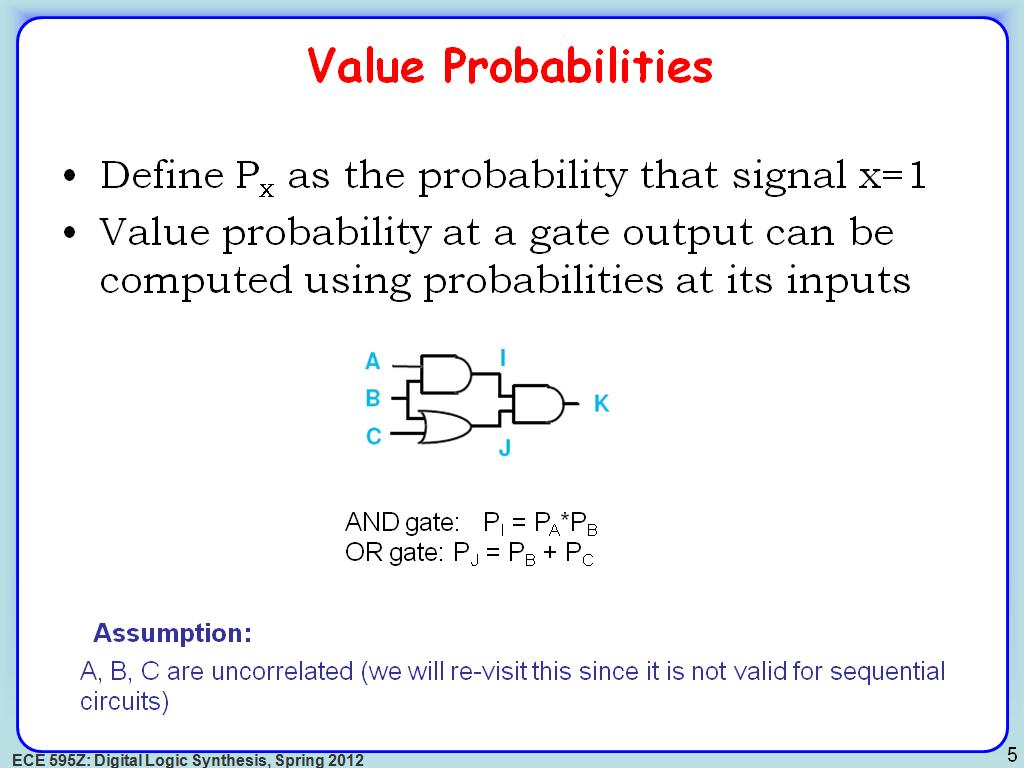 5. Value Probabilities
814.18084751418087
00:00/00:00
5. Value Probabilities
814.18084751418087
00:00/00:00 -
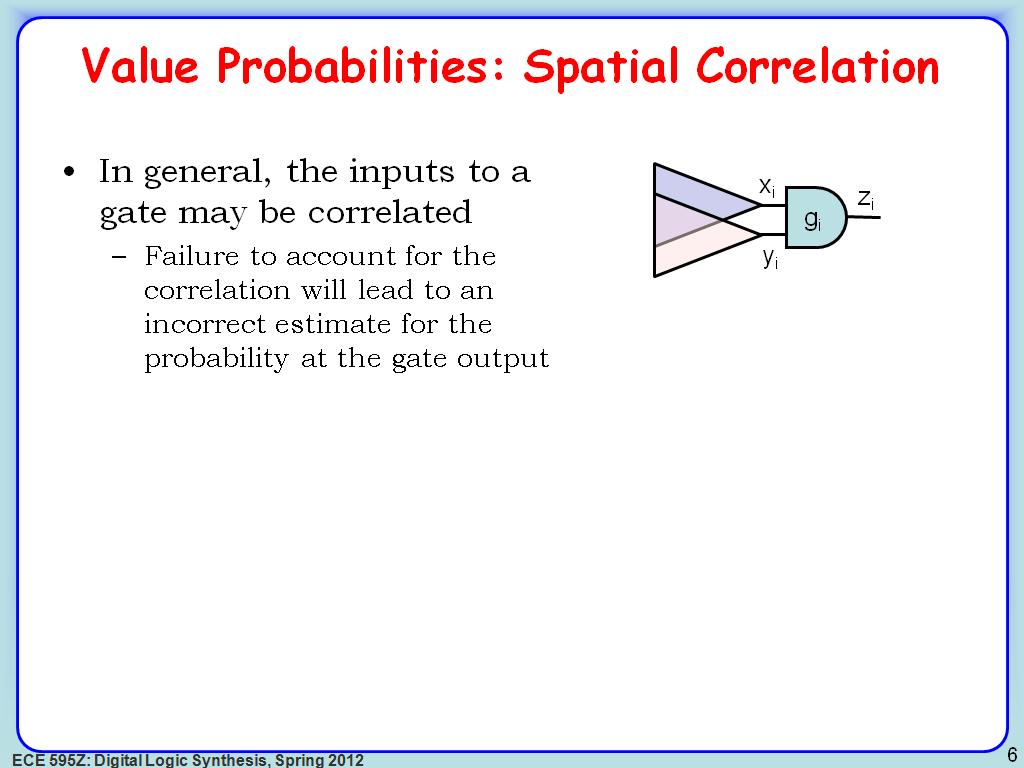
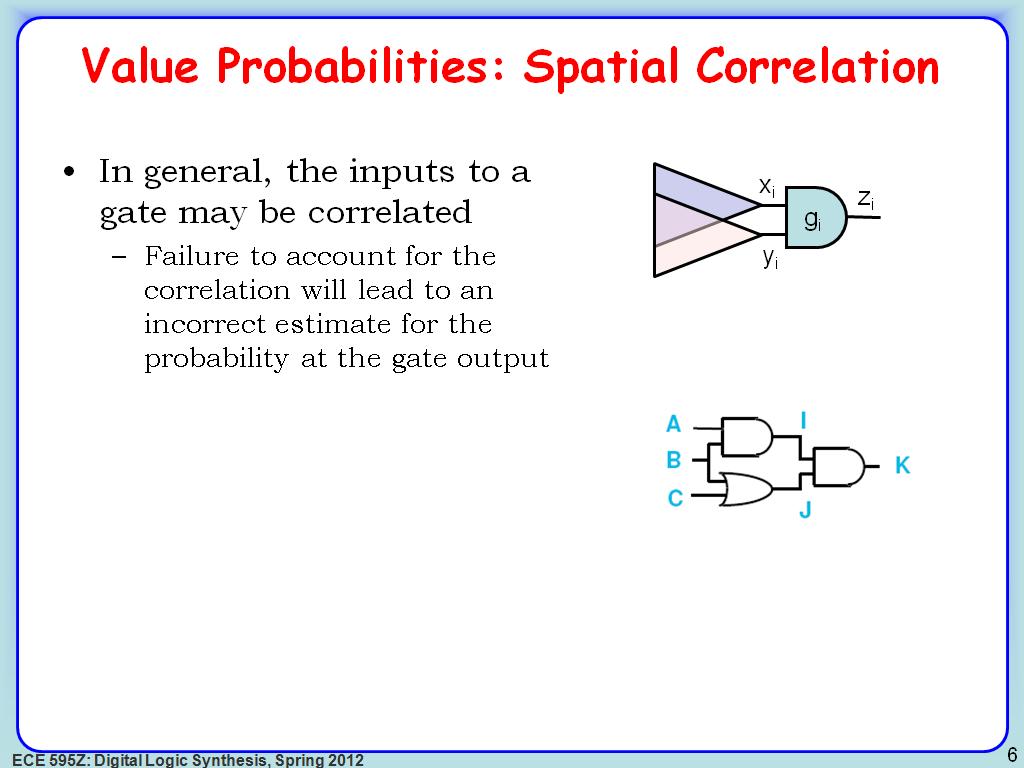
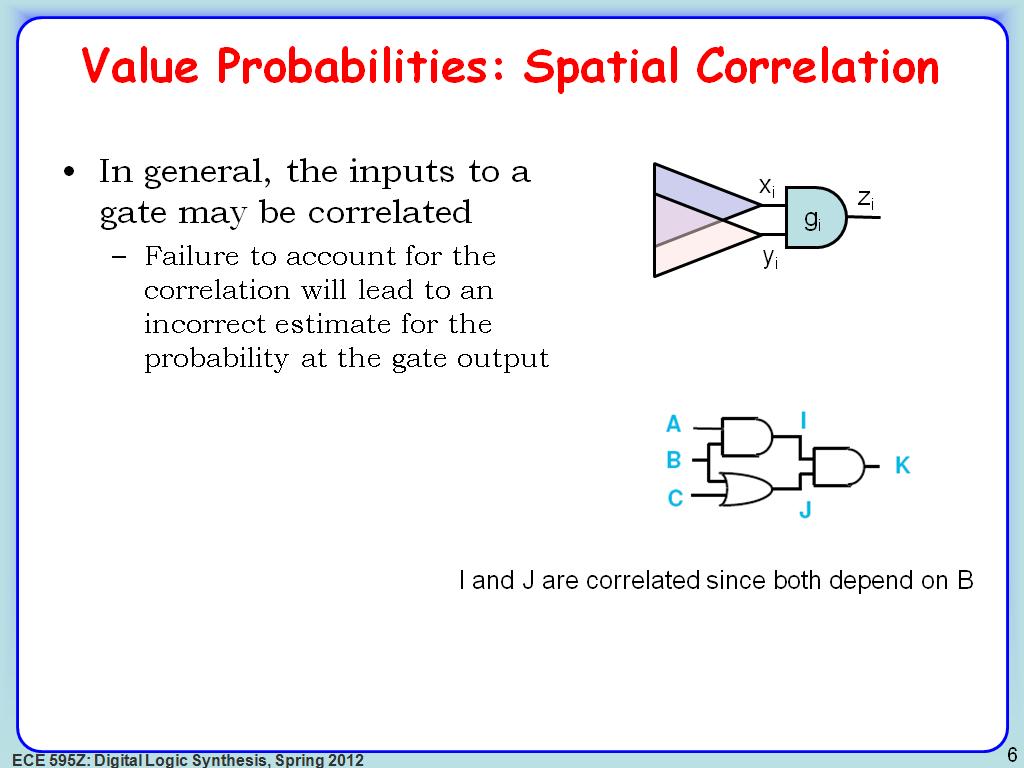
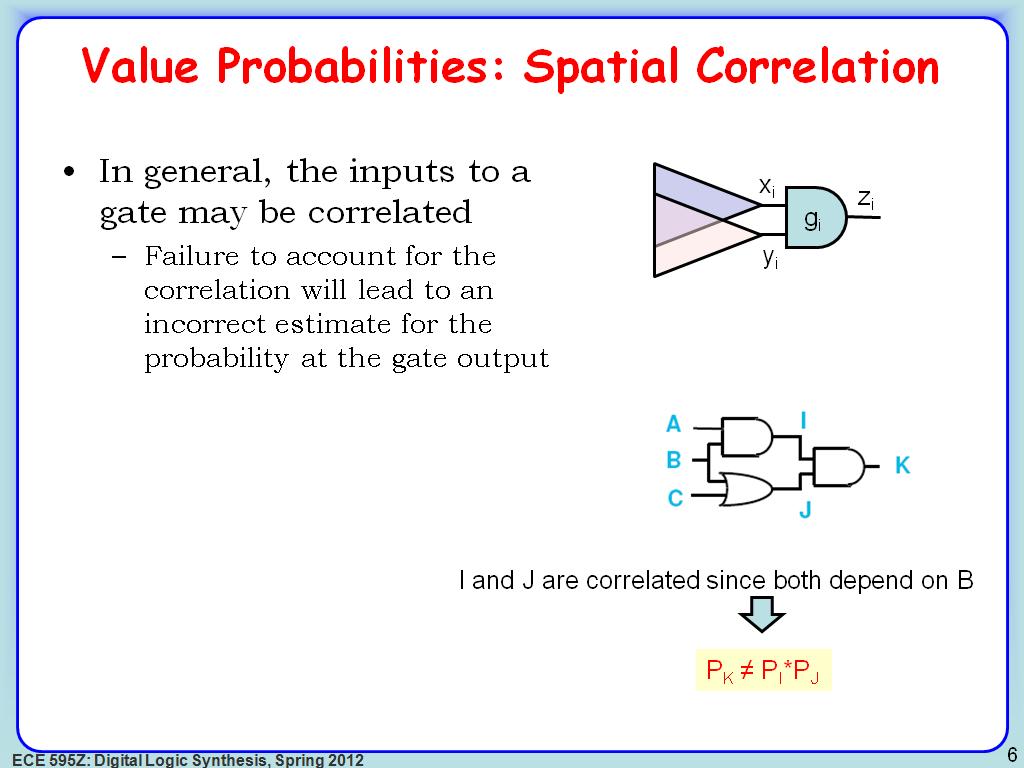 6. Value Probabilities: Spatial C…
1007.8745412078746
00:00/00:00
6. Value Probabilities: Spatial C…
1007.8745412078746
00:00/00:00 -
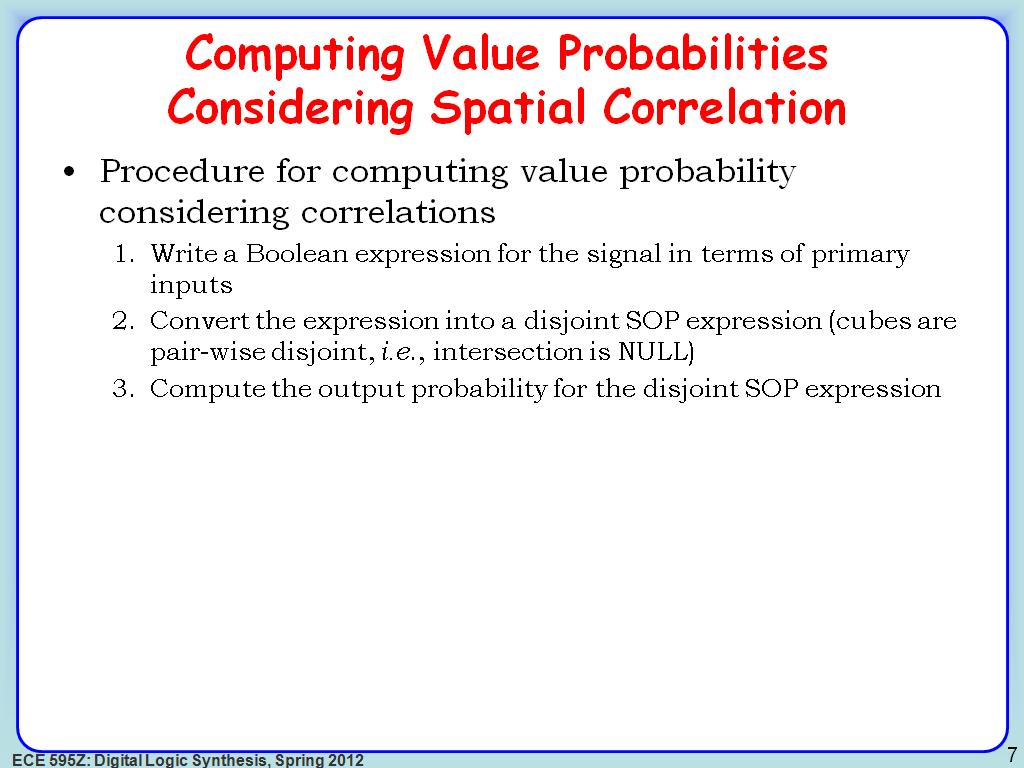
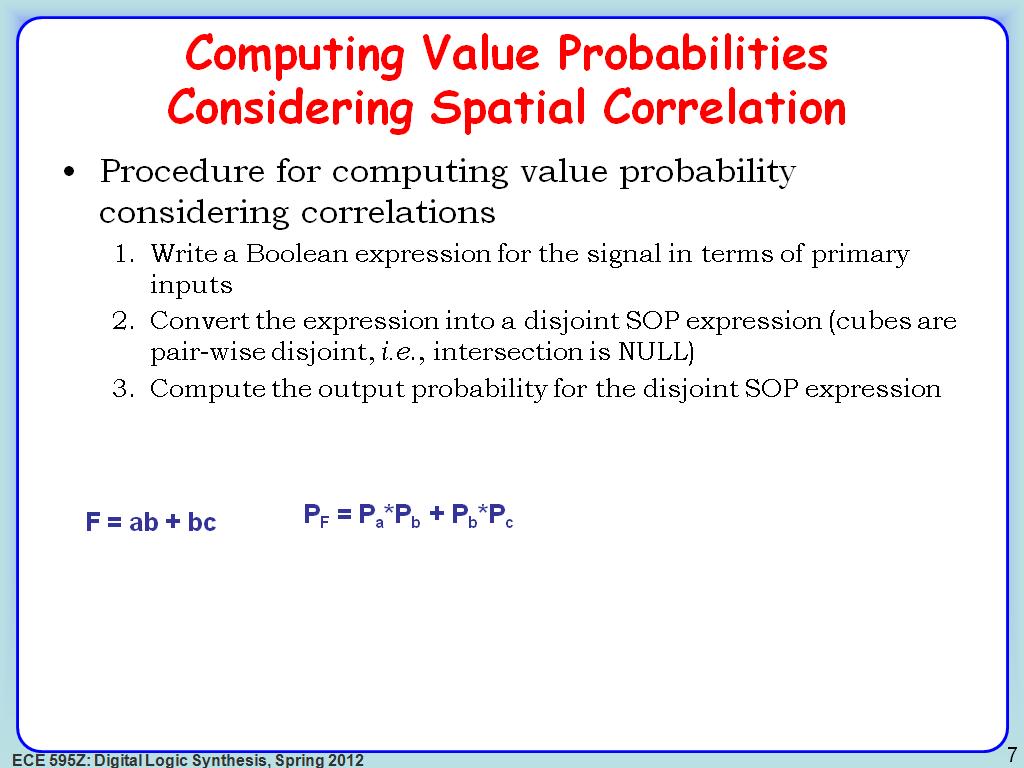
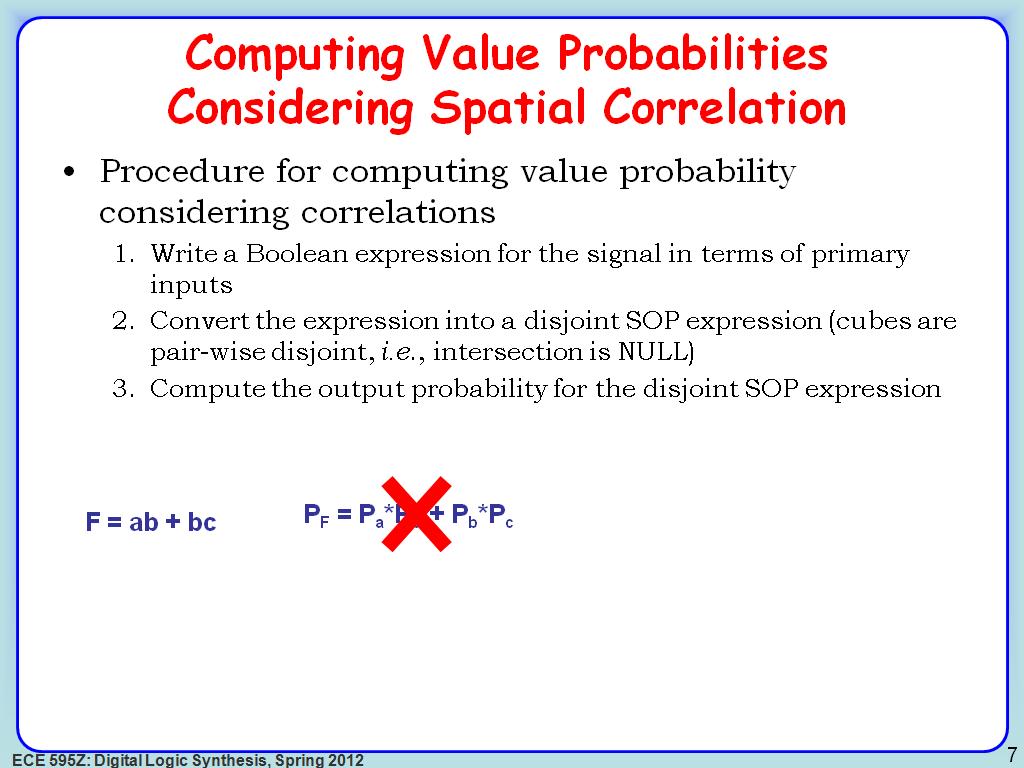
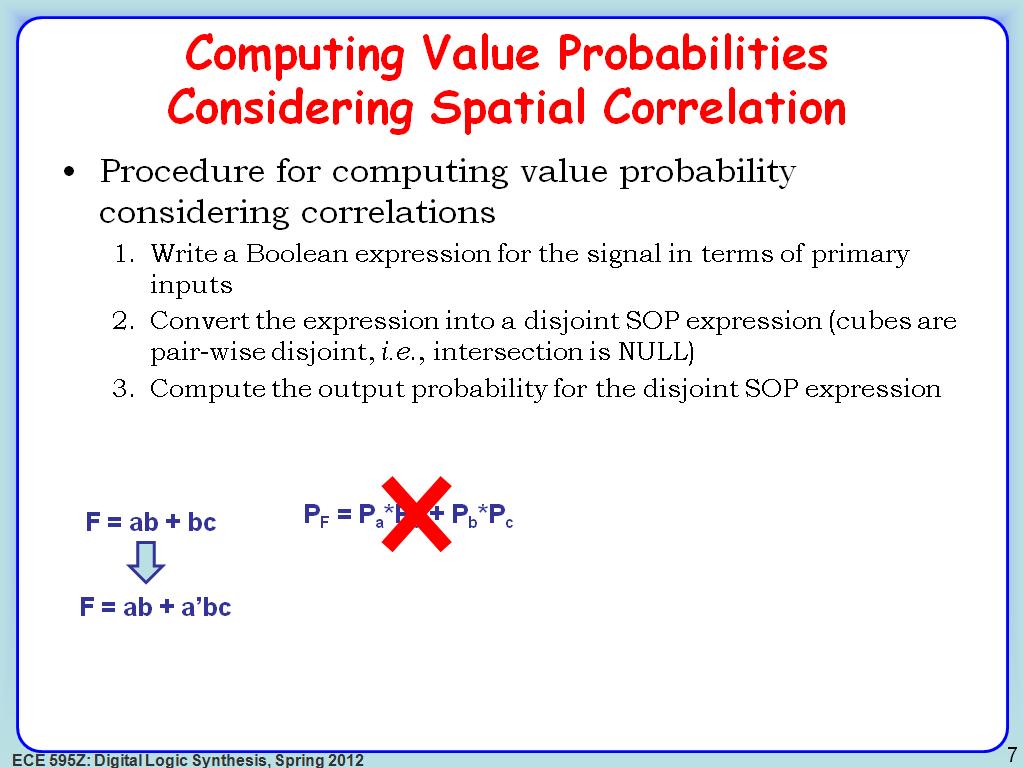
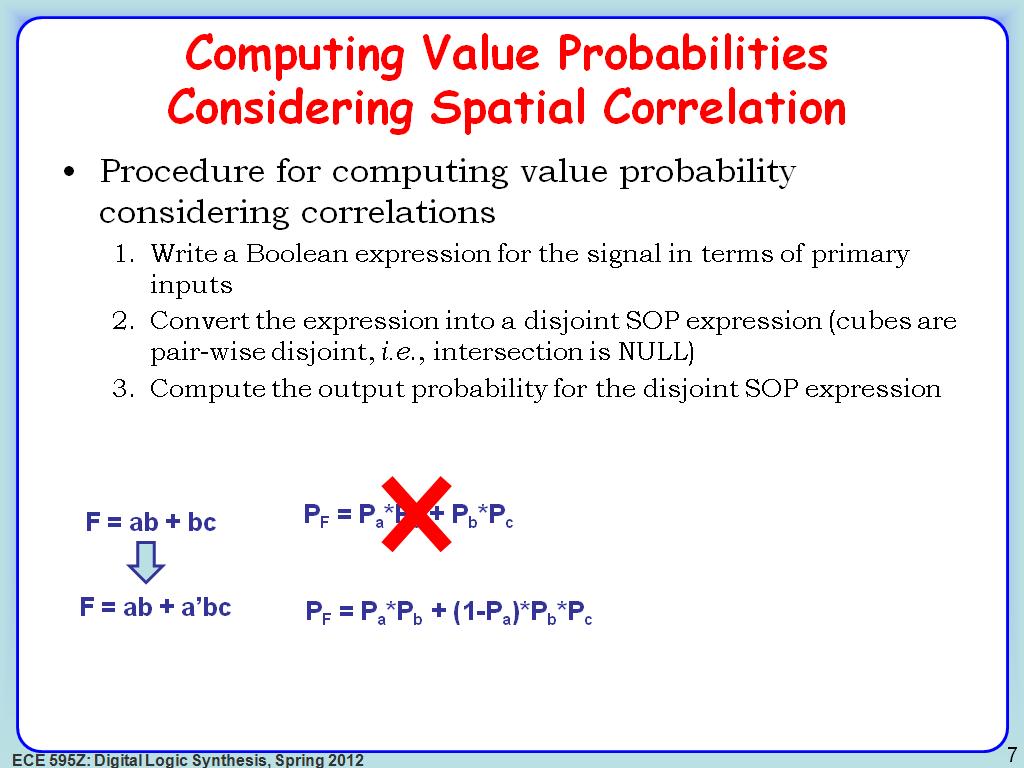
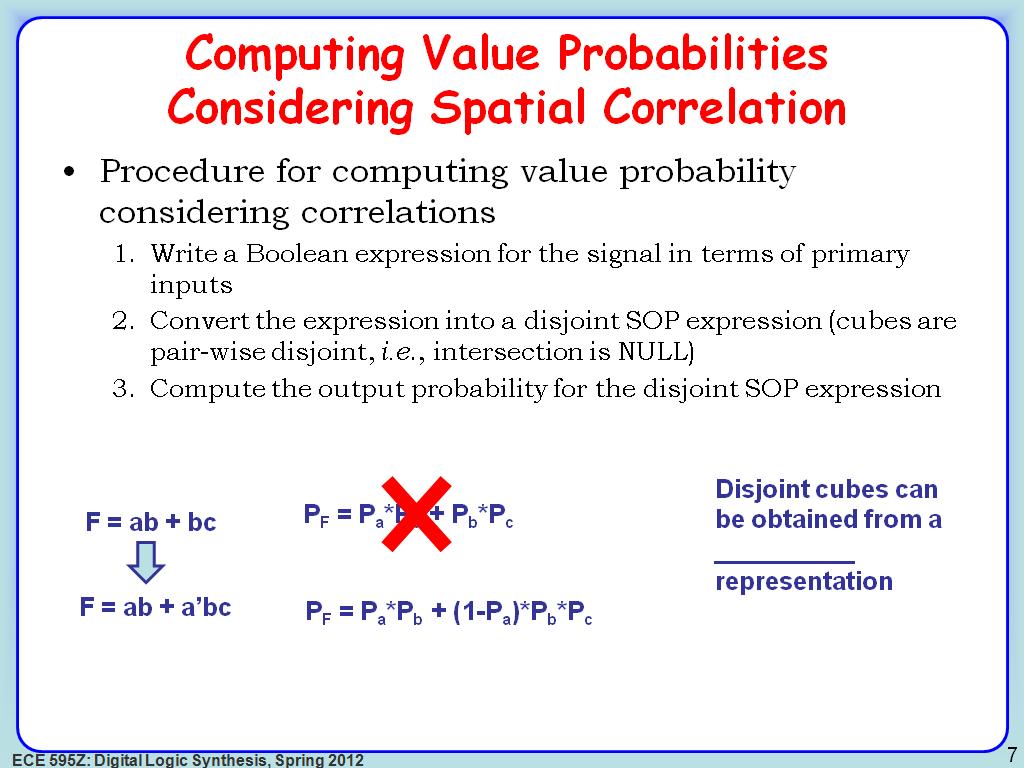 7. Computing Value Probabilities …
1070.236903570237
00:00/00:00
7. Computing Value Probabilities …
1070.236903570237
00:00/00:00 -
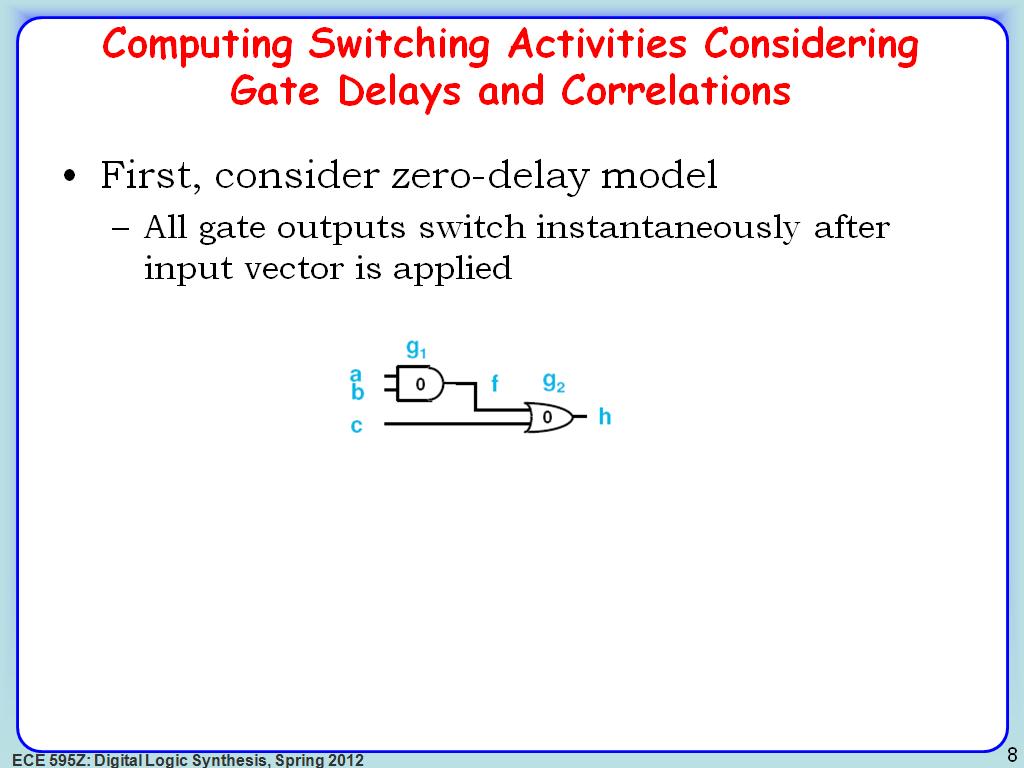
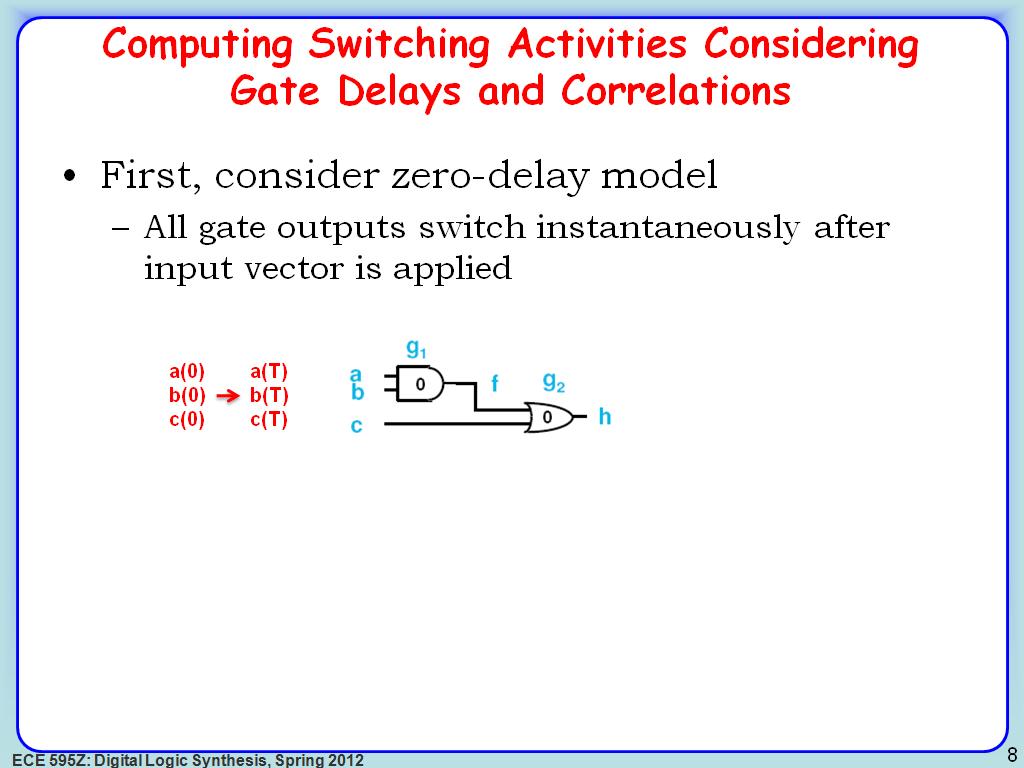
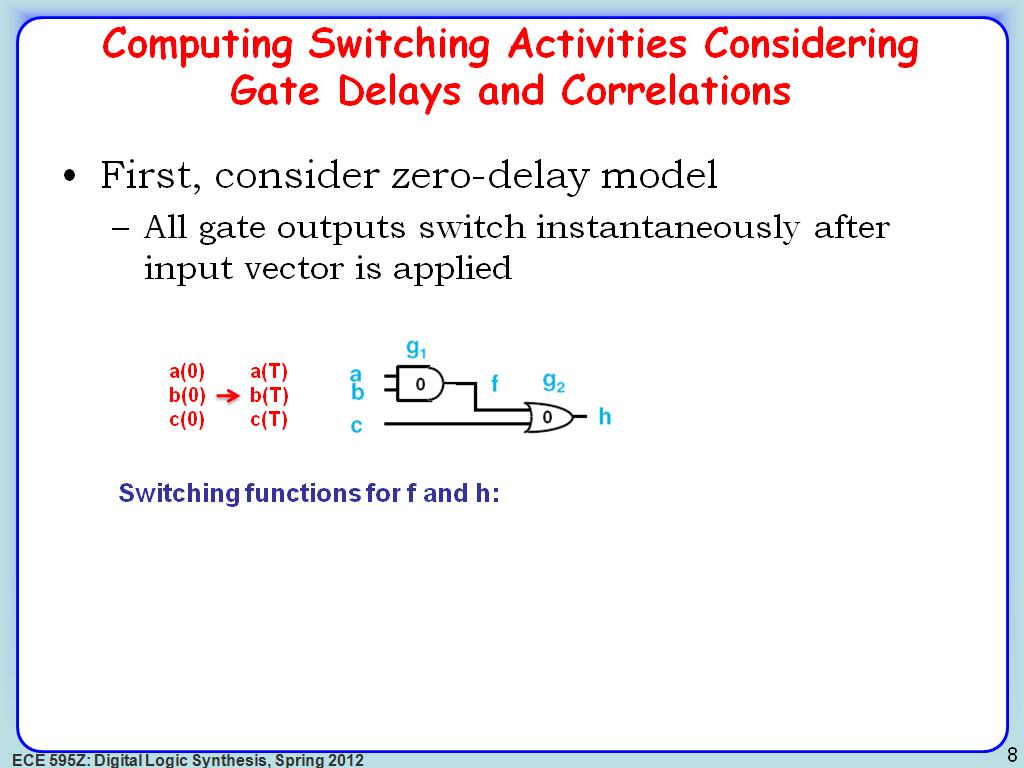
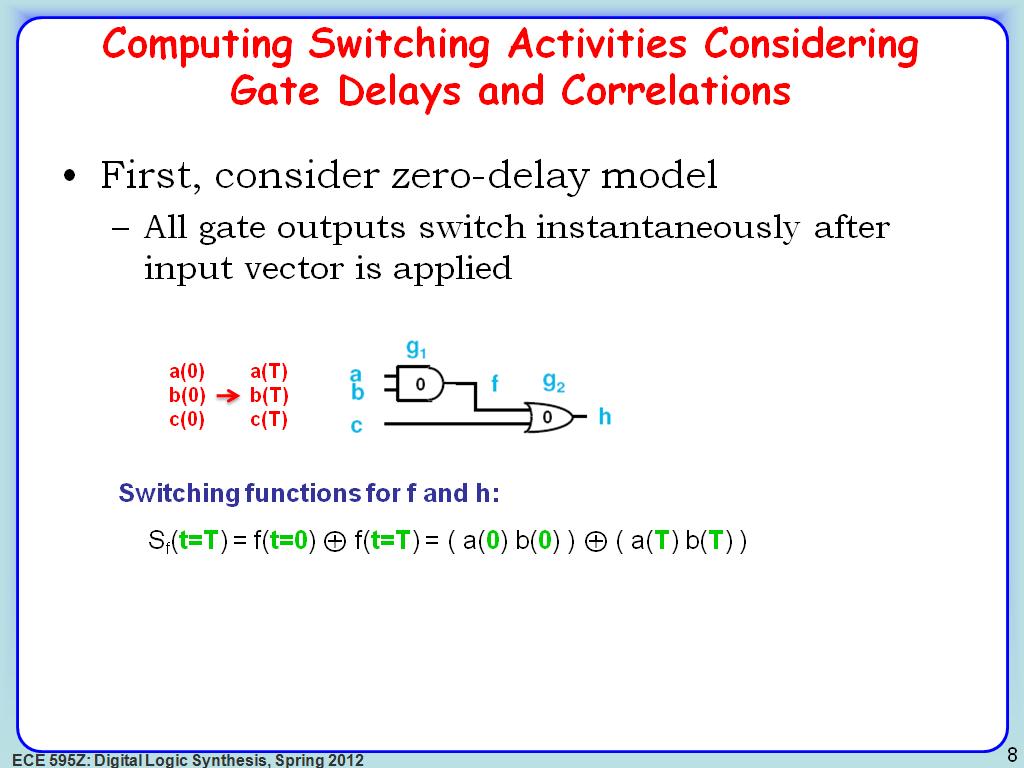
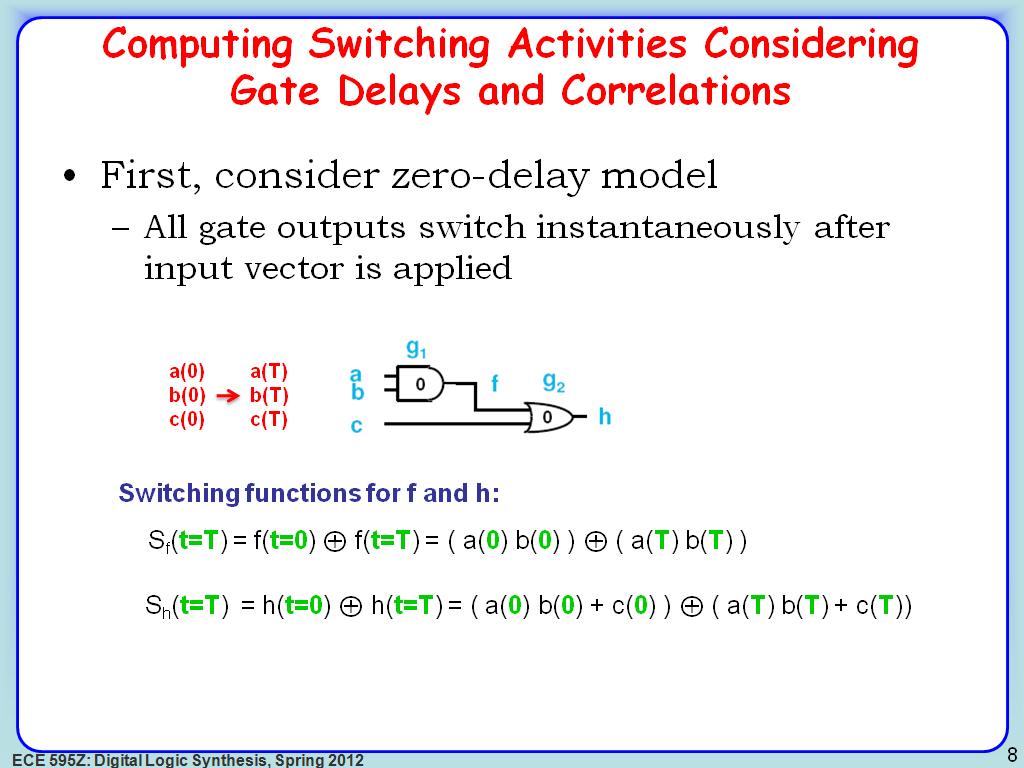
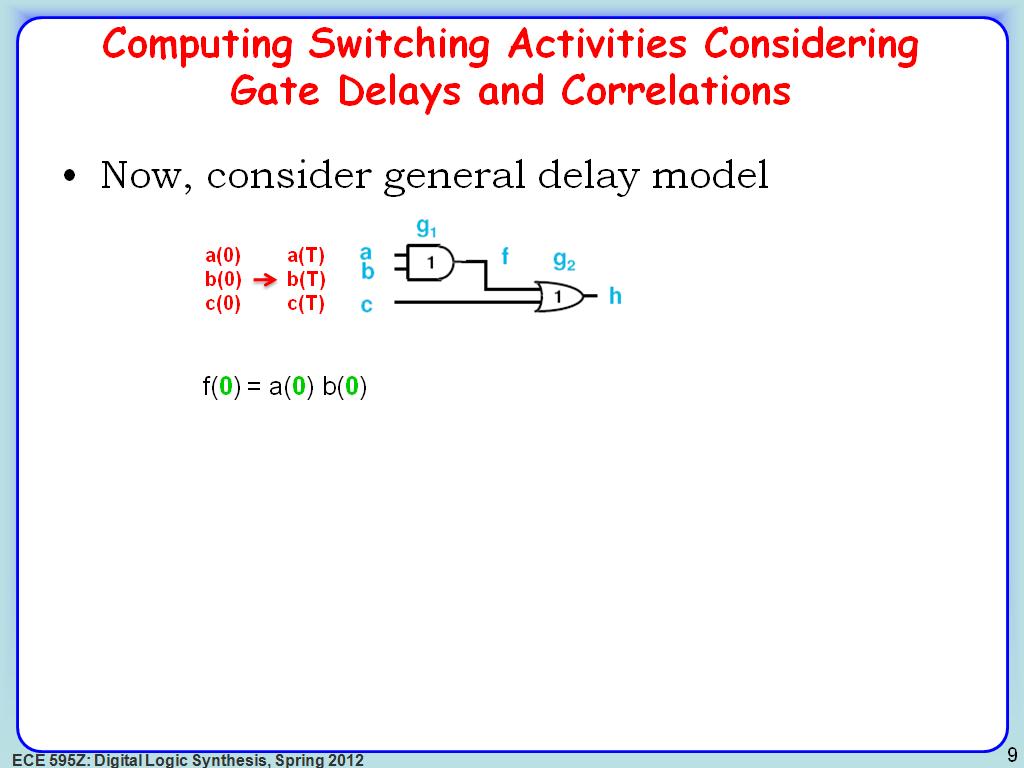
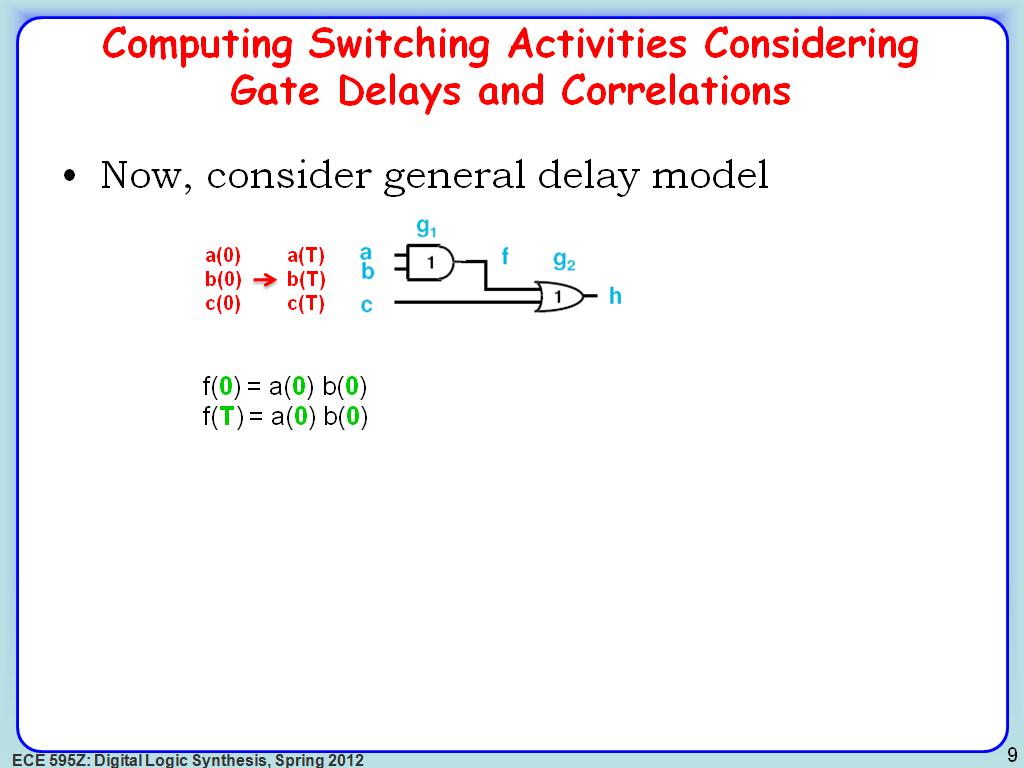
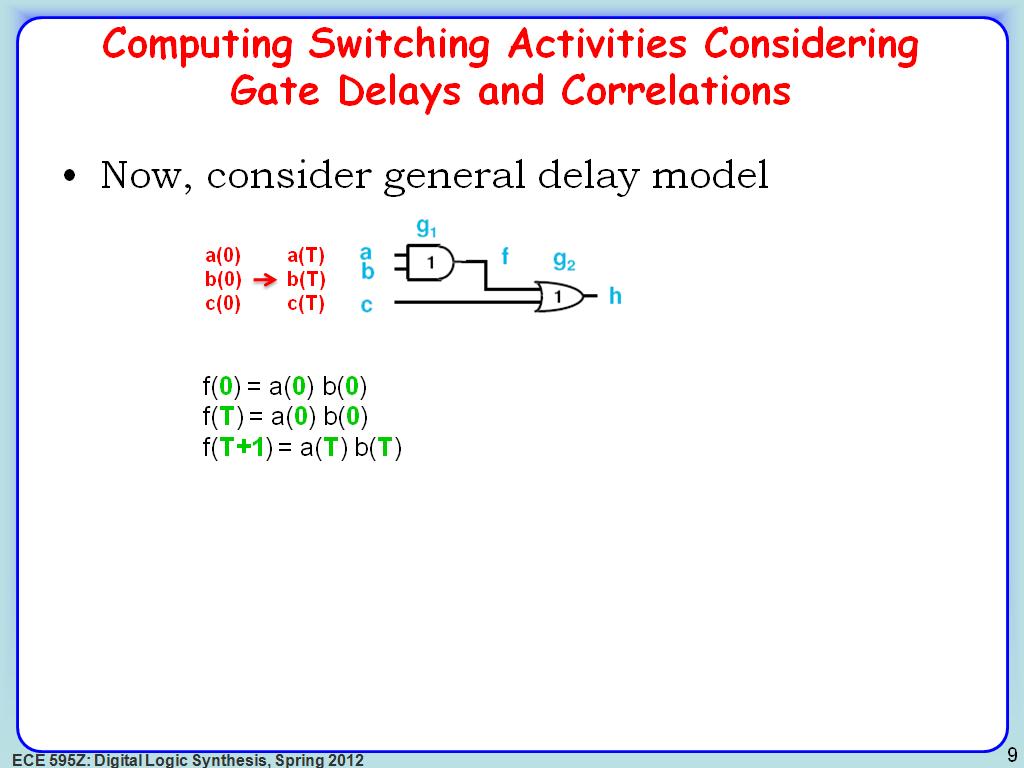
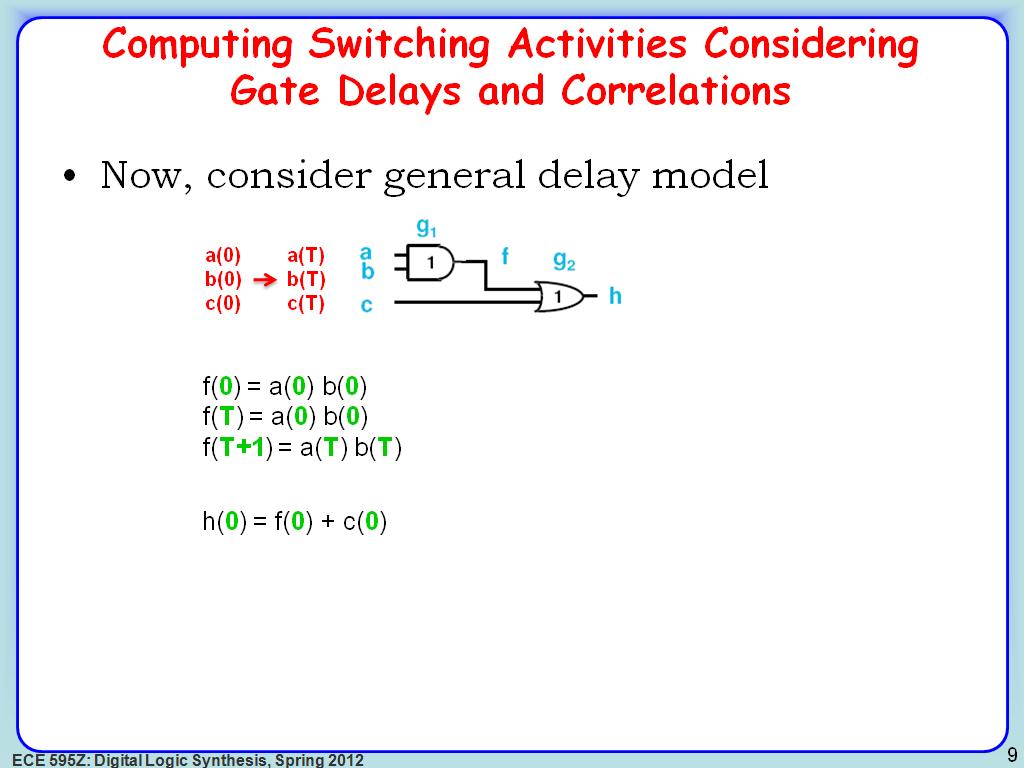
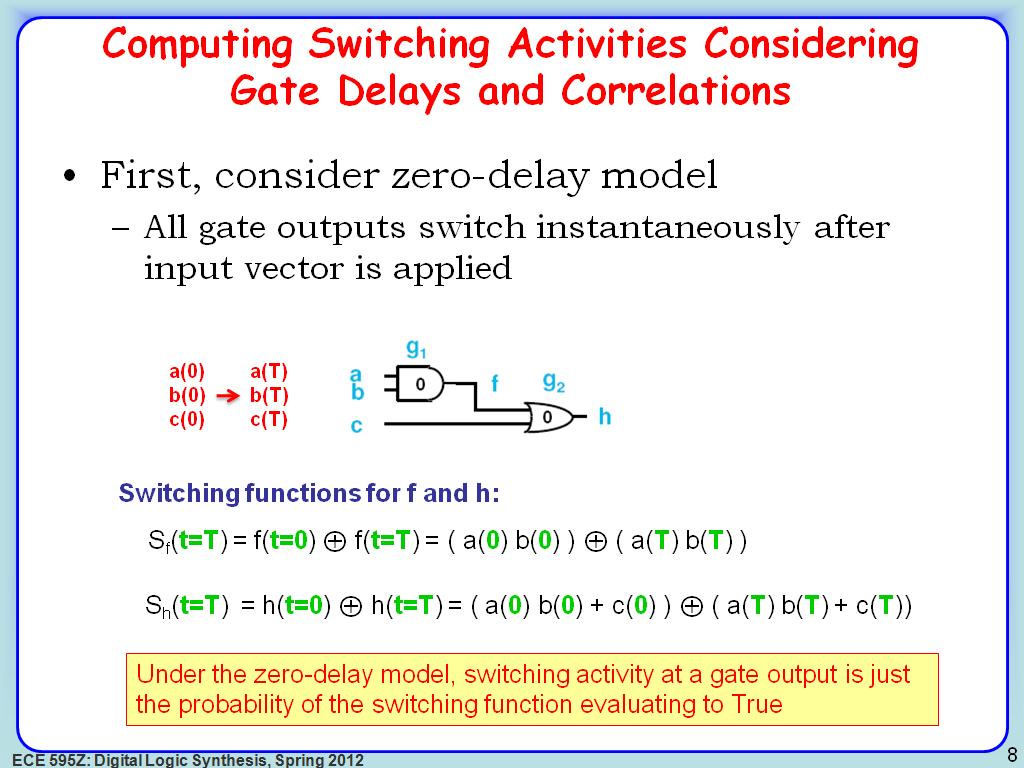 8. Computing Switching Activities…
1440.2736069402736
00:00/00:00
8. Computing Switching Activities…
1440.2736069402736
00:00/00:00 -
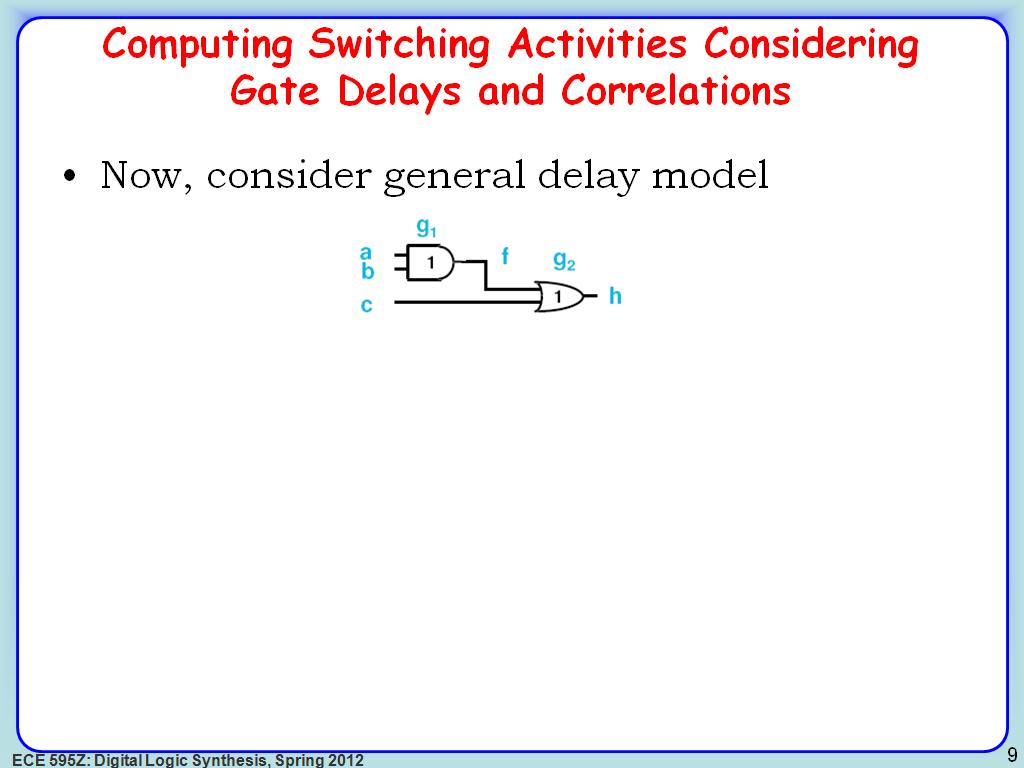
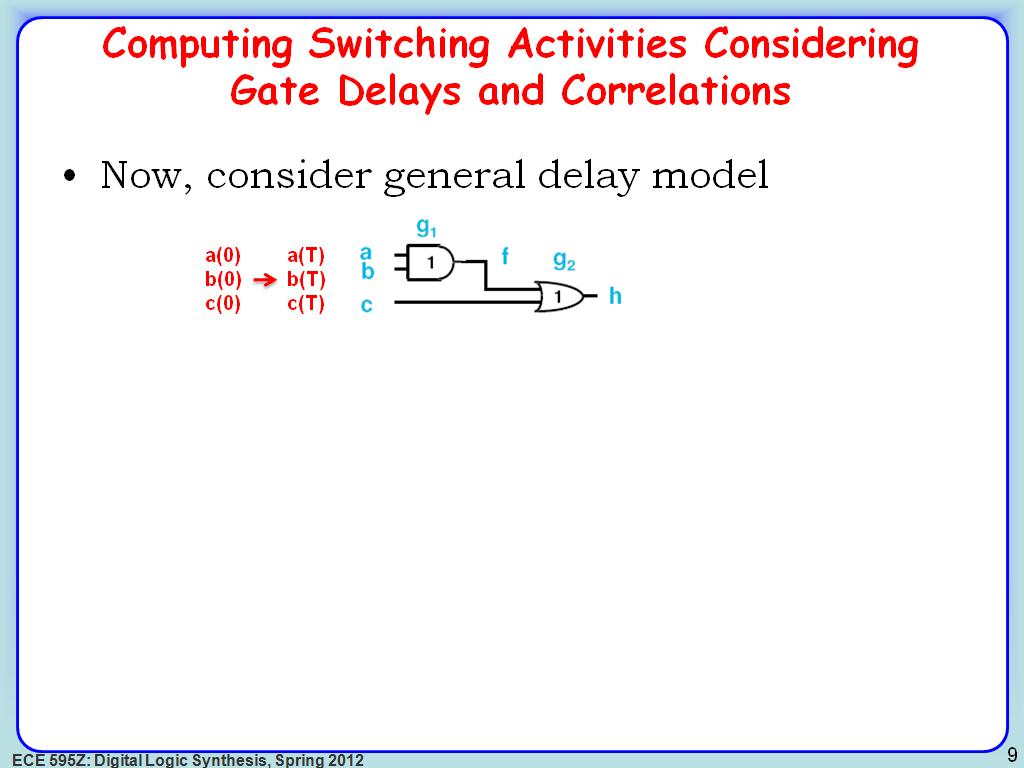
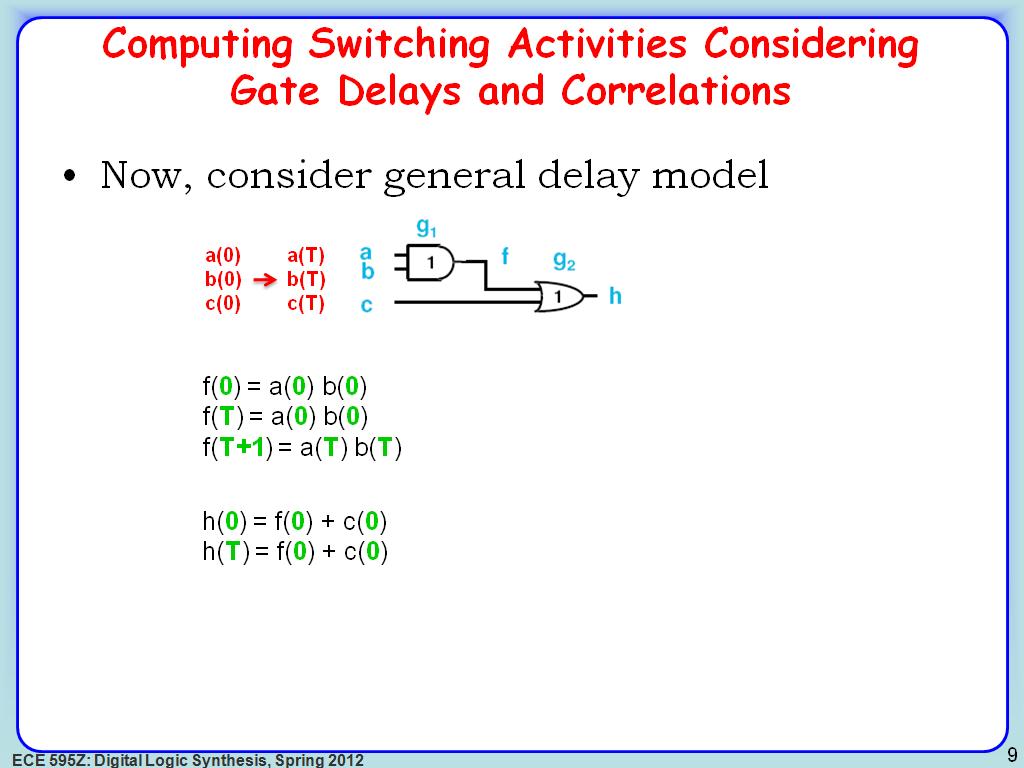
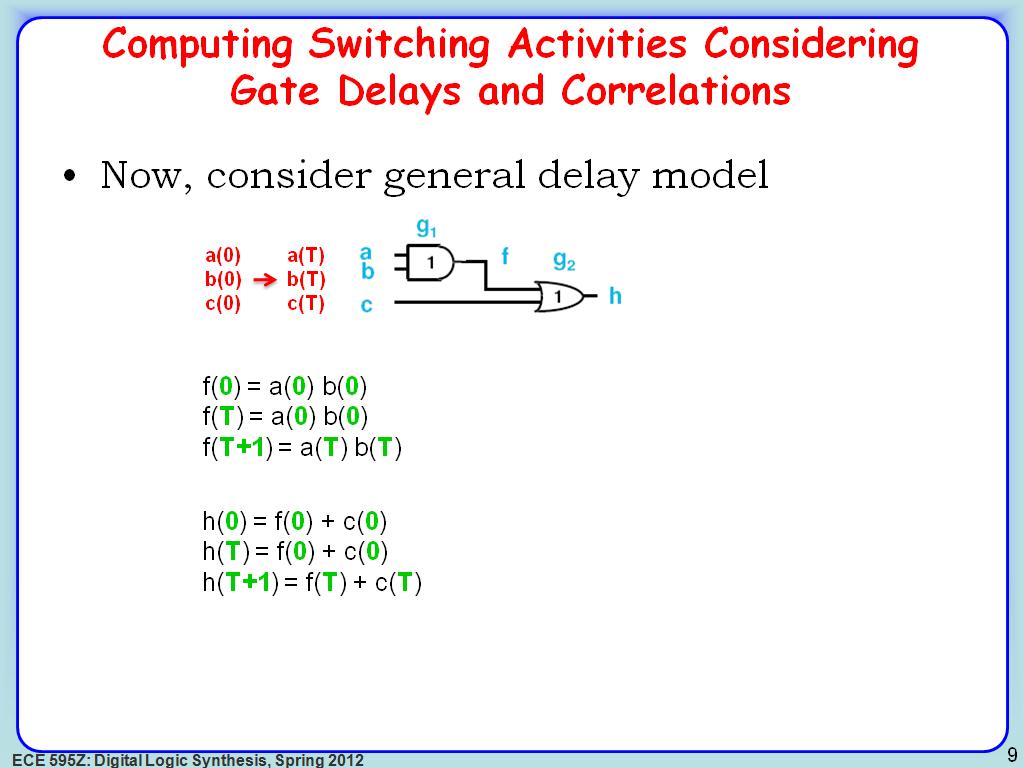
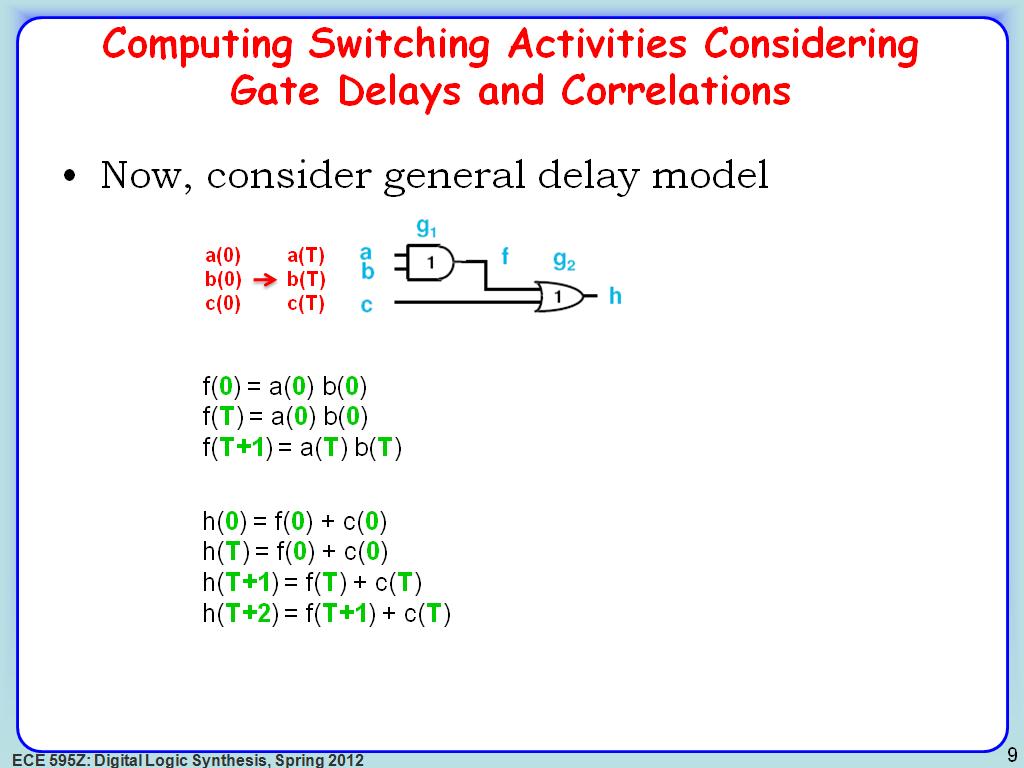
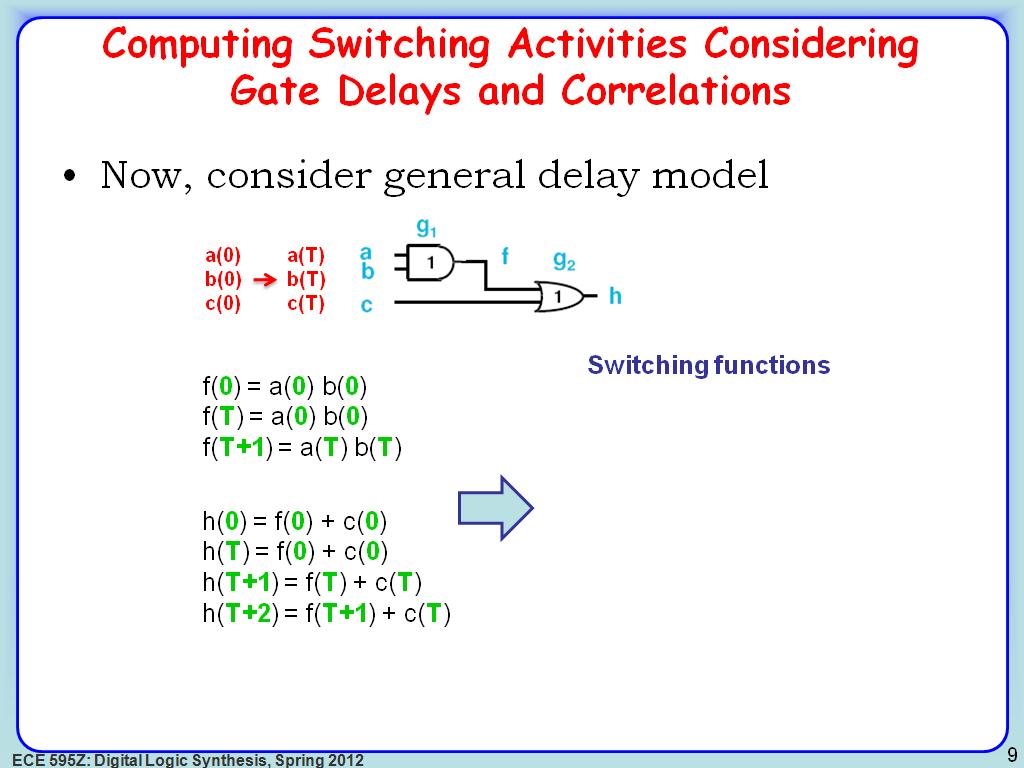
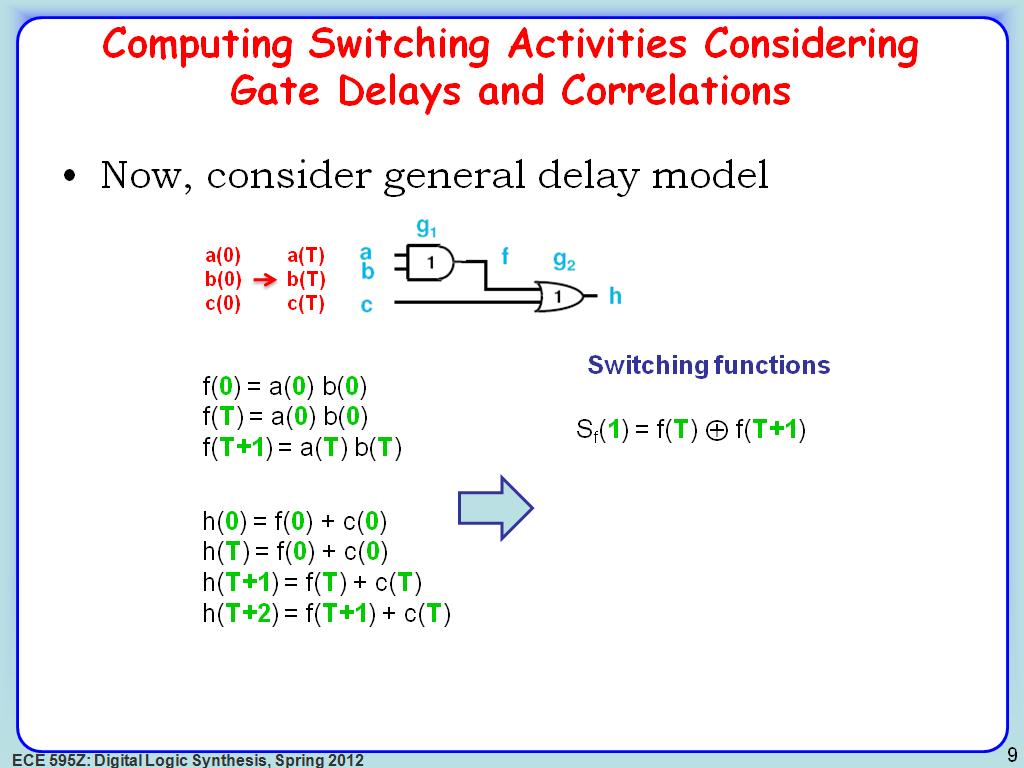
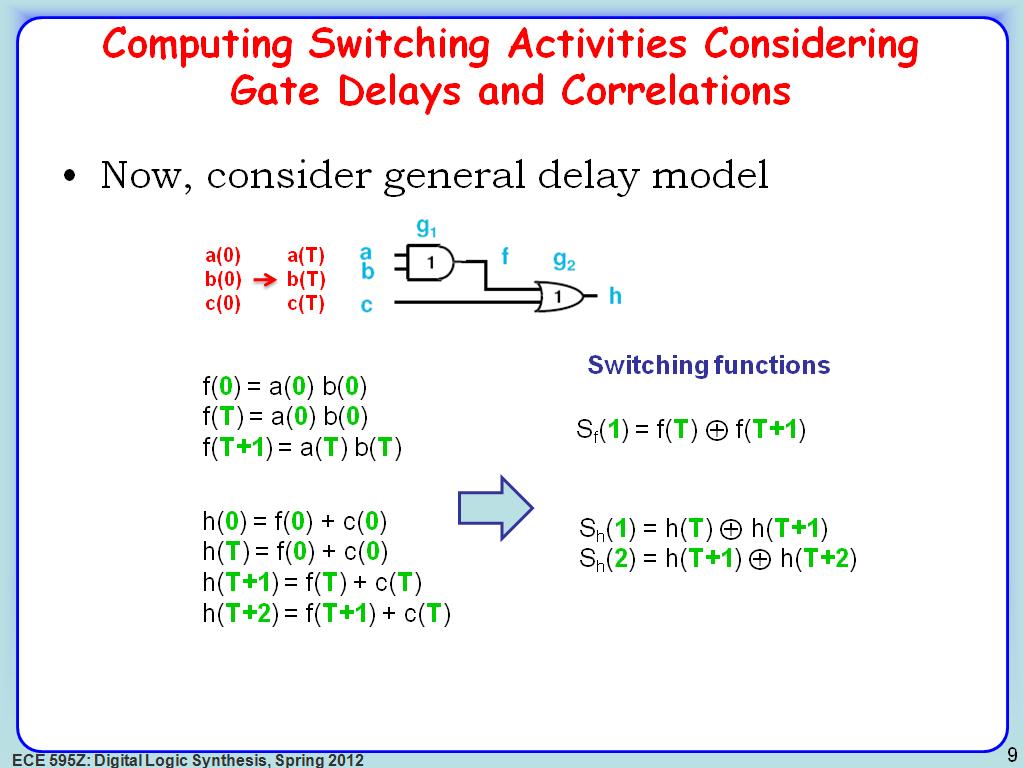
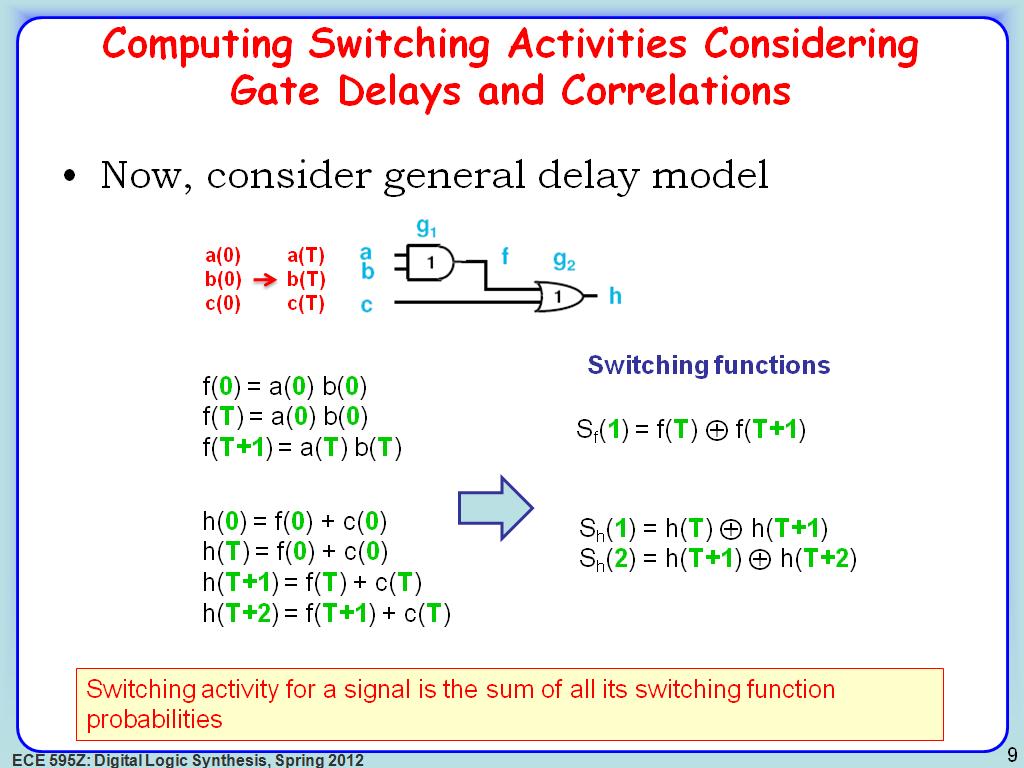
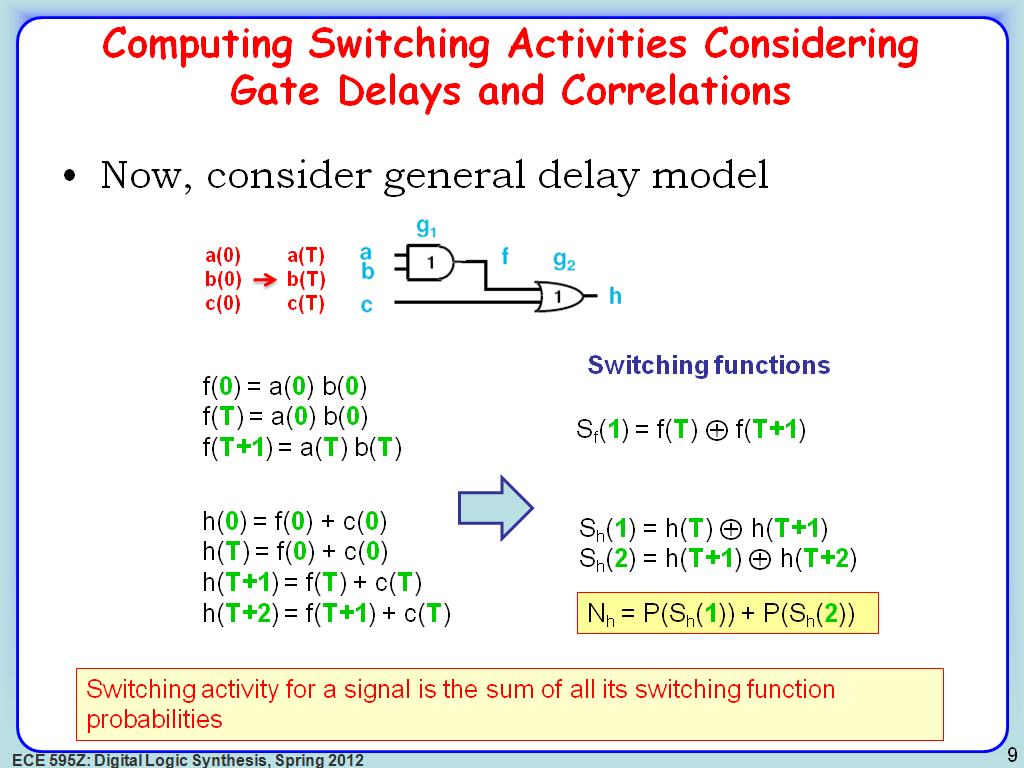
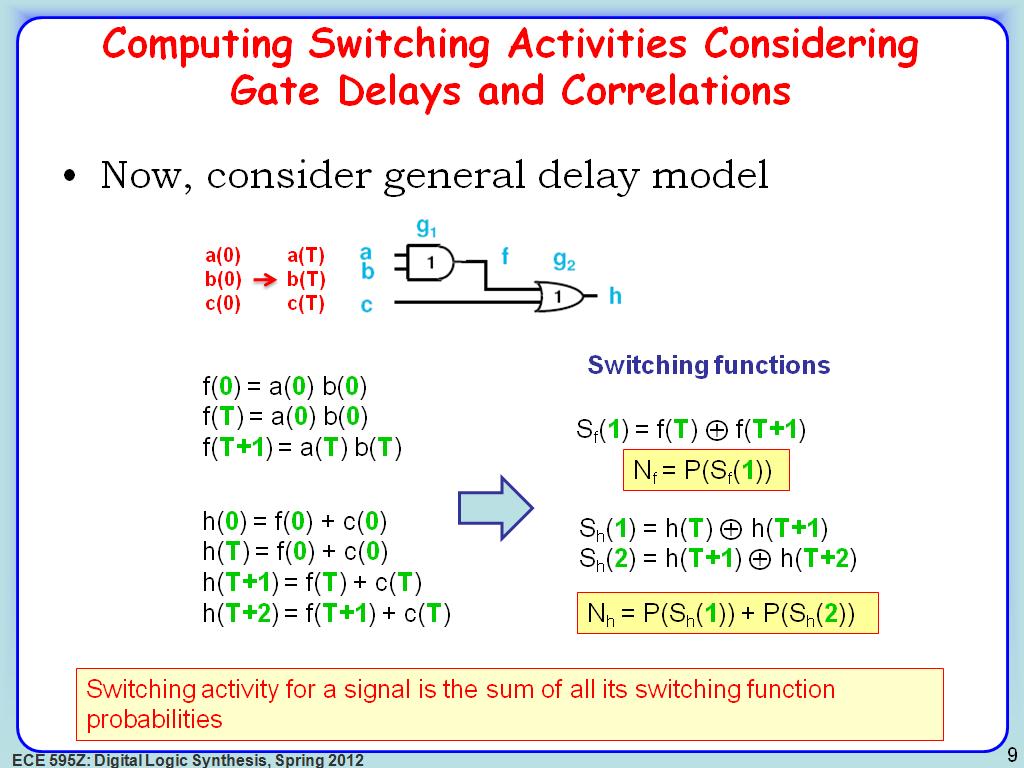 9. Computing Switching Activities…
1690.7907907907909
00:00/00:00
9. Computing Switching Activities…
1690.7907907907909
00:00/00:00 -
 10. Computing Switching Activities…
2013.646980313647
00:00/00:00
10. Computing Switching Activities…
2013.646980313647
00:00/00:00 -
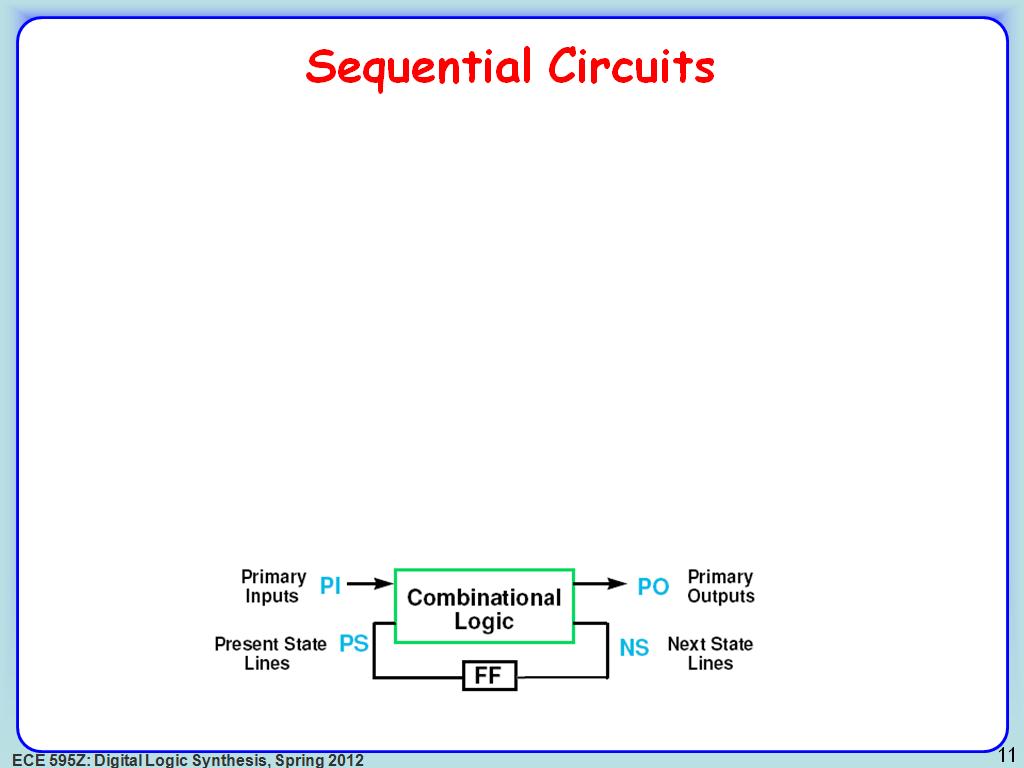
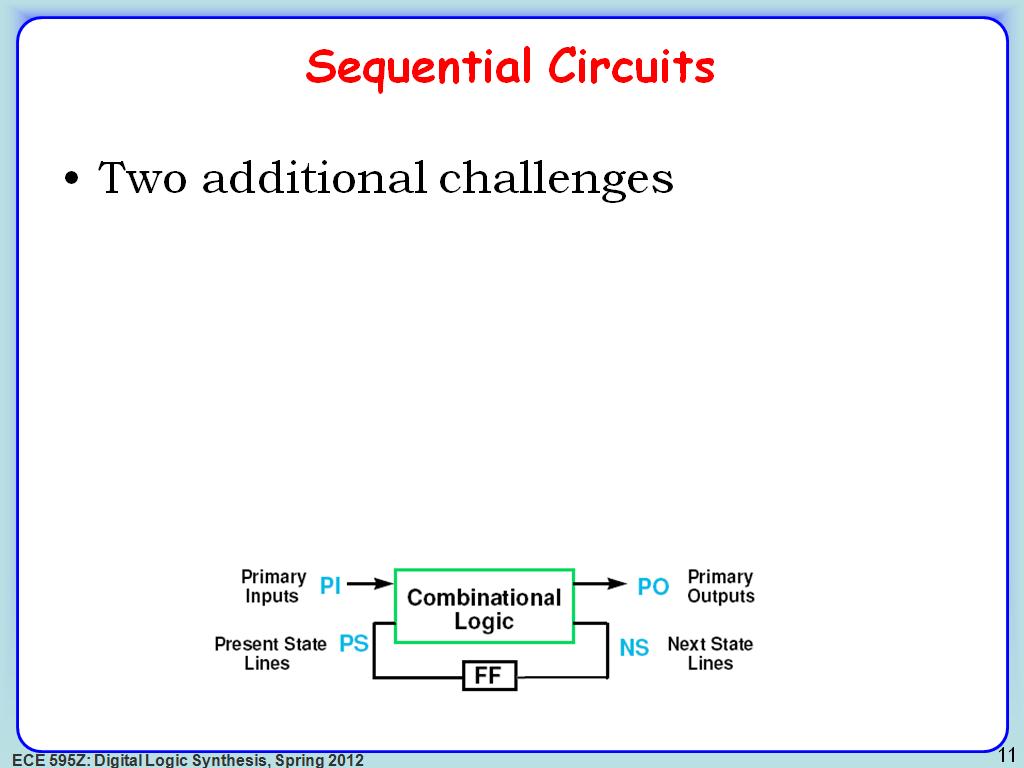
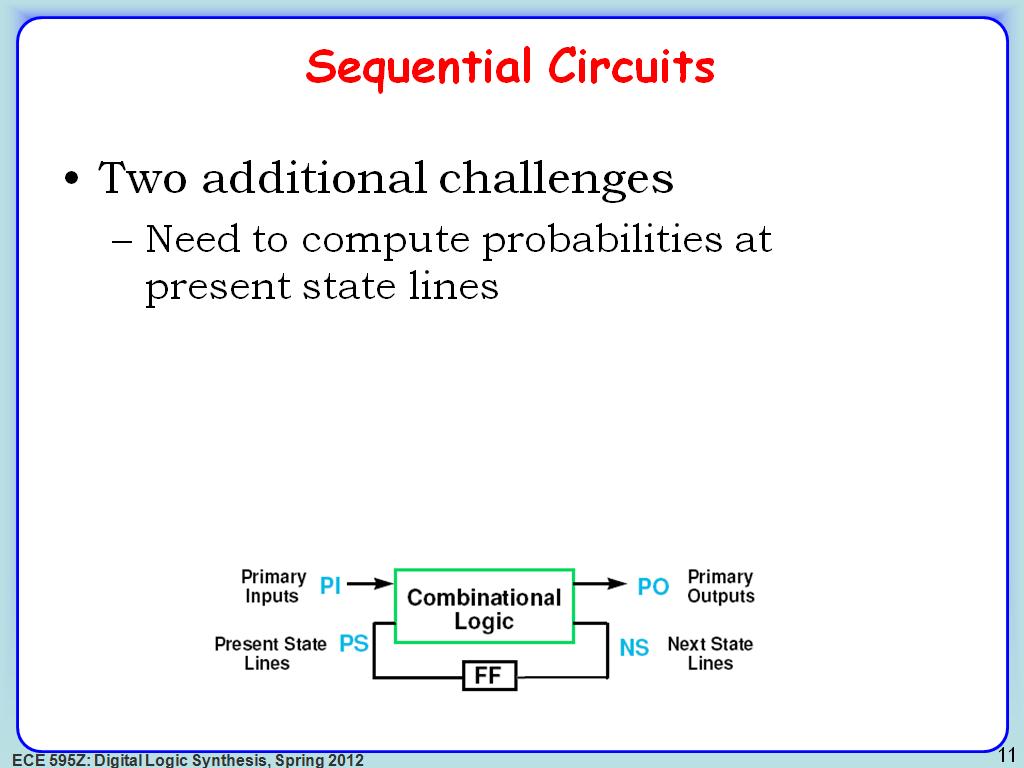
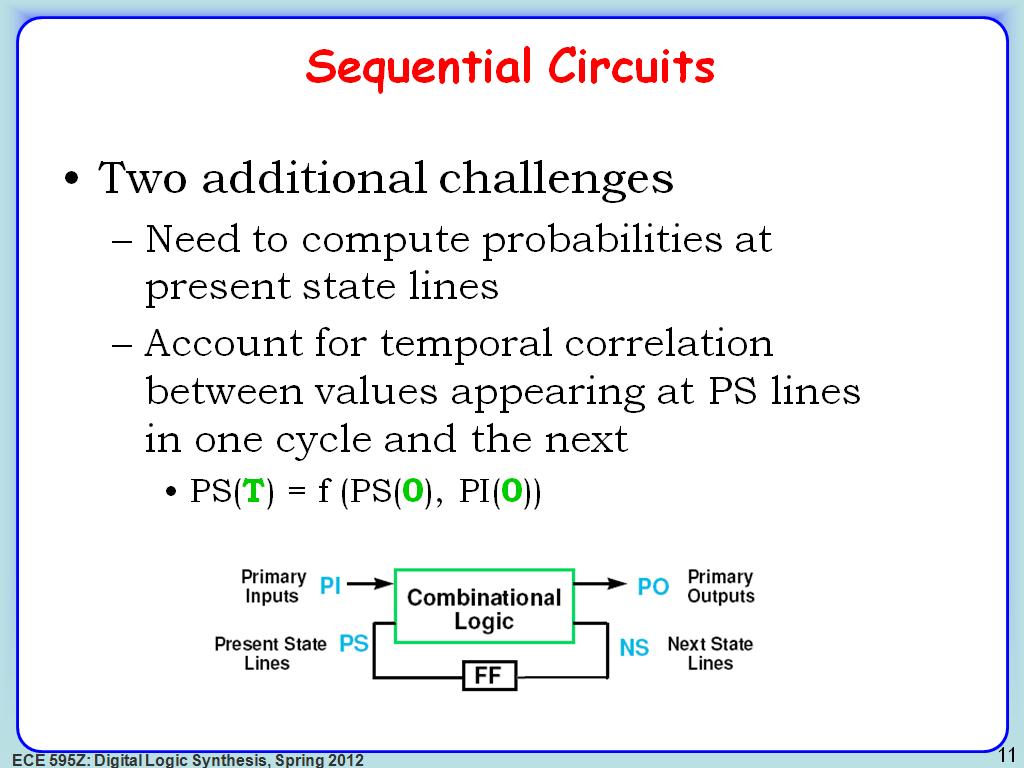 11. Sequential Circuits
2151.7183850517185
00:00/00:00
11. Sequential Circuits
2151.7183850517185
00:00/00:00 -
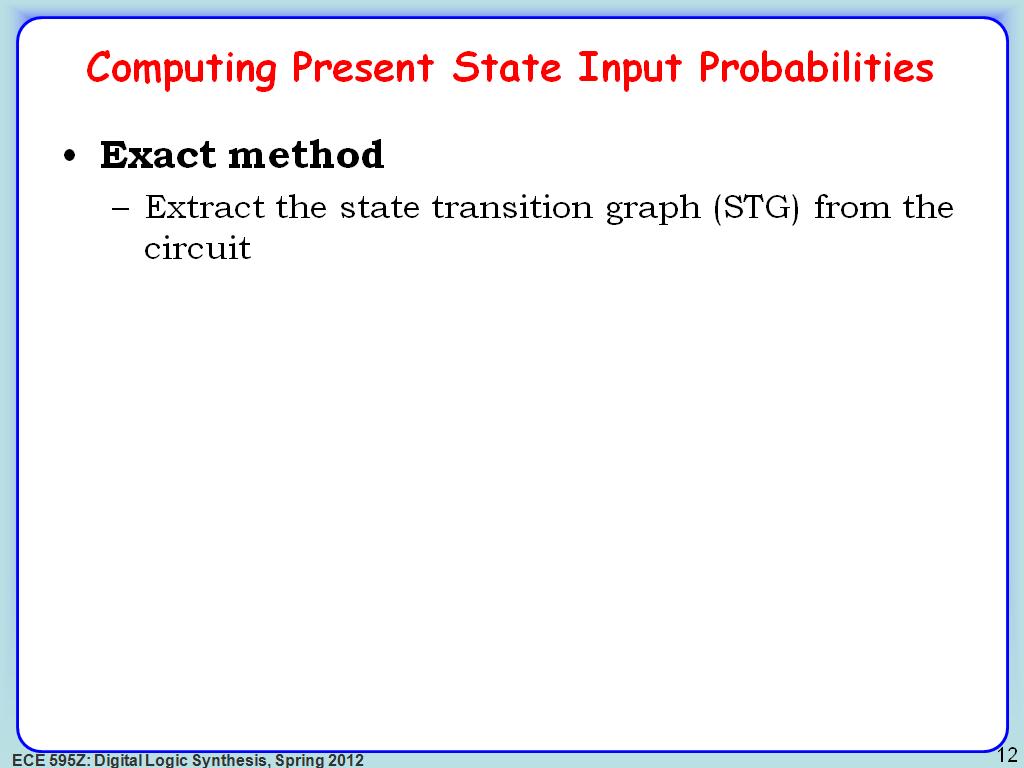
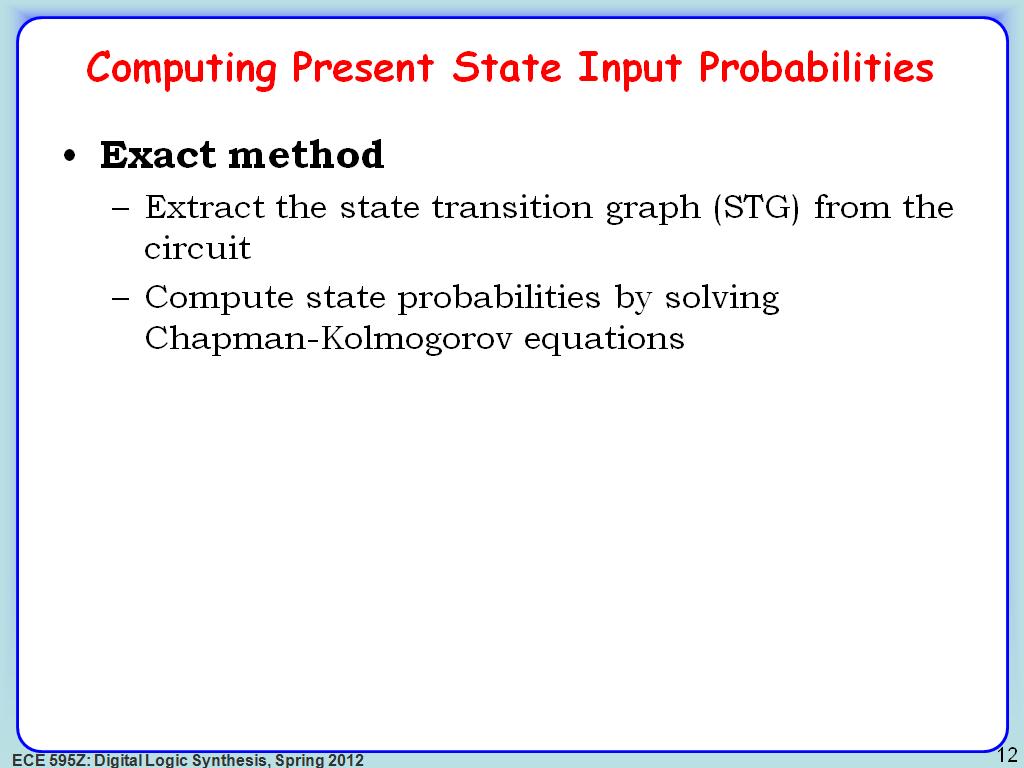
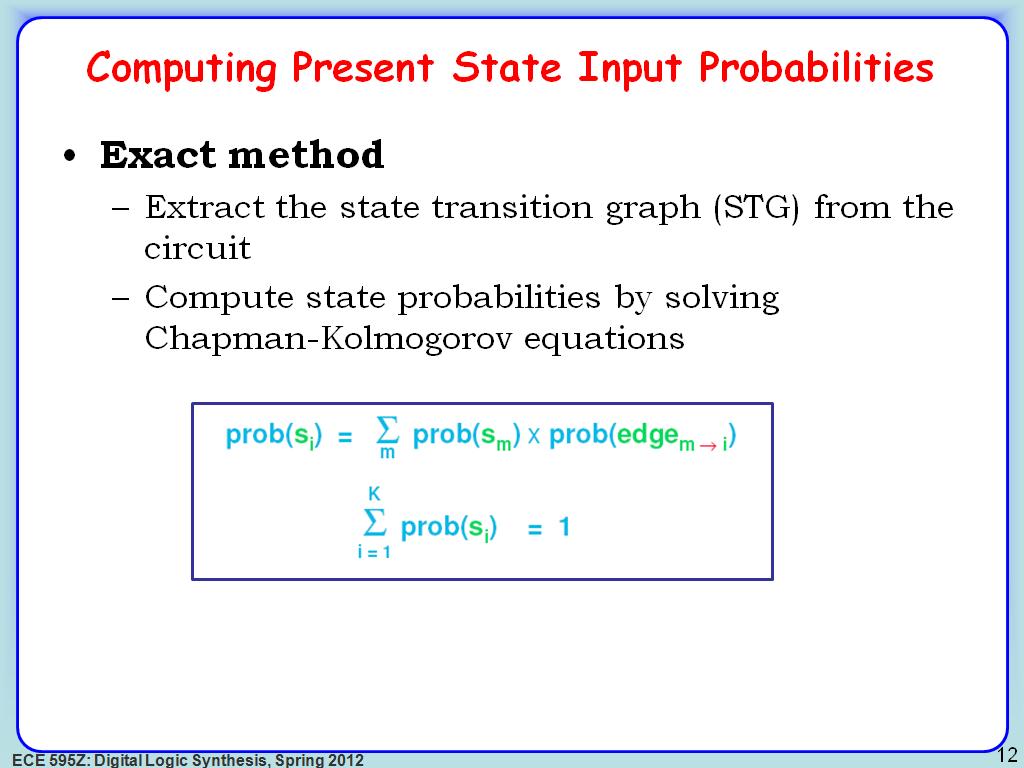
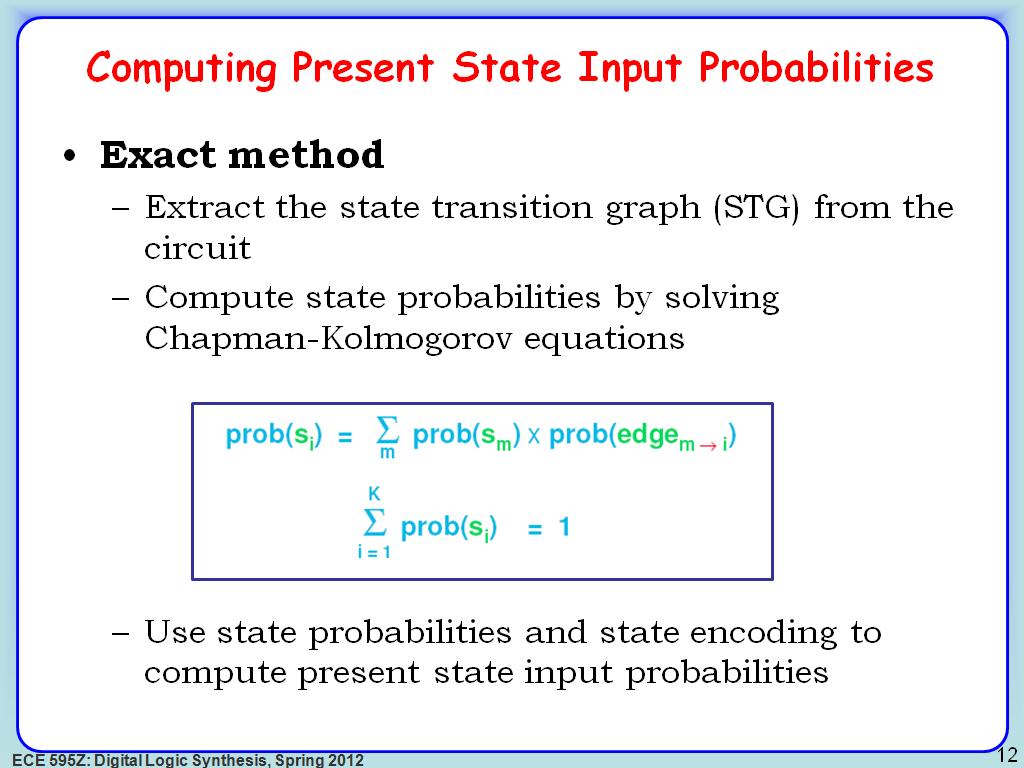 12. Computing Present State Input …
2233.5335335335335
00:00/00:00
12. Computing Present State Input …
2233.5335335335335
00:00/00:00 -
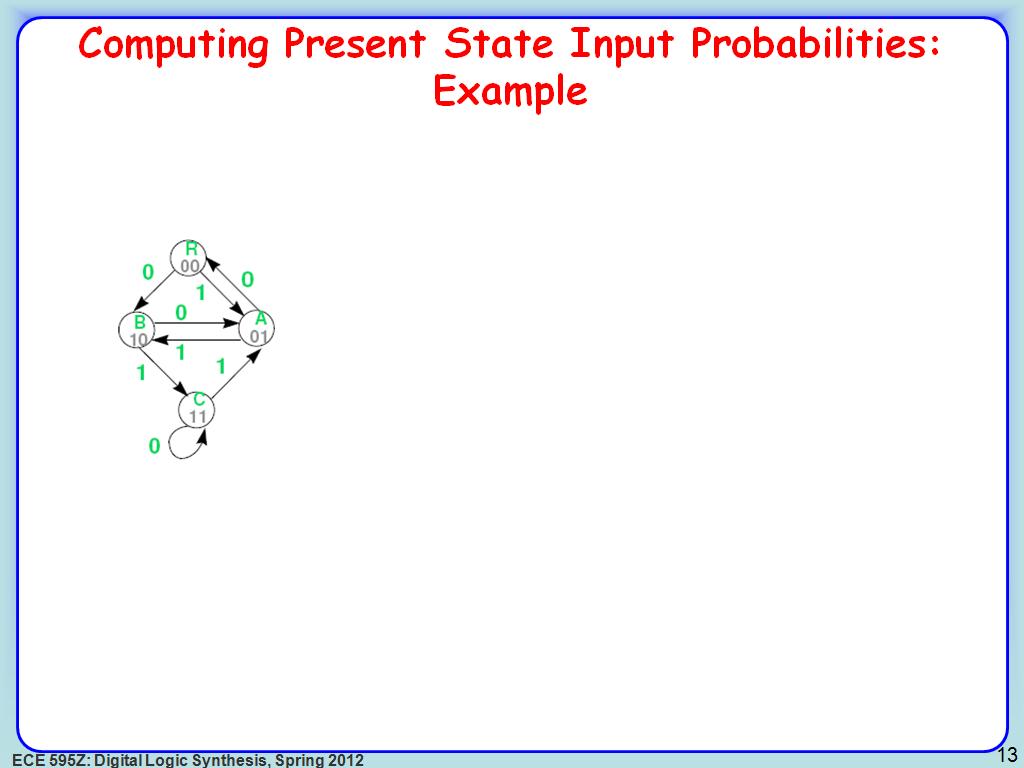
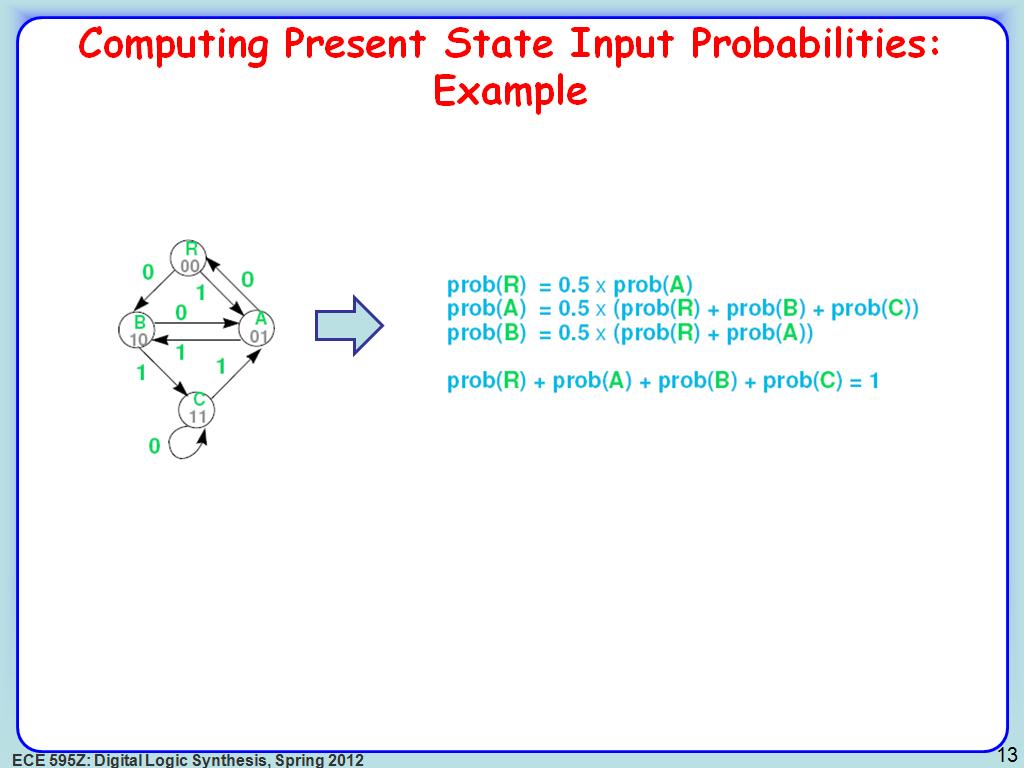
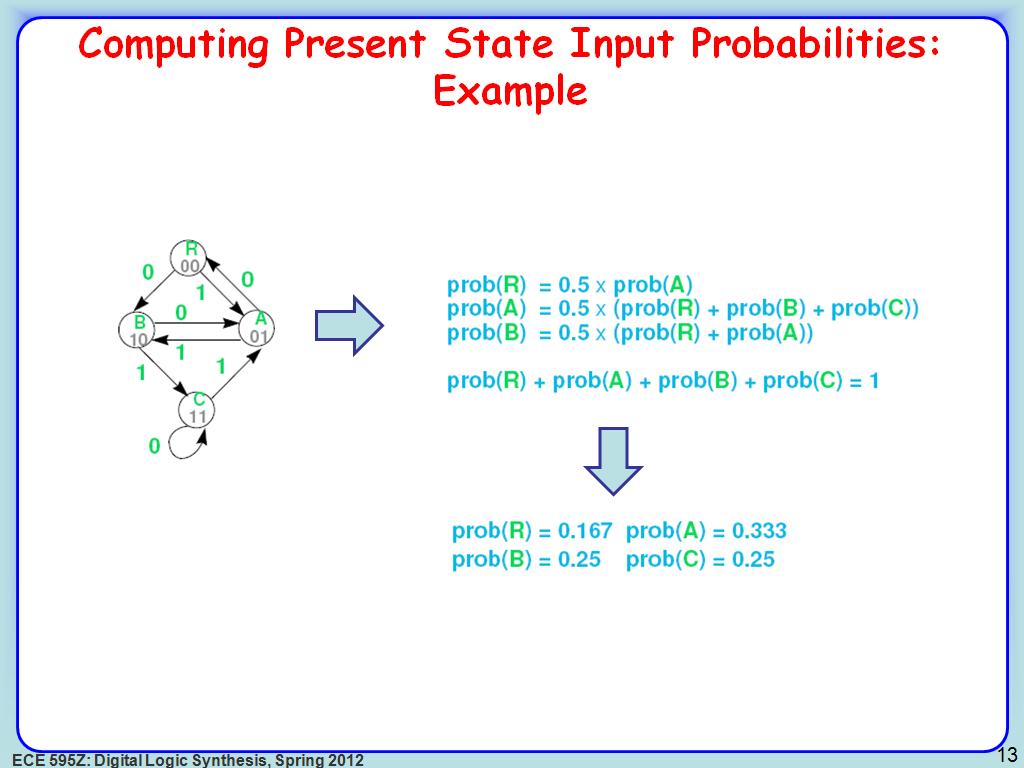 13. Computing Present State Input …
2347.4140807474141
00:00/00:00
13. Computing Present State Input …
2347.4140807474141
00:00/00:00 -
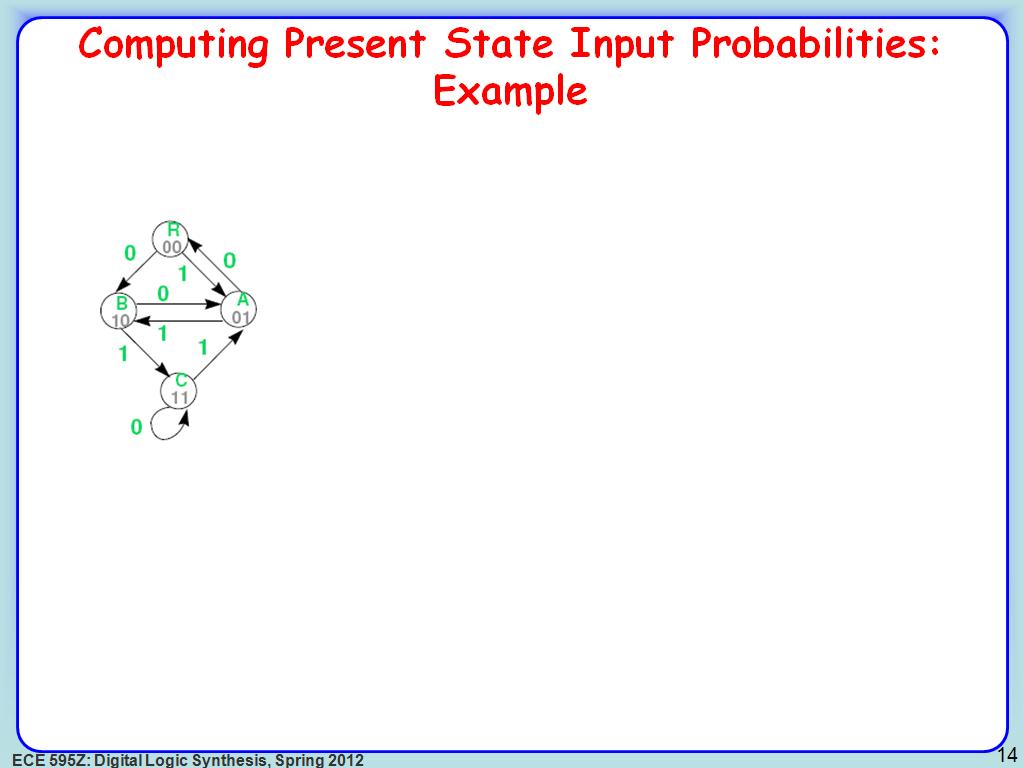
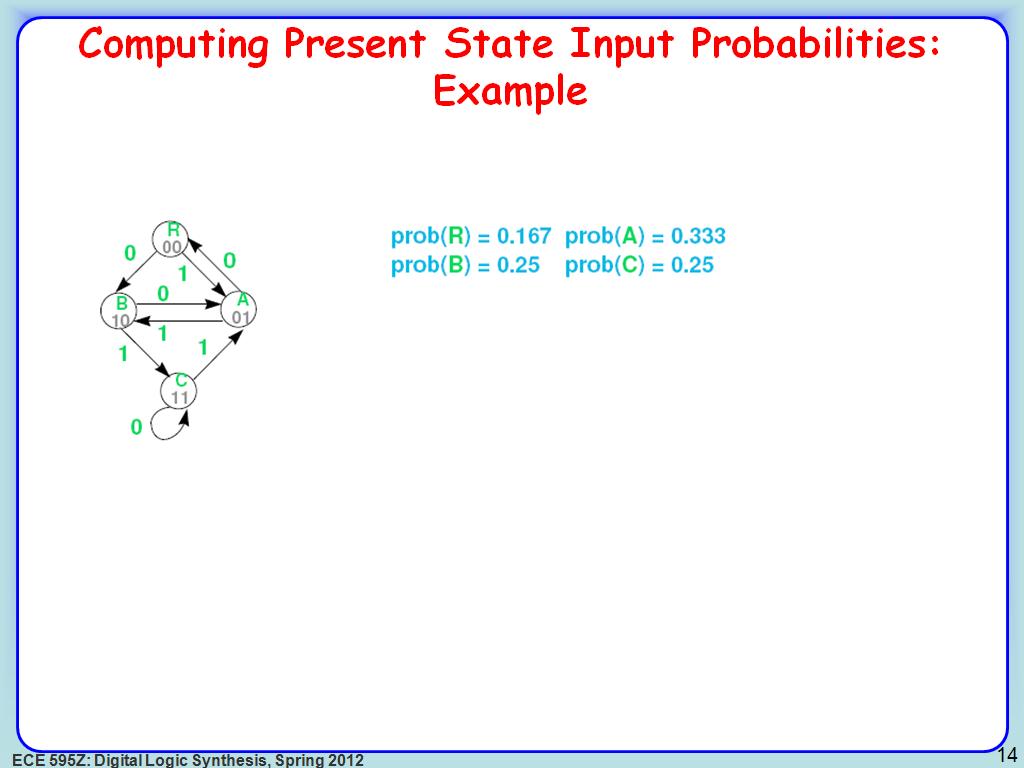
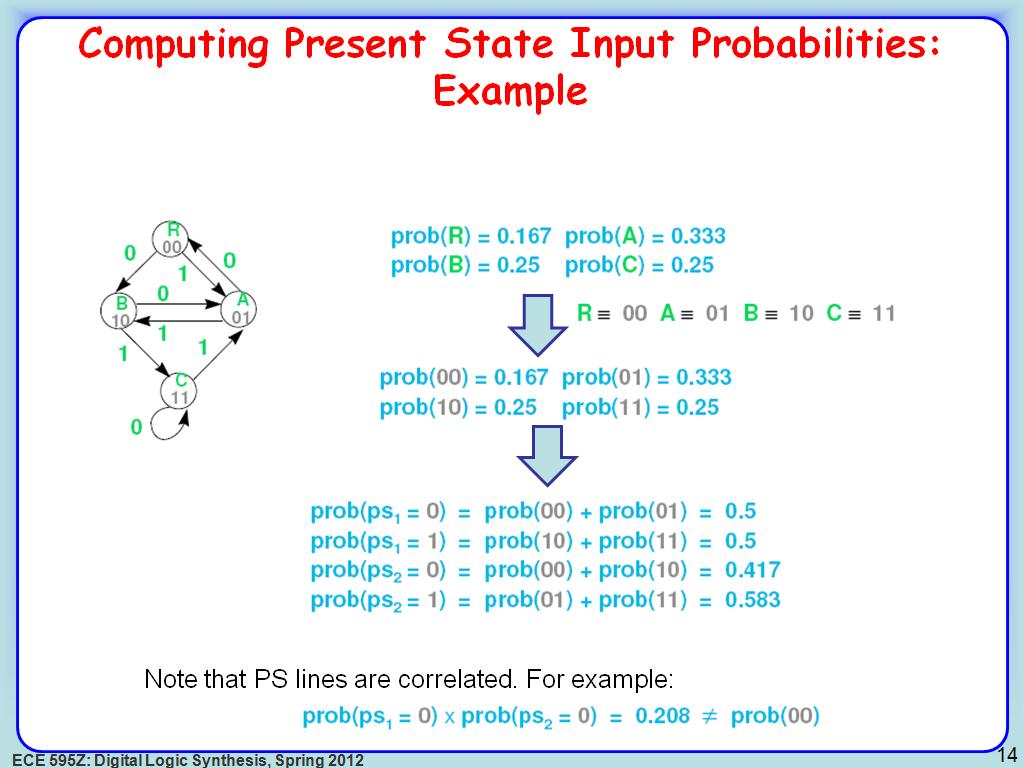 14. Computing Present State Input …
2450.7507507507507
00:00/00:00
14. Computing Present State Input …
2450.7507507507507
00:00/00:00 -
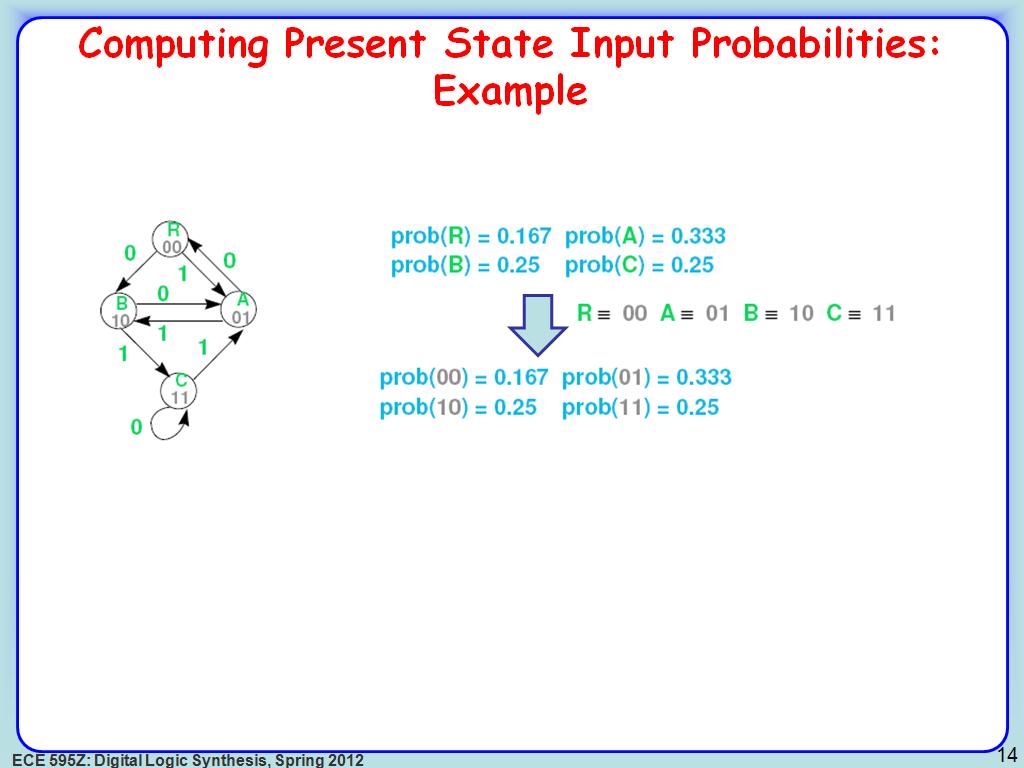
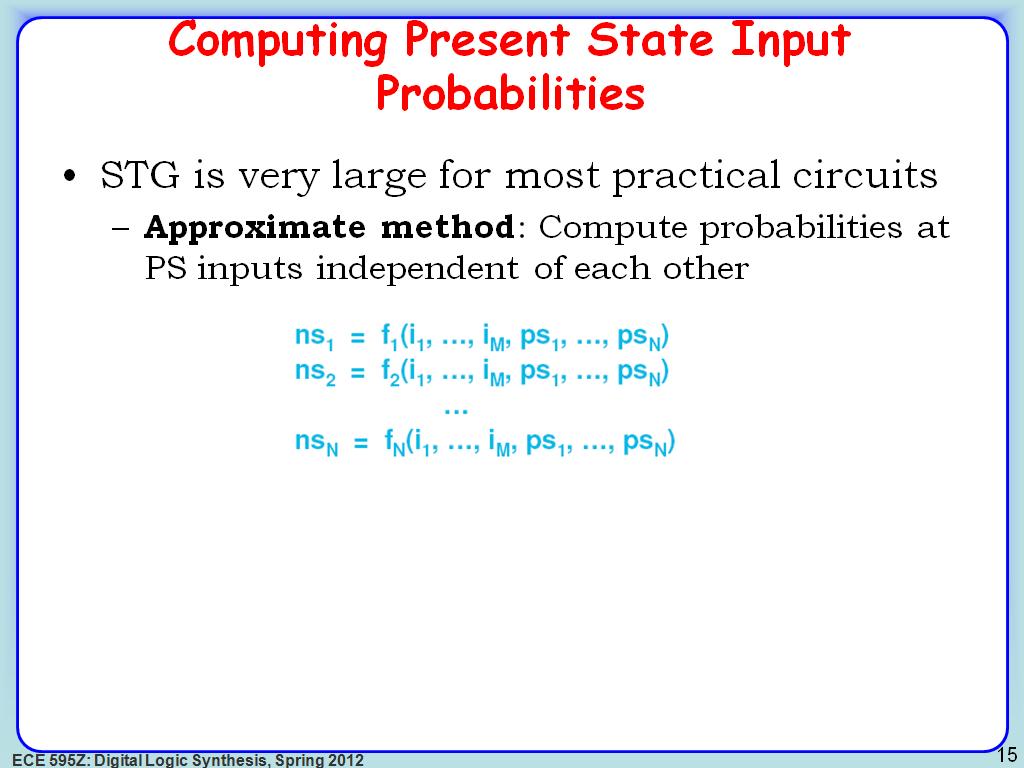
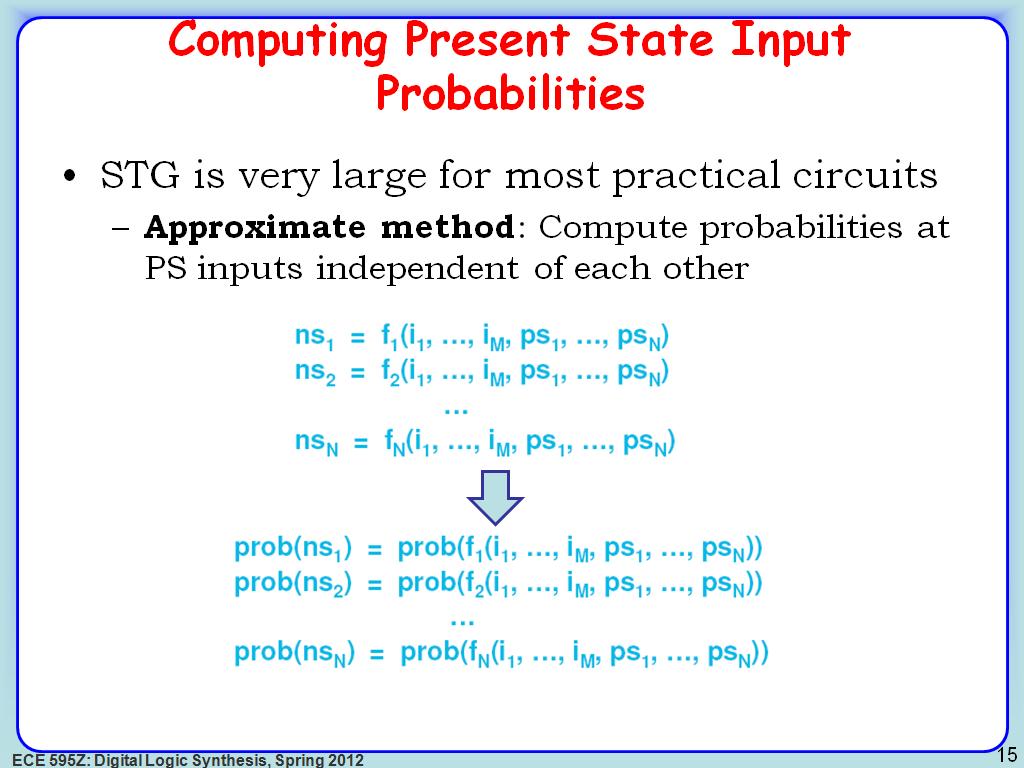 15. Computing Present State Input …
2574.607941274608
00:00/00:00
15. Computing Present State Input …
2574.607941274608
00:00/00:00 -
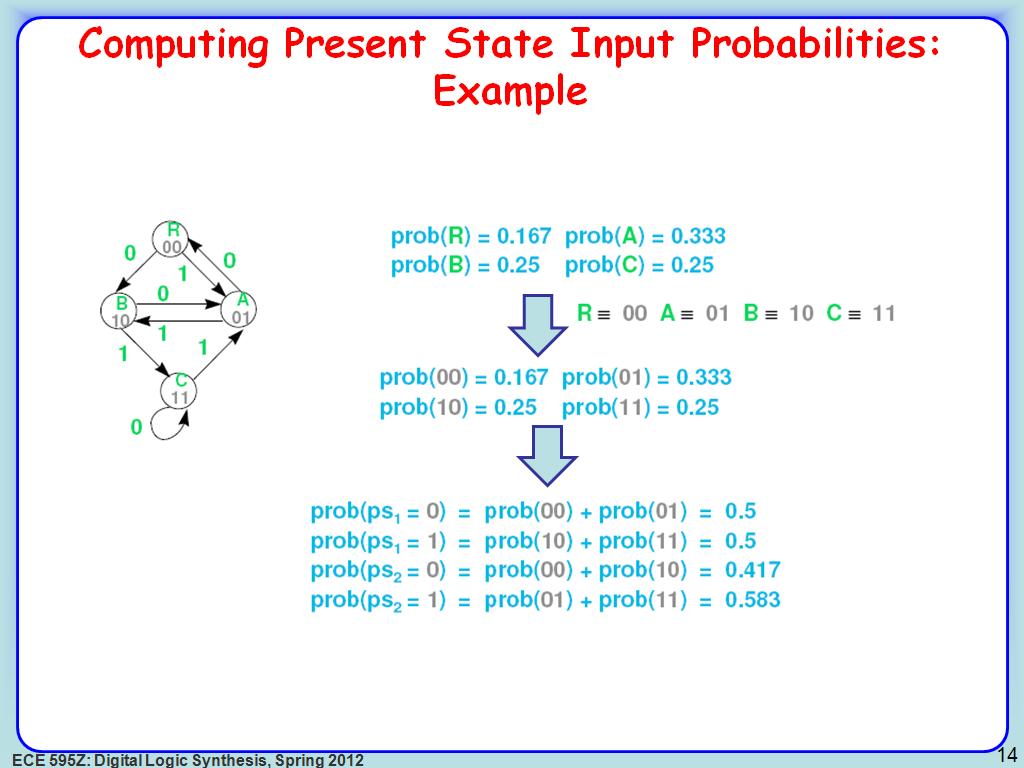
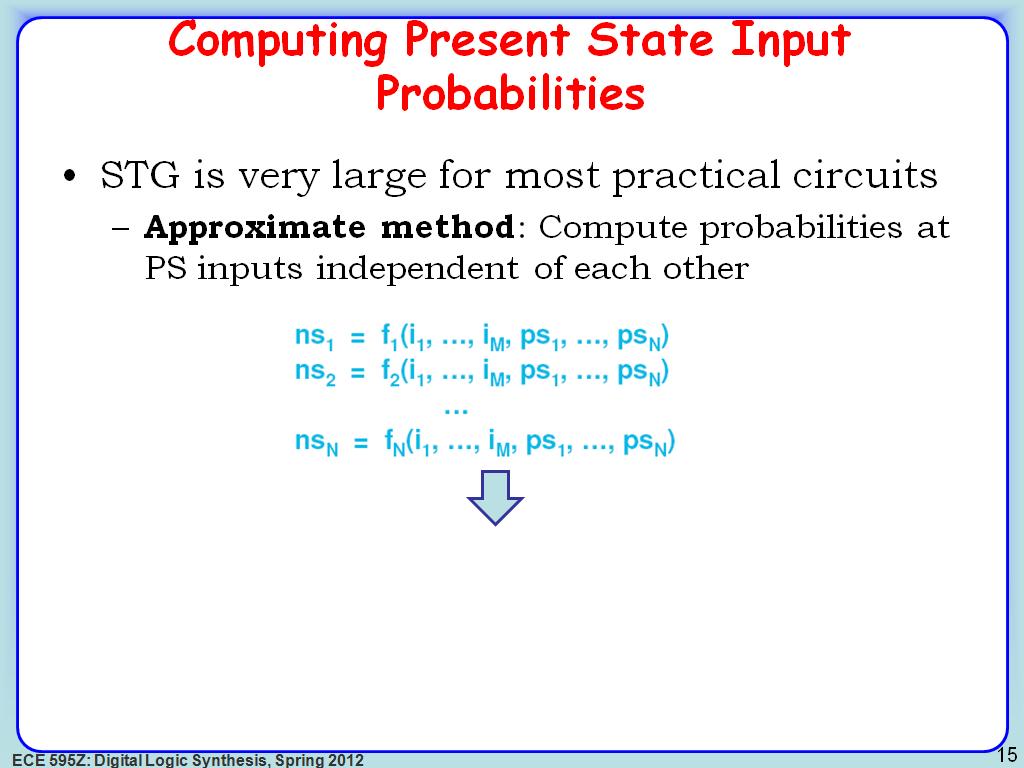
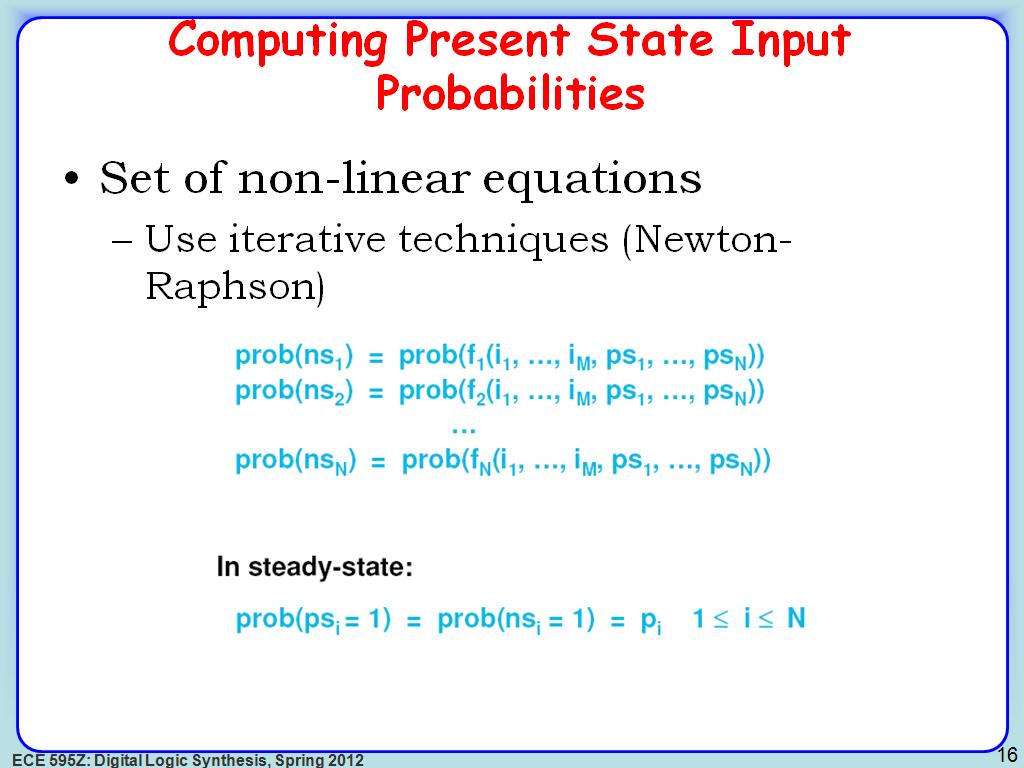 16. Computing Present State Input …
2665.9993326659996
00:00/00:00
16. Computing Present State Input …
2665.9993326659996
00:00/00:00 -
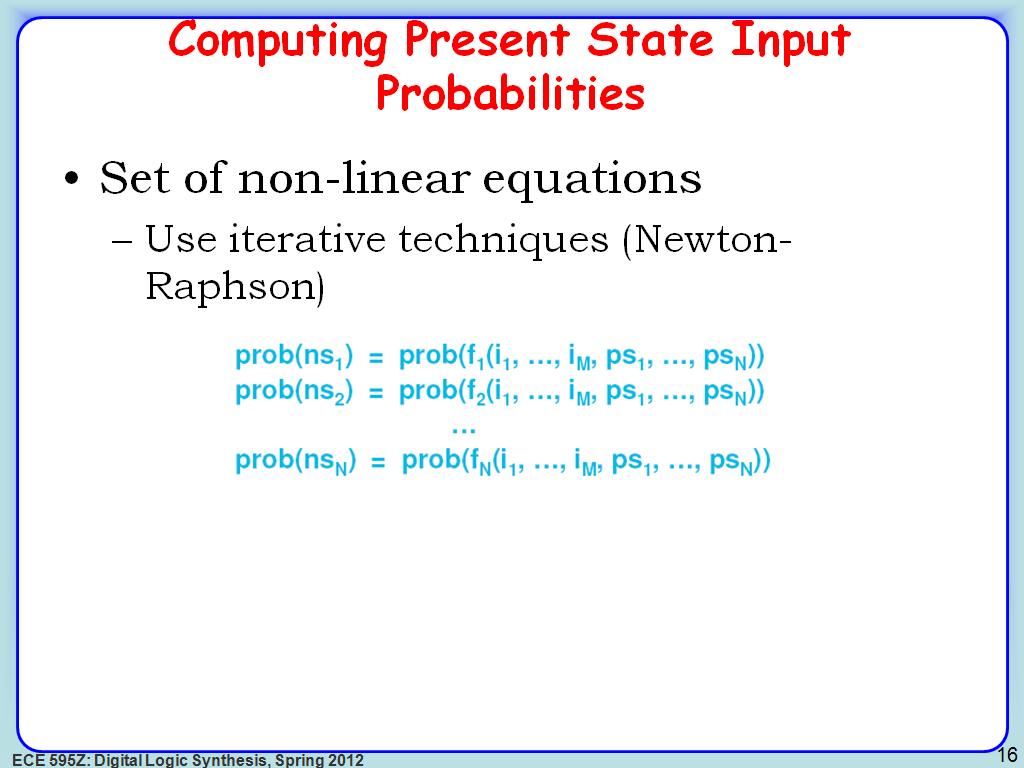
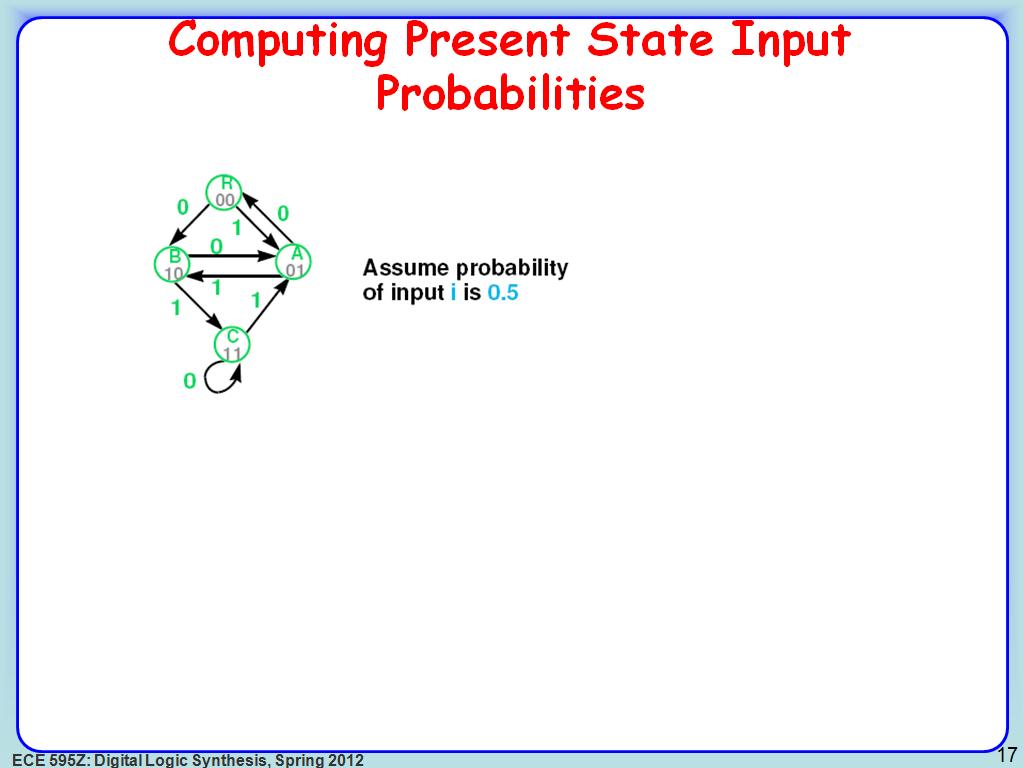
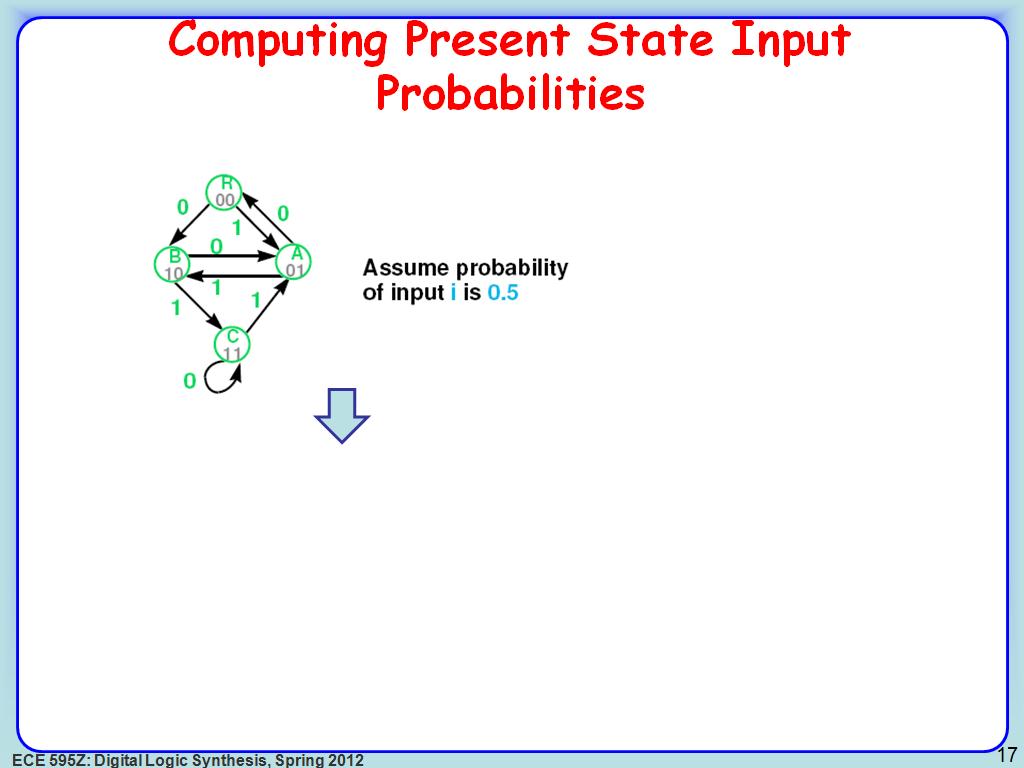
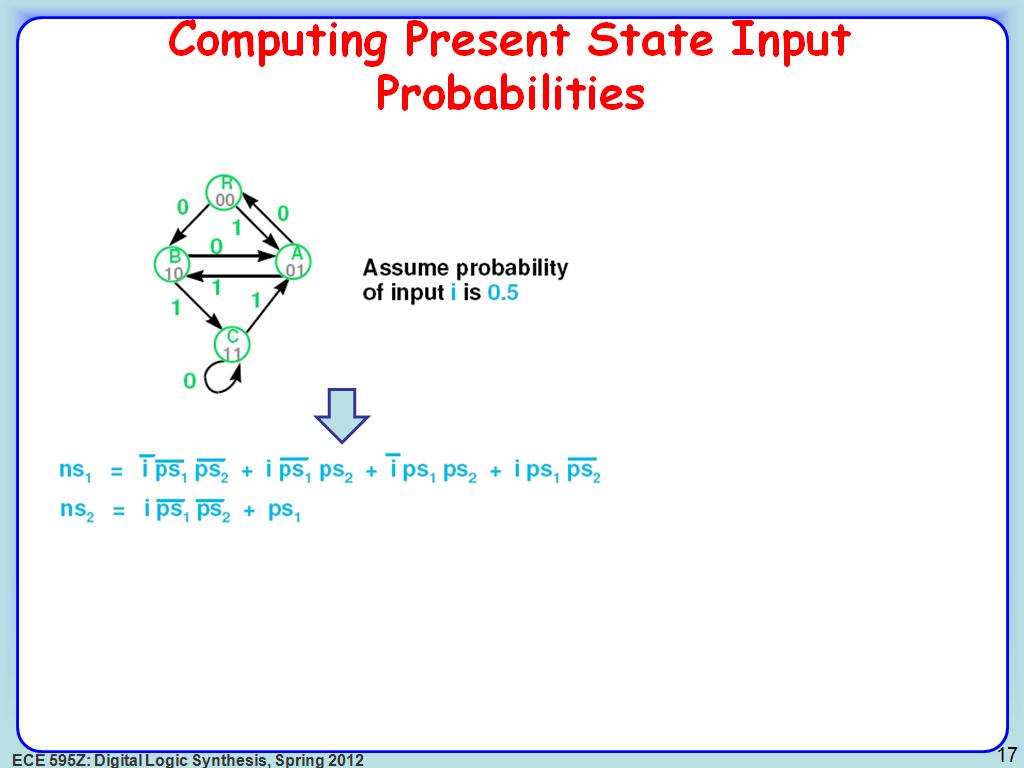
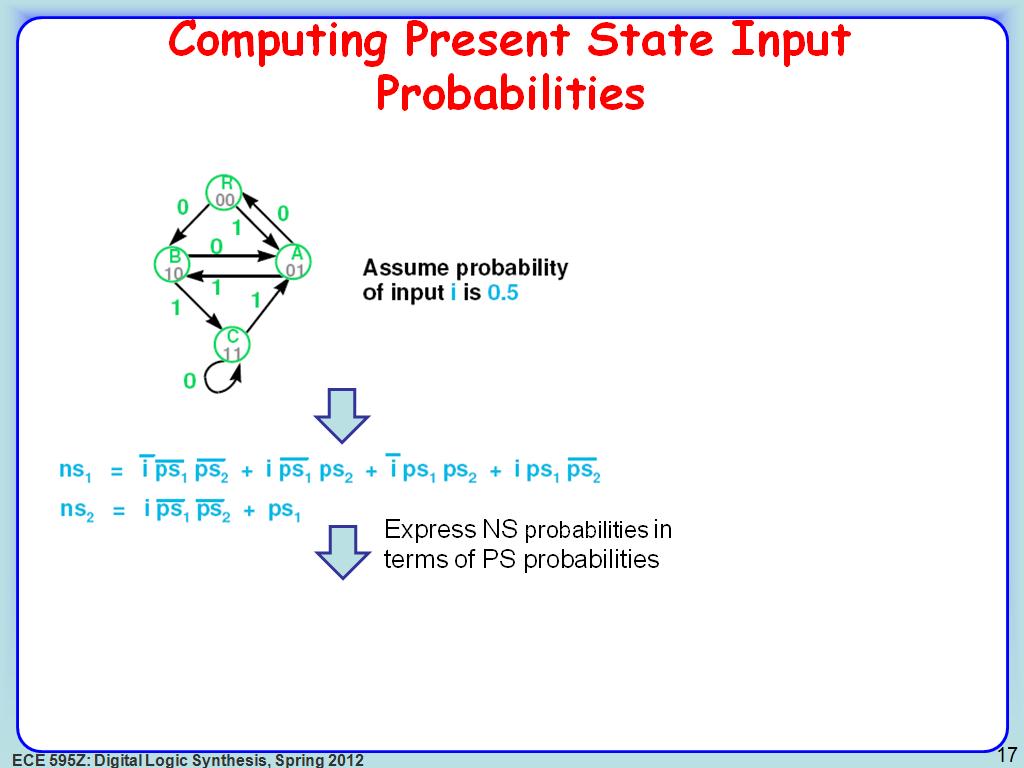
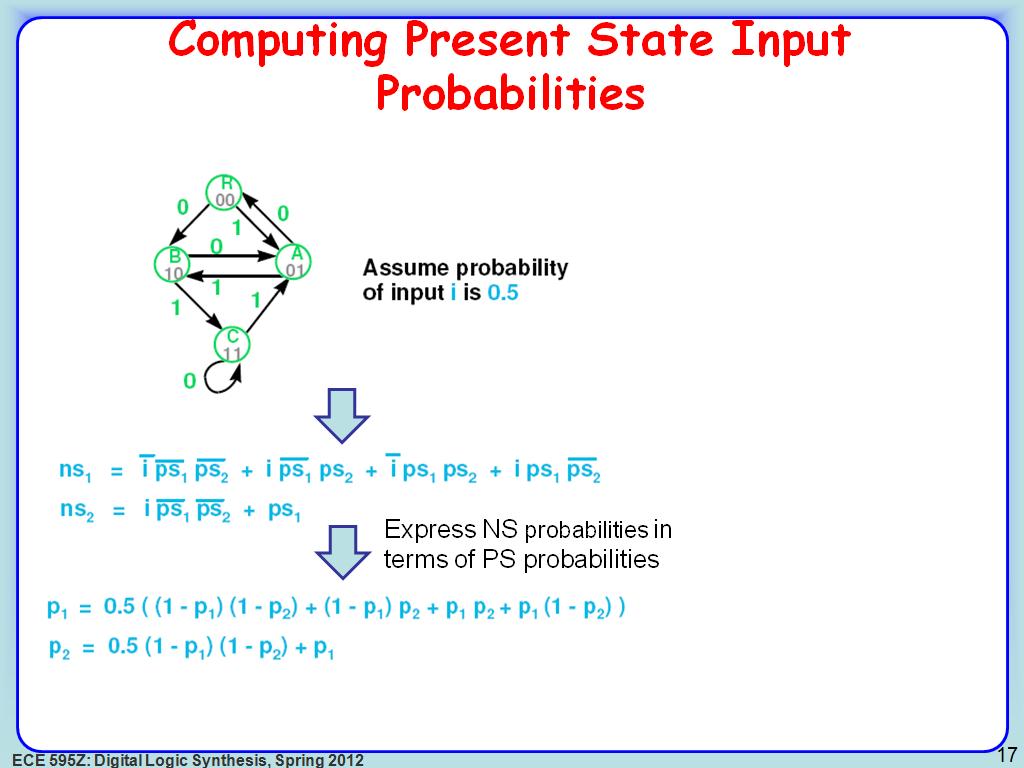
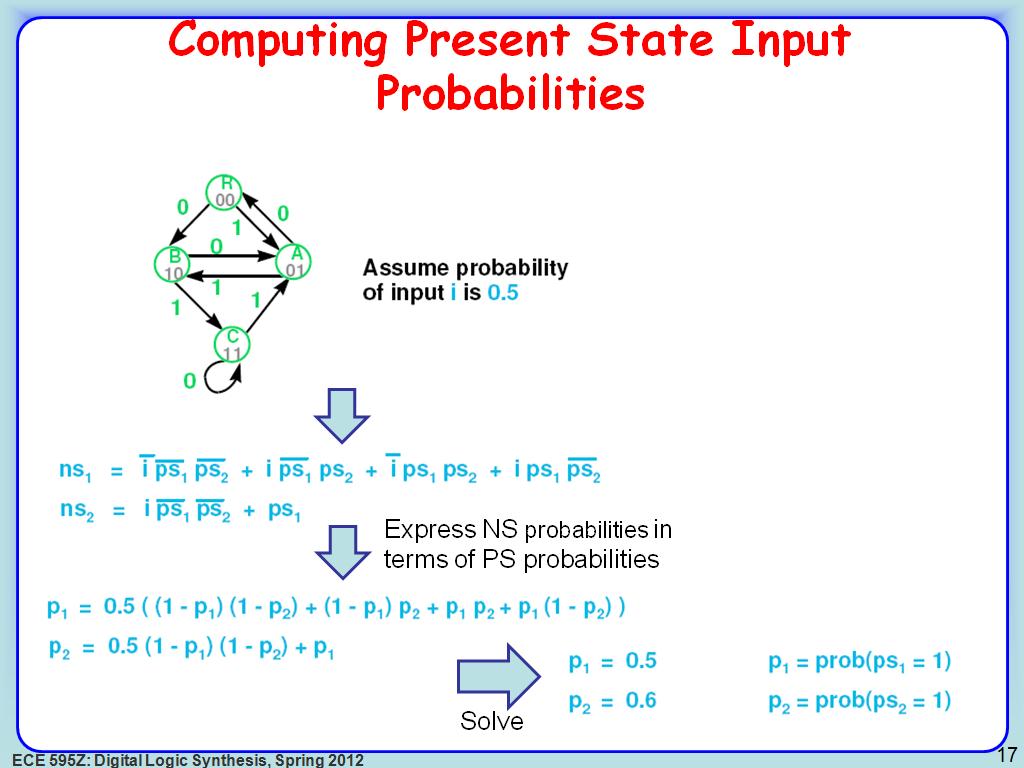 17. Computing Present State Input …
2711.4781448114782
00:00/00:00
17. Computing Present State Input …
2711.4781448114782
00:00/00:00 -
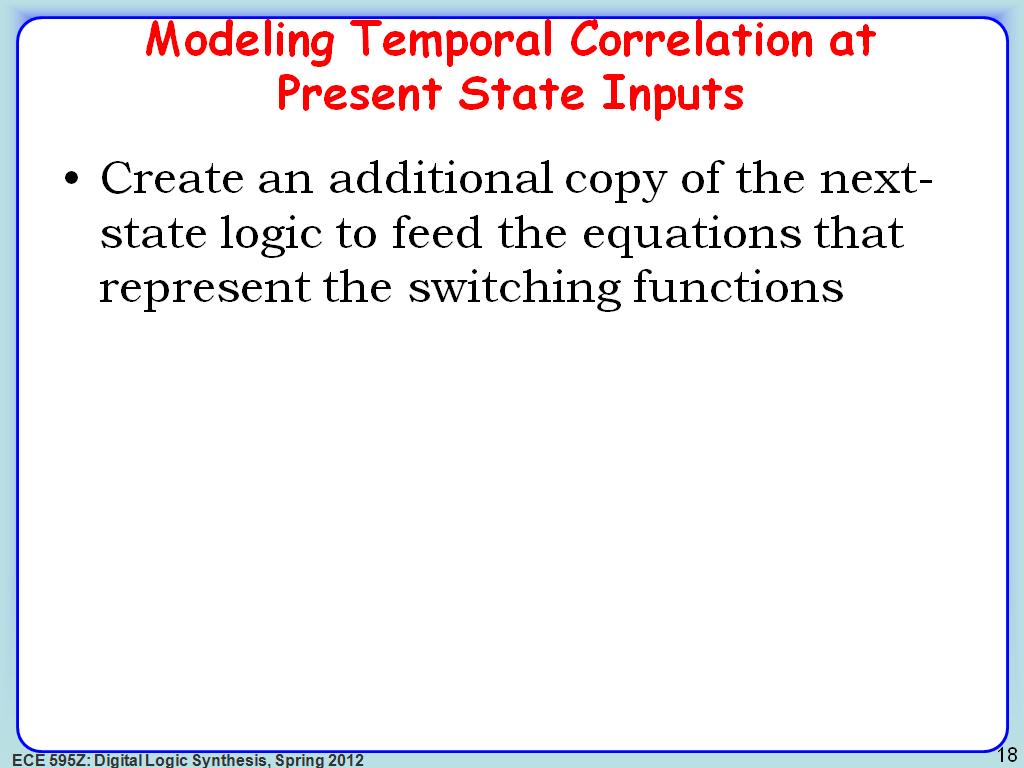
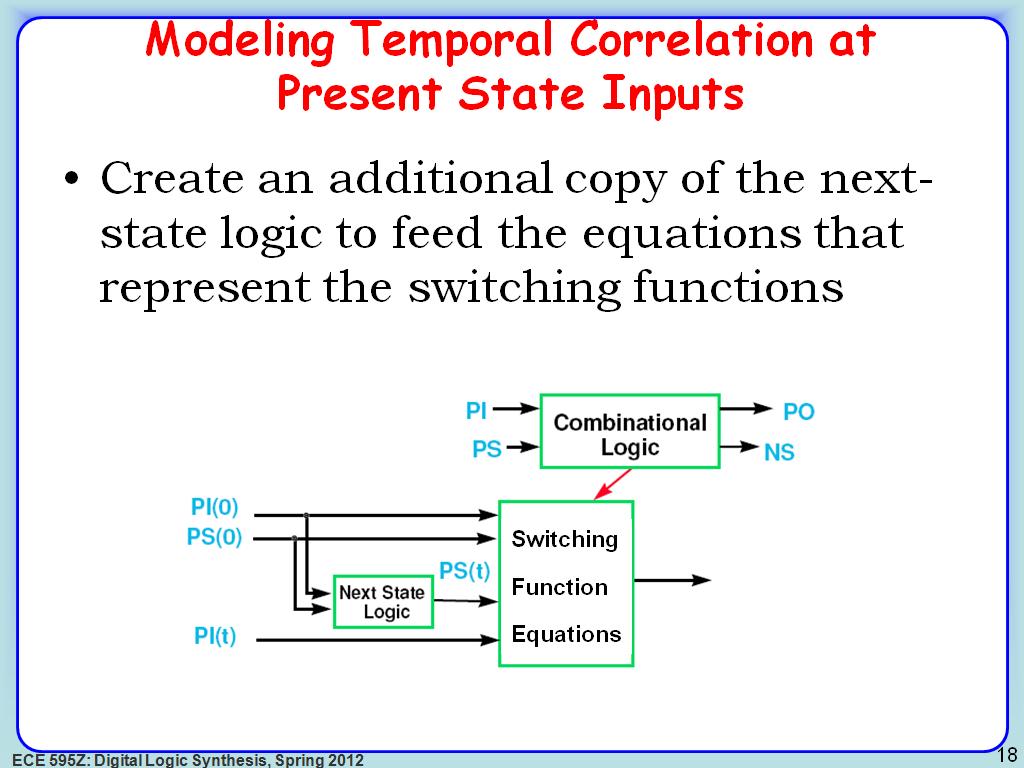 18. Modeling Temporal Correlation …
2828.1948615281949
00:00/00:00
18. Modeling Temporal Correlation …
2828.1948615281949
00:00/00:00 -
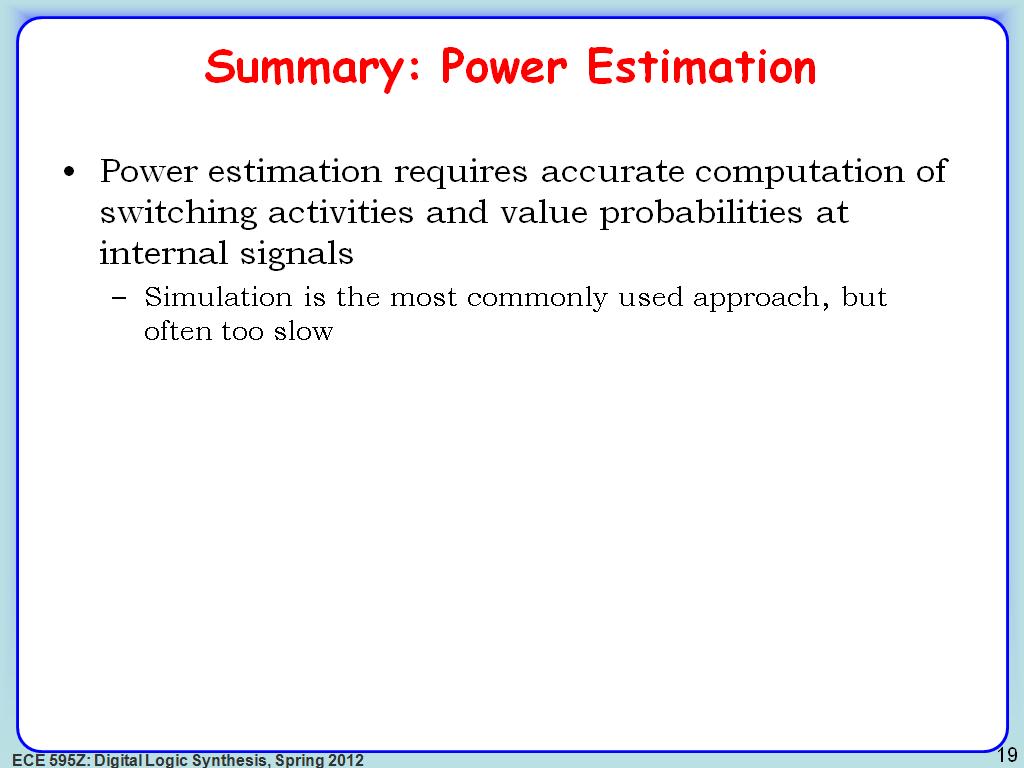
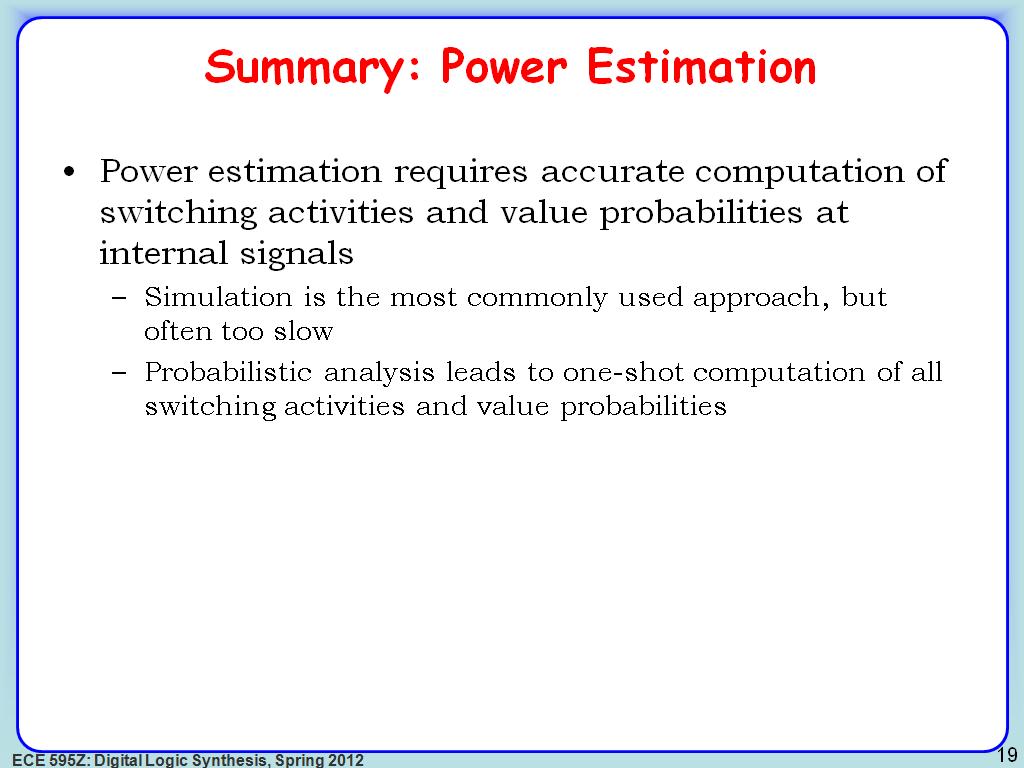
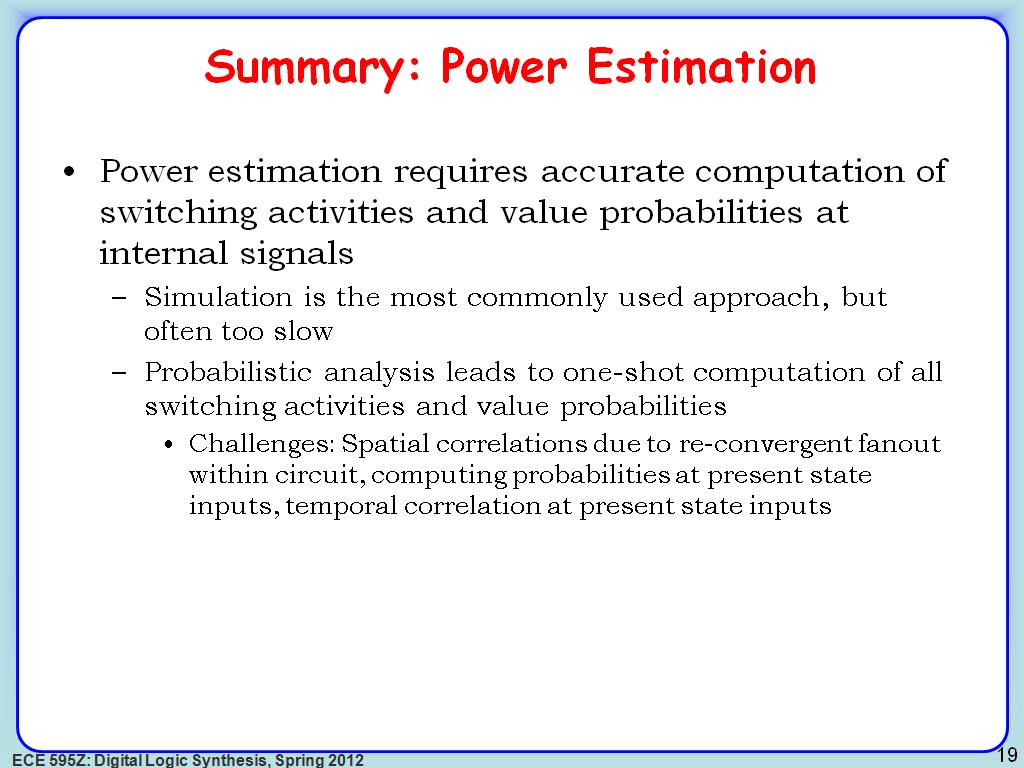
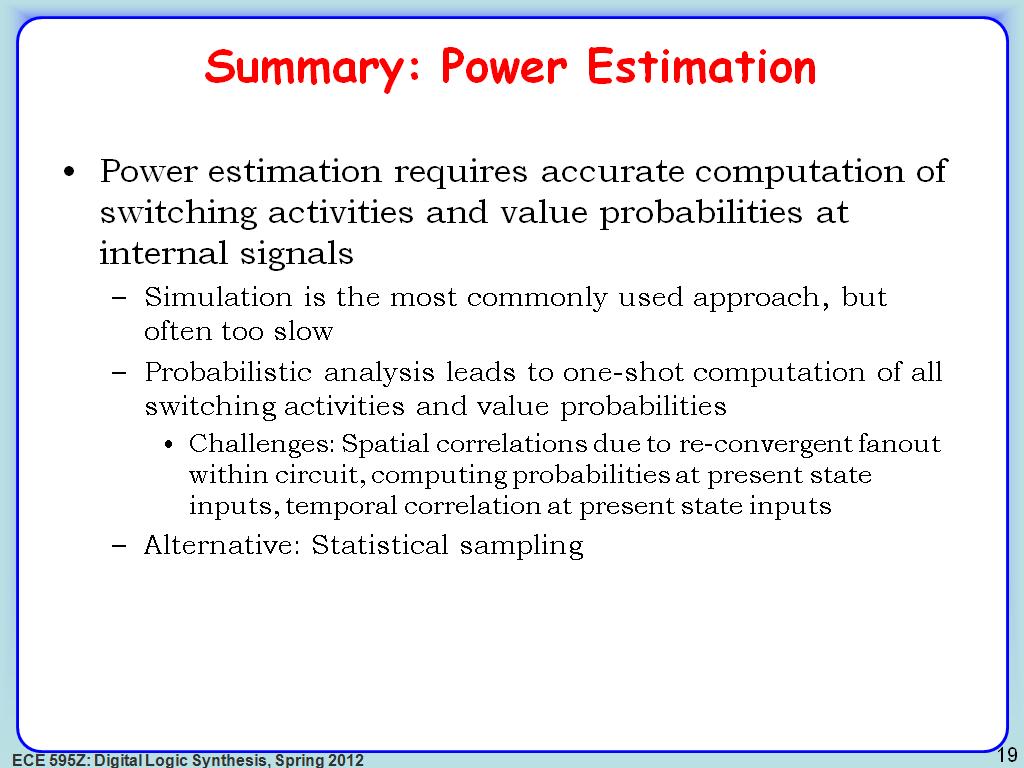
 19. Summary: Power Estimation
2894.1274607941277
00:00/00:00
19. Summary: Power Estimation
2894.1274607941277
00:00/00:00 -
 20. Automatic Power Reduction
2987.3873873873877
00:00/00:00
20. Automatic Power Reduction
2987.3873873873877
00:00/00:00 -
 21. Outline
2991.0910910910911
00:00/00:00
21. Outline
2991.0910910910911
00:00/00:00 -
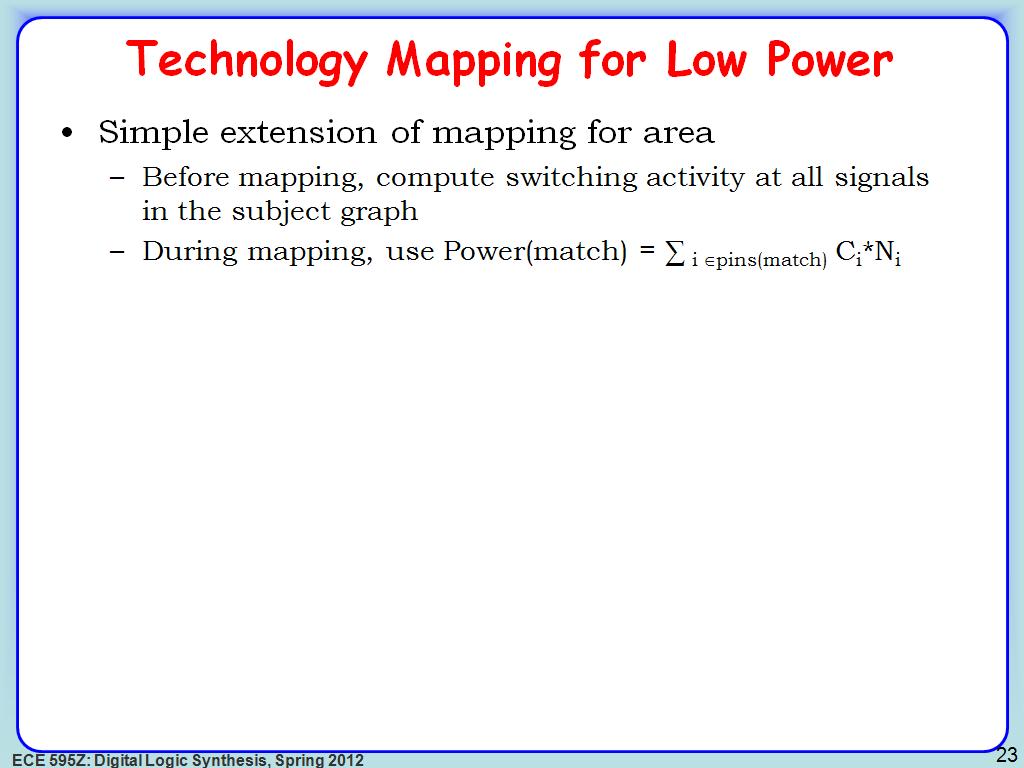
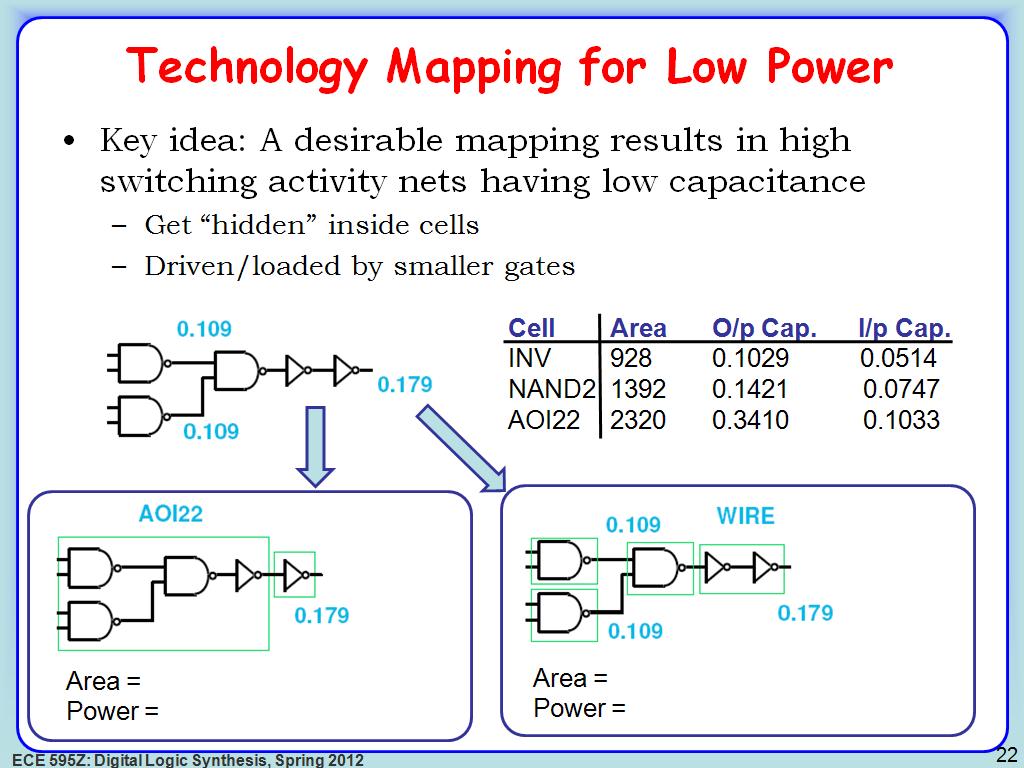 22. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3076.2095428762095
00:00/00:00
22. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3076.2095428762095
00:00/00:00 -
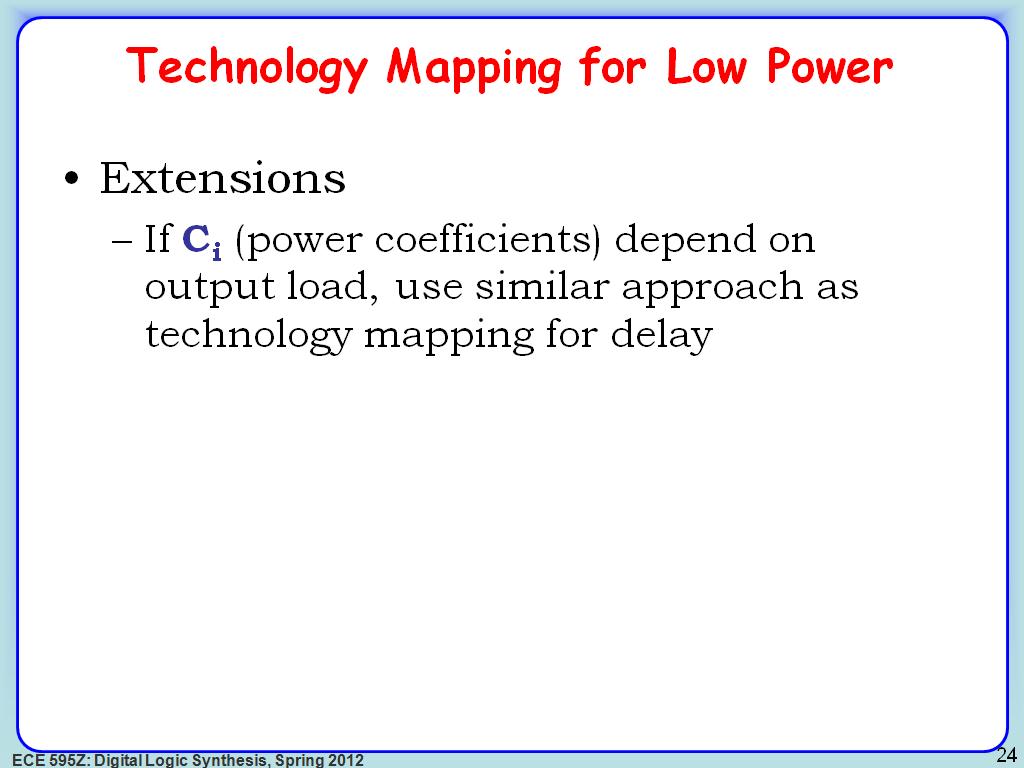
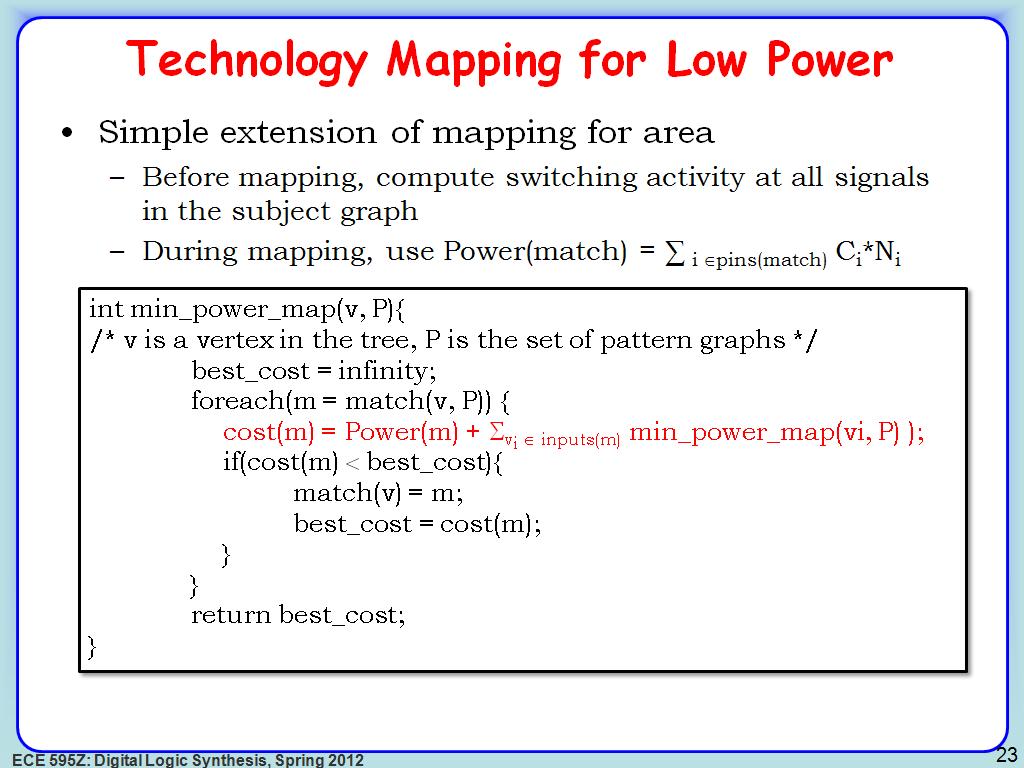 23. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3295.9626292959629
00:00/00:00
23. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3295.9626292959629
00:00/00:00 -
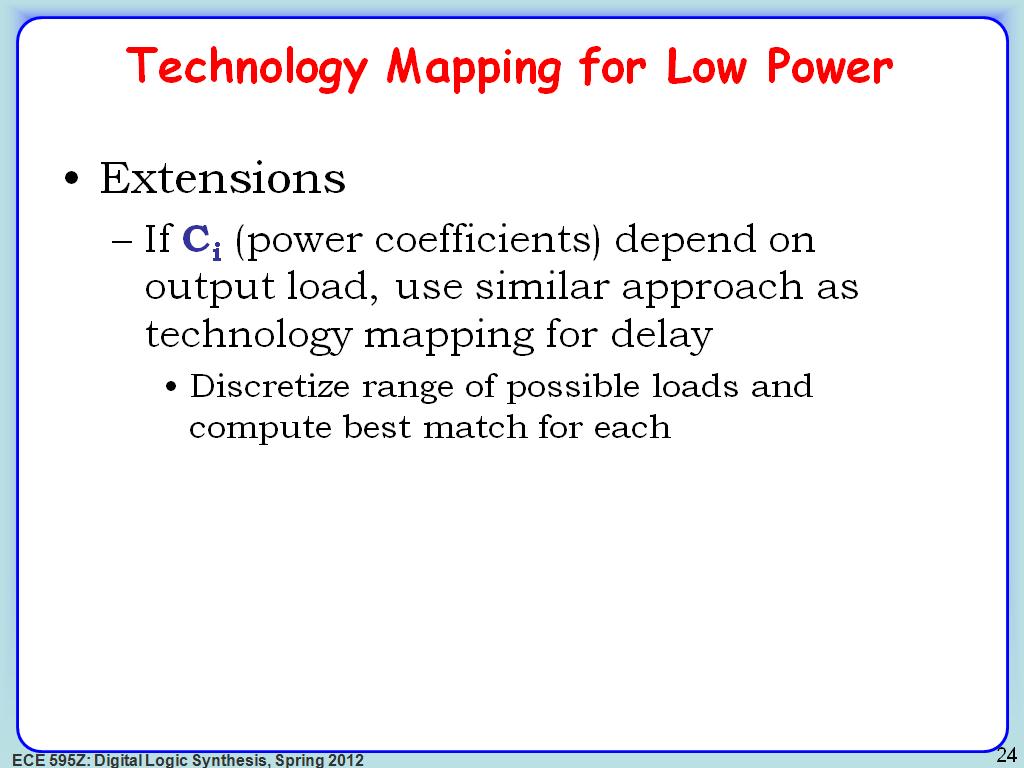
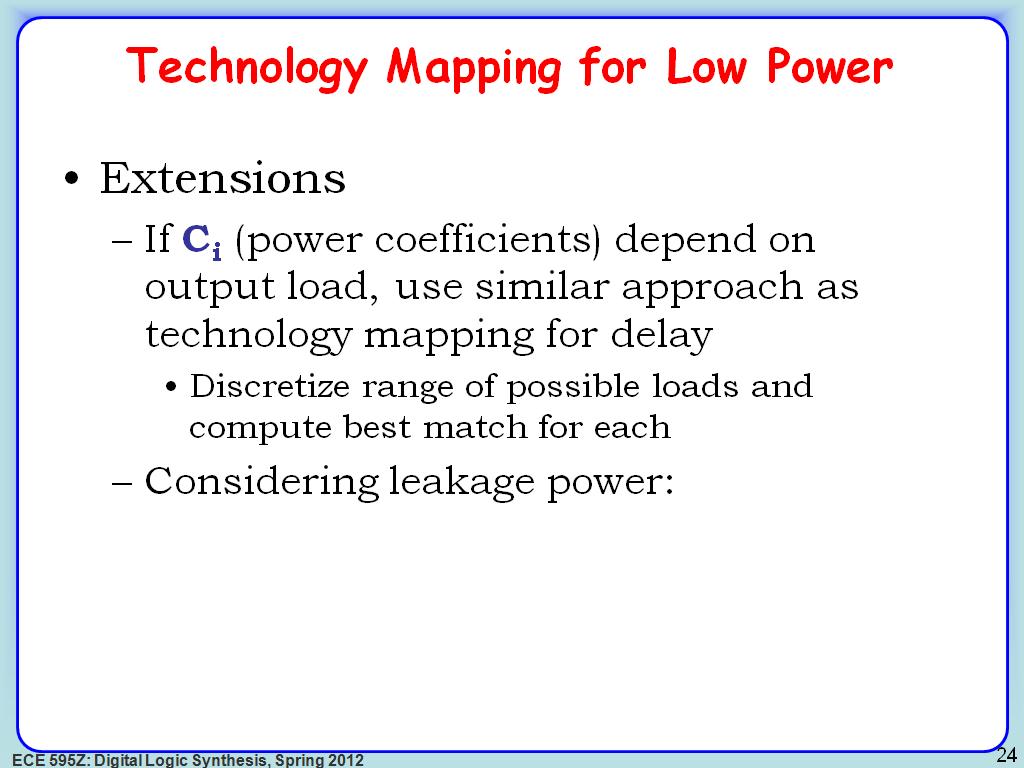
 24. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3308.1748415081752
00:00/00:00
24. Technology Mapping for Low Pow…
3308.1748415081752
00:00/00:00 -
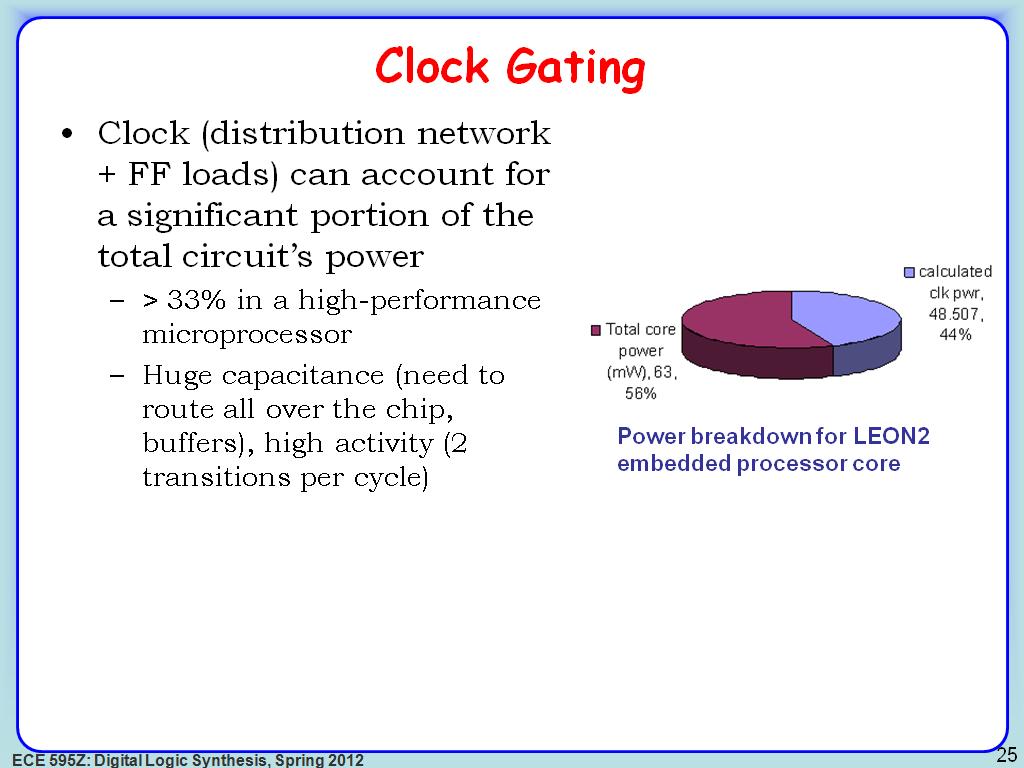 25. Clock Gating
3386.41975308642
00:00/00:00
25. Clock Gating
3386.41975308642
00:00/00:00 -
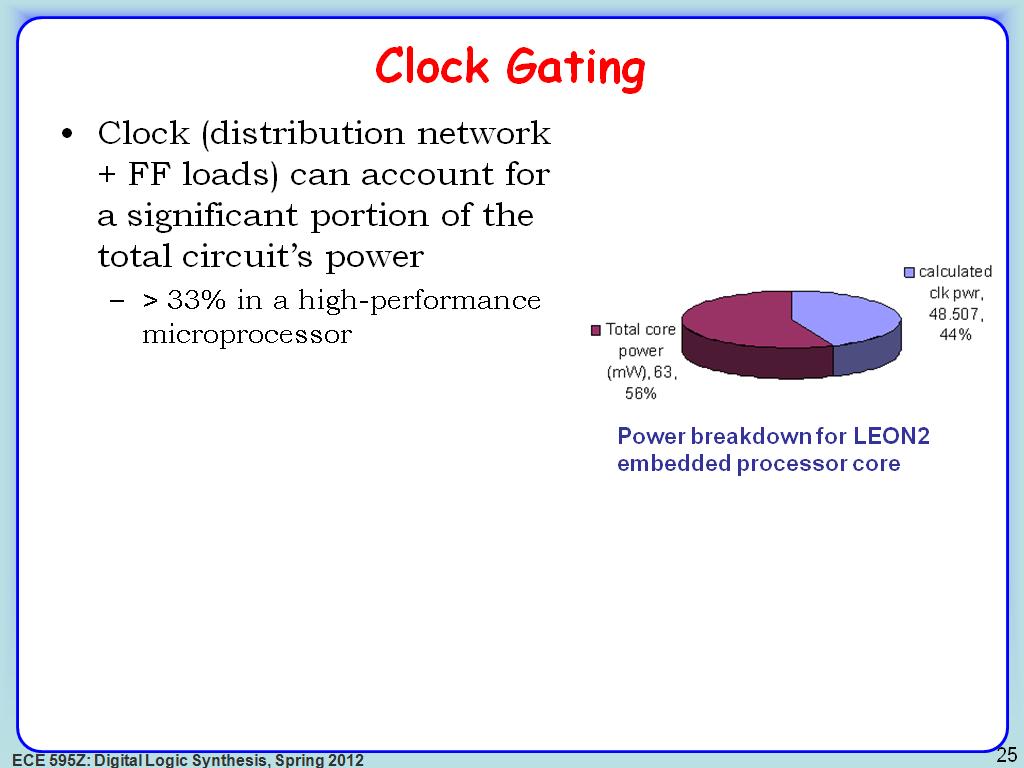
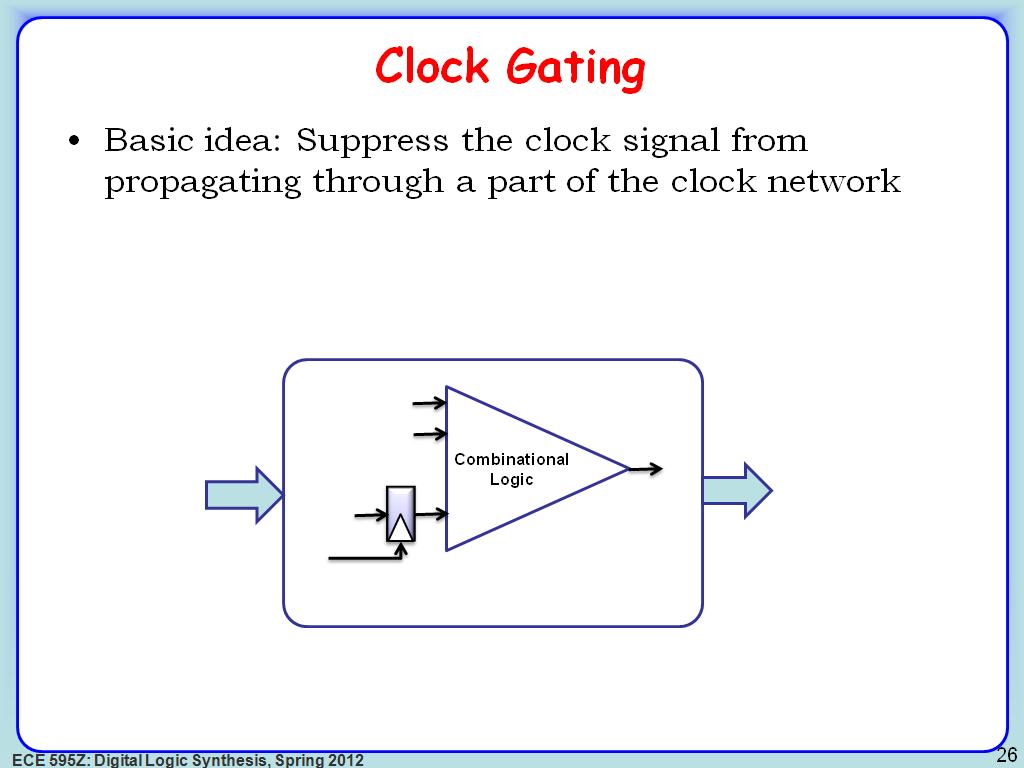
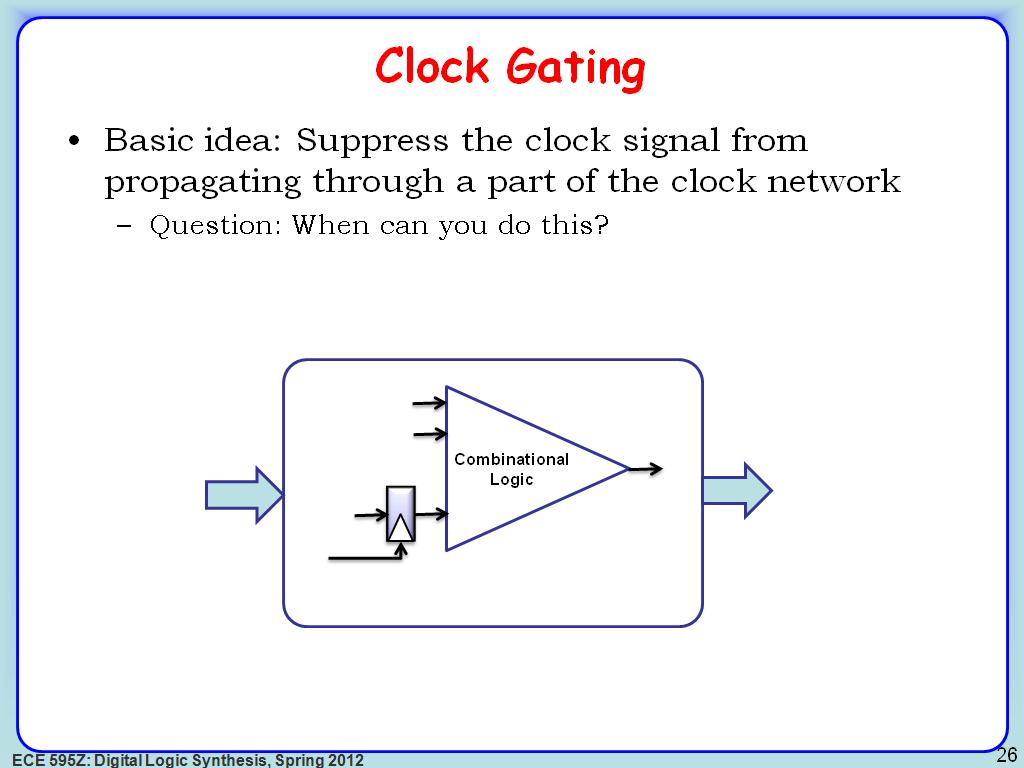 26. Clock Gating
3457.8244911578245
00:00/00:00
26. Clock Gating
3457.8244911578245
00:00/00:00 -
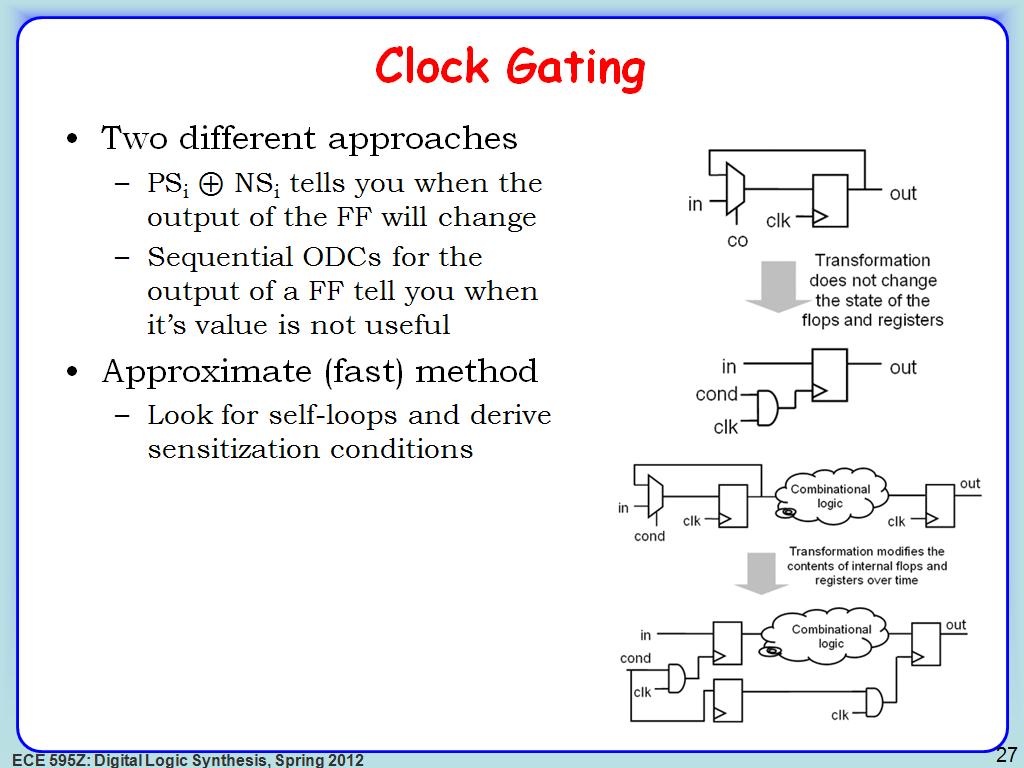 27. Clock Gating
3497.7310643977312
00:00/00:00
27. Clock Gating
3497.7310643977312
00:00/00:00 -
 28. Summary: Power Reduction
3692.5258591925258
00:00/00:00
28. Summary: Power Reduction
3692.5258591925258
00:00/00:00