Tutorial Lecture: Potentiometric Sensors Ion Selective Sensors - An Introduction
Tutorial Lecture: Potentiometric Sensors Ion Selective Sensors - An Introduction
-
 1. Tutorial Lecture: Potentiometr…
0
00:00/00:00
1. Tutorial Lecture: Potentiometr…
0
00:00/00:00 -
 2. Outline
46.279612946279613
00:00/00:00
2. Outline
46.279612946279613
00:00/00:00 -
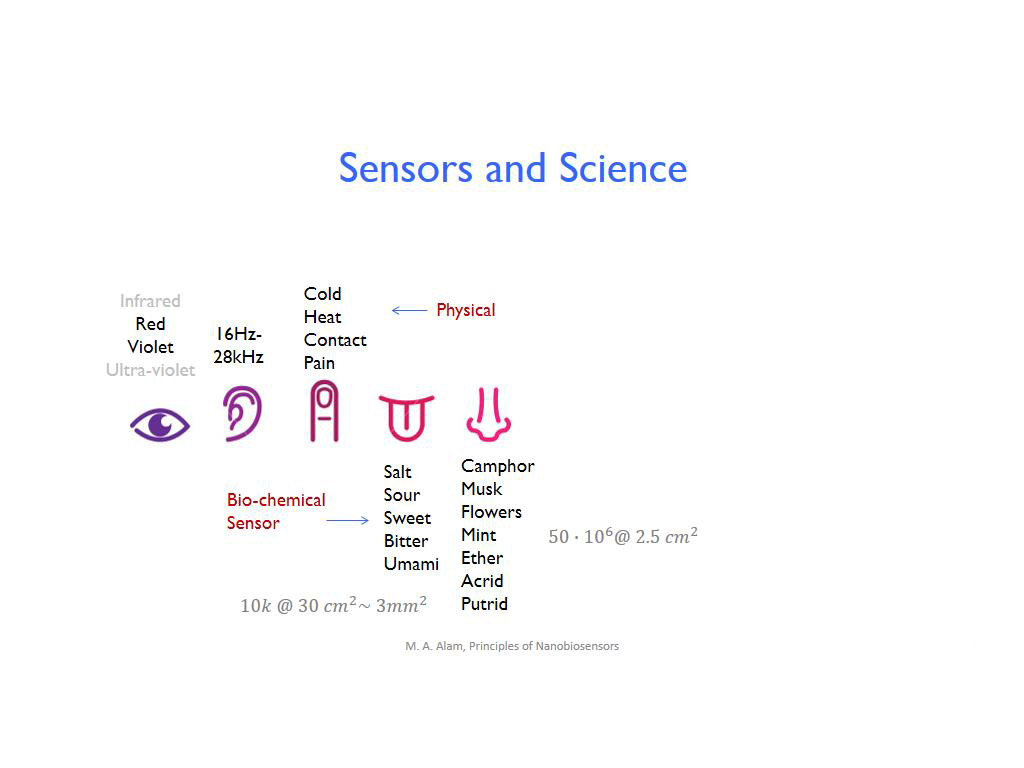
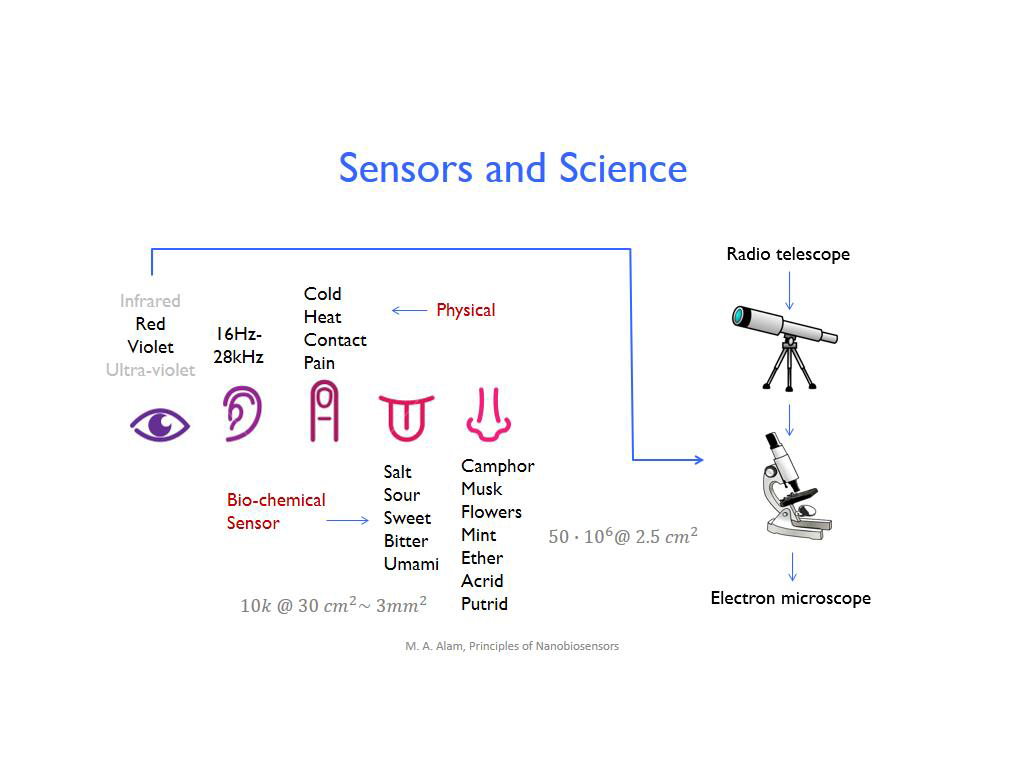 3. Sensors and Science
104.07073740407074
00:00/00:00
3. Sensors and Science
104.07073740407074
00:00/00:00 -
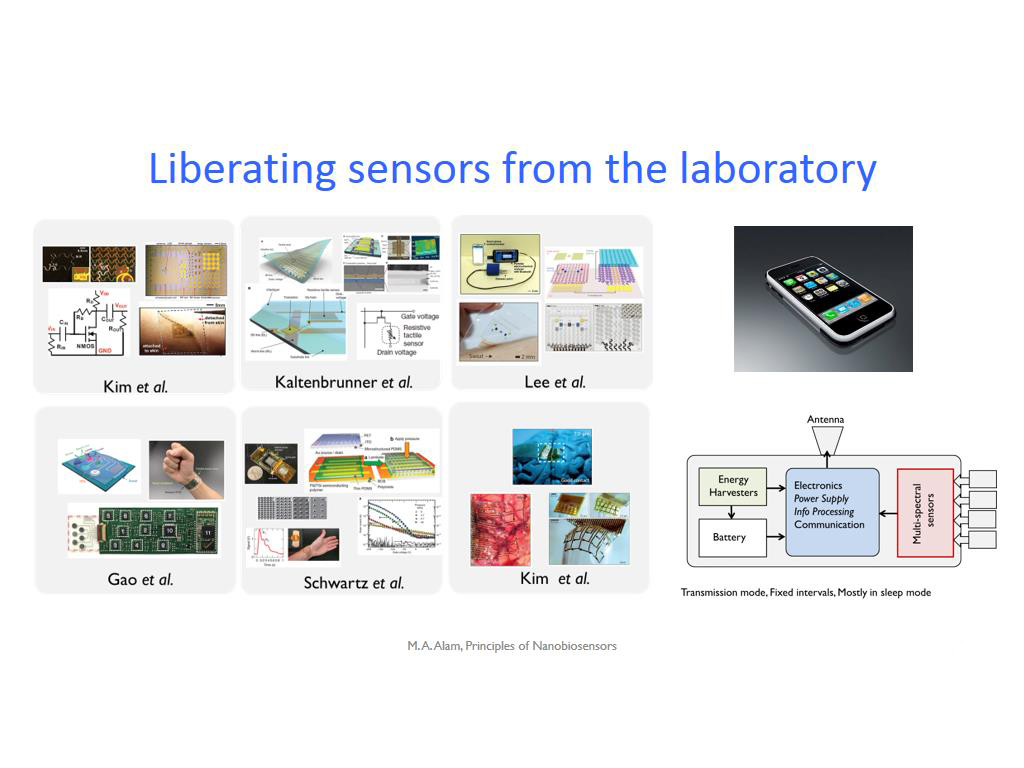 4. Liberating sensors from the la…
163.16316316316318
00:00/00:00
4. Liberating sensors from the la…
163.16316316316318
00:00/00:00 -
 5. Many applications of Ion-sensi…
275.64230897564232
00:00/00:00
5. Many applications of Ion-sensi…
275.64230897564232
00:00/00:00 -
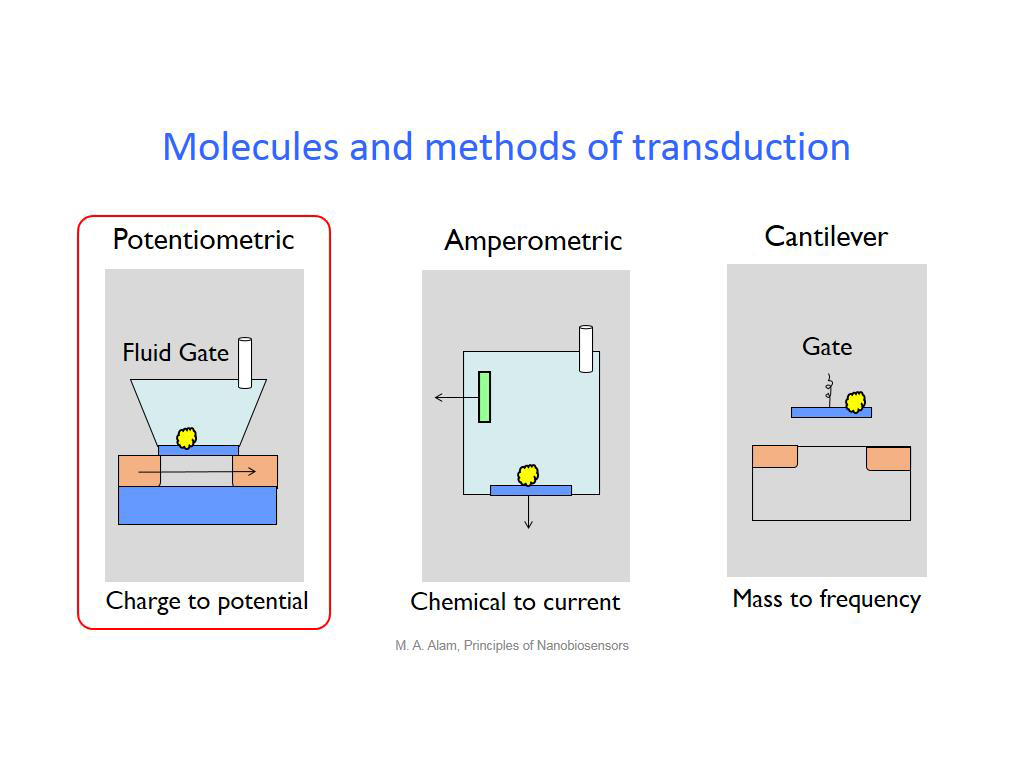 6. Molecules and methods of trans…
328.32832832832833
00:00/00:00
6. Molecules and methods of trans…
328.32832832832833
00:00/00:00 -
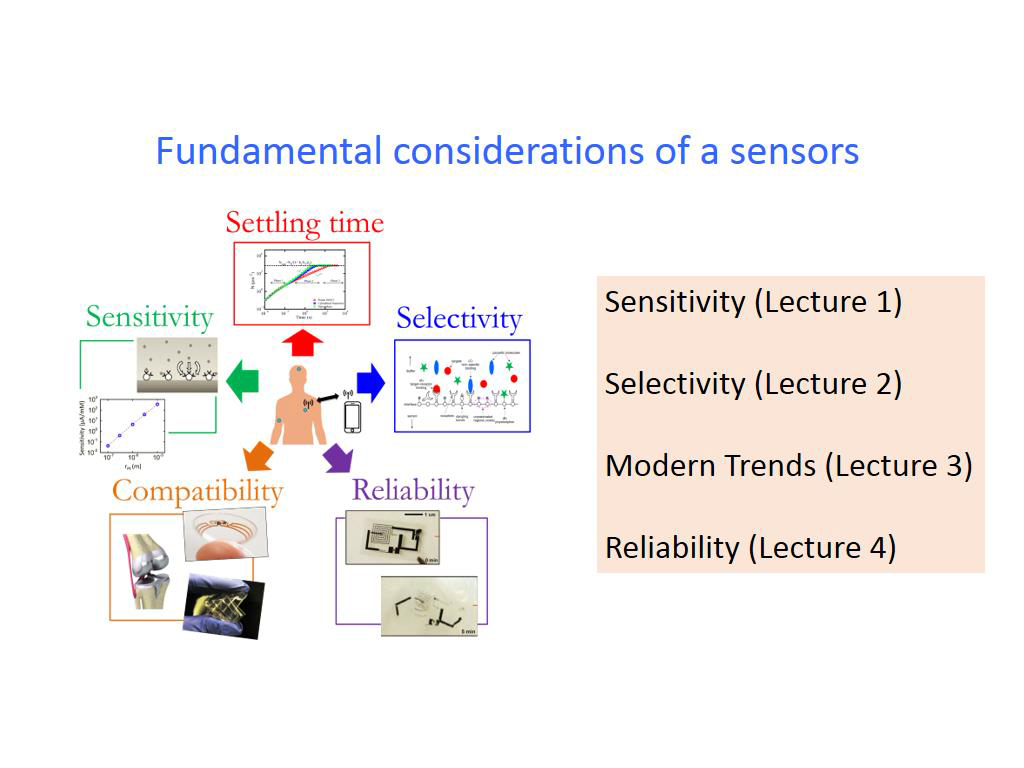 7. Fundamental considerations of …
439.93993993993996
00:00/00:00
7. Fundamental considerations of …
439.93993993993996
00:00/00:00 -
 8. Outline
512.51251251251256
00:00/00:00
8. Outline
512.51251251251256
00:00/00:00 -
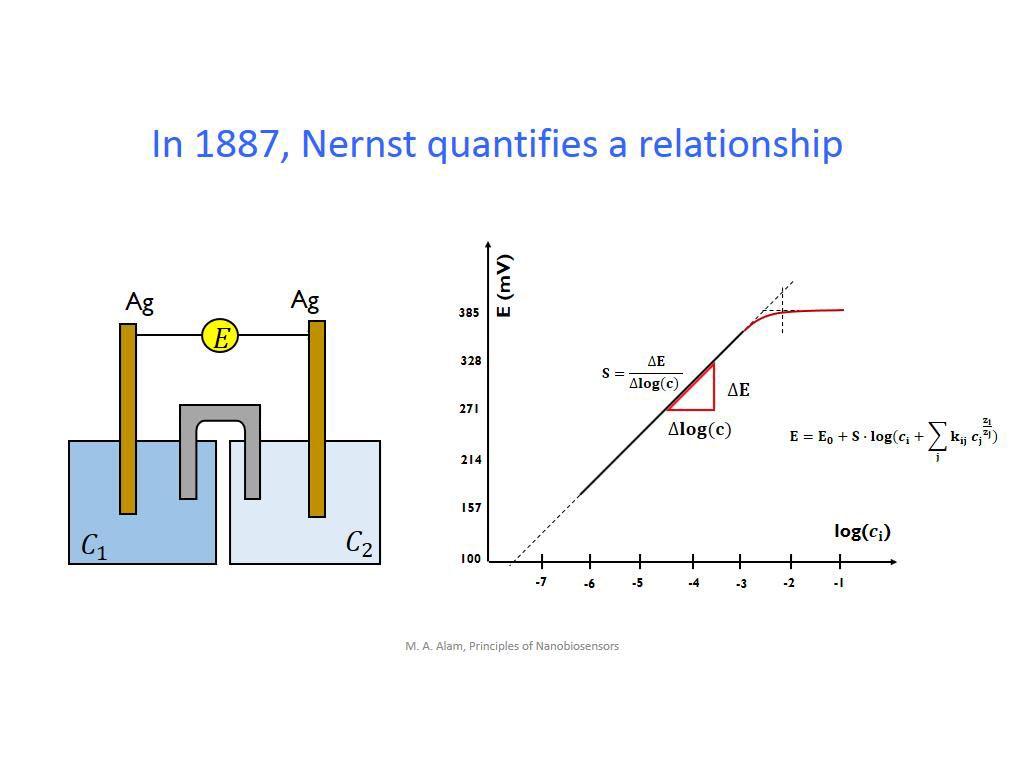
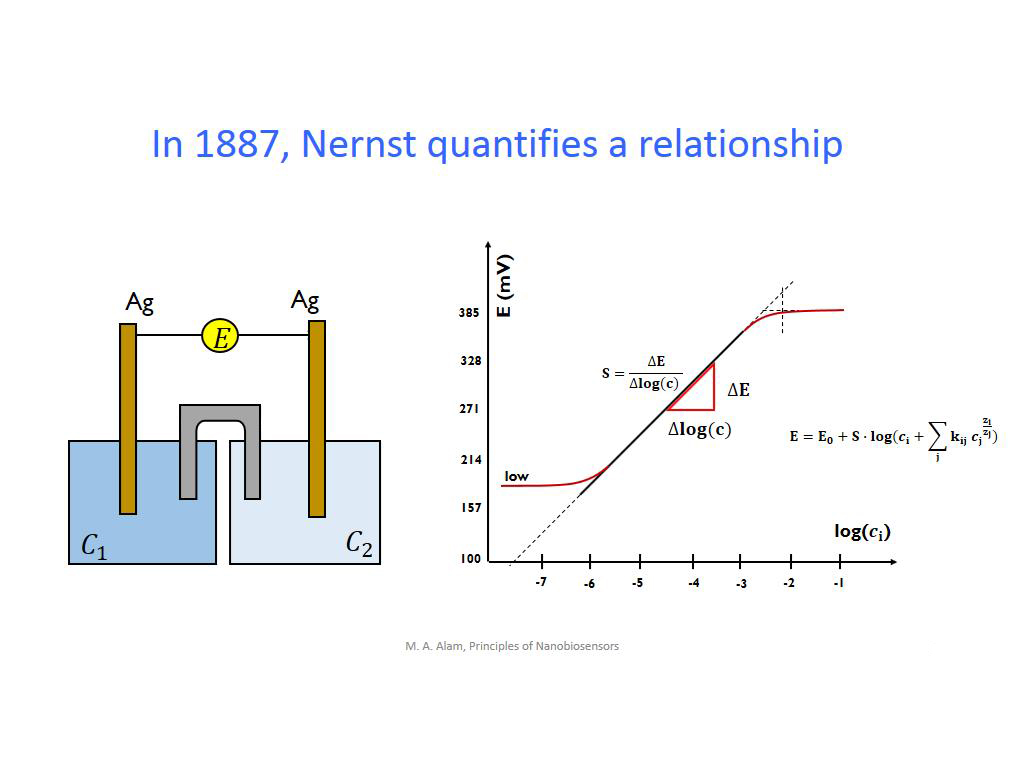
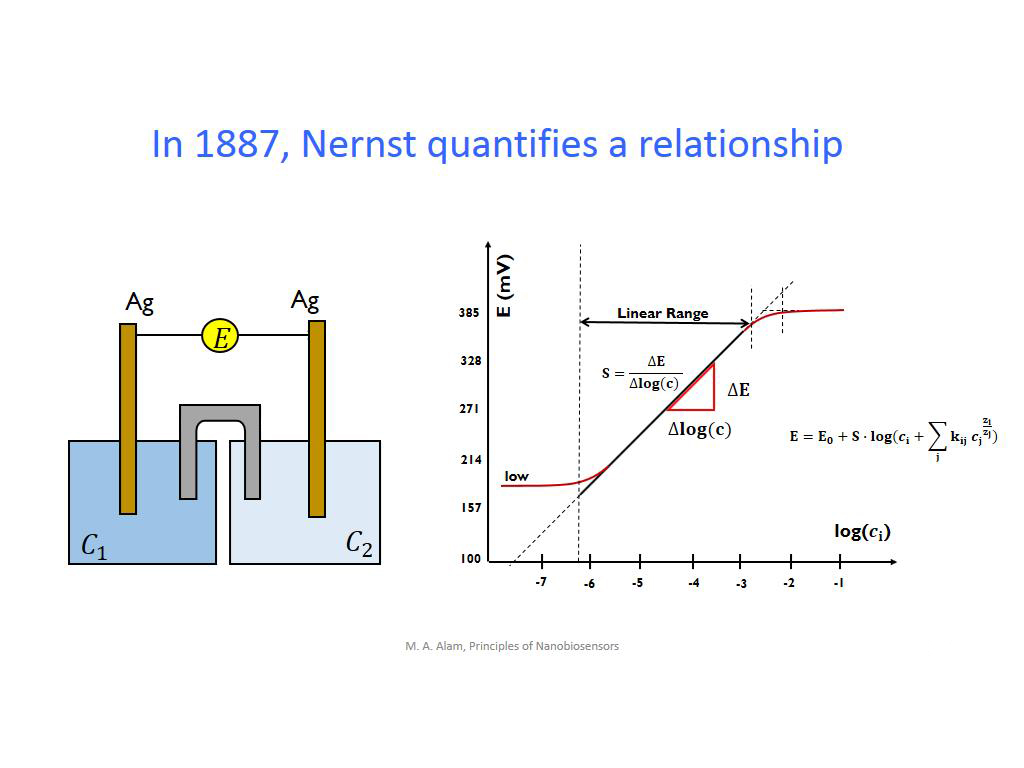
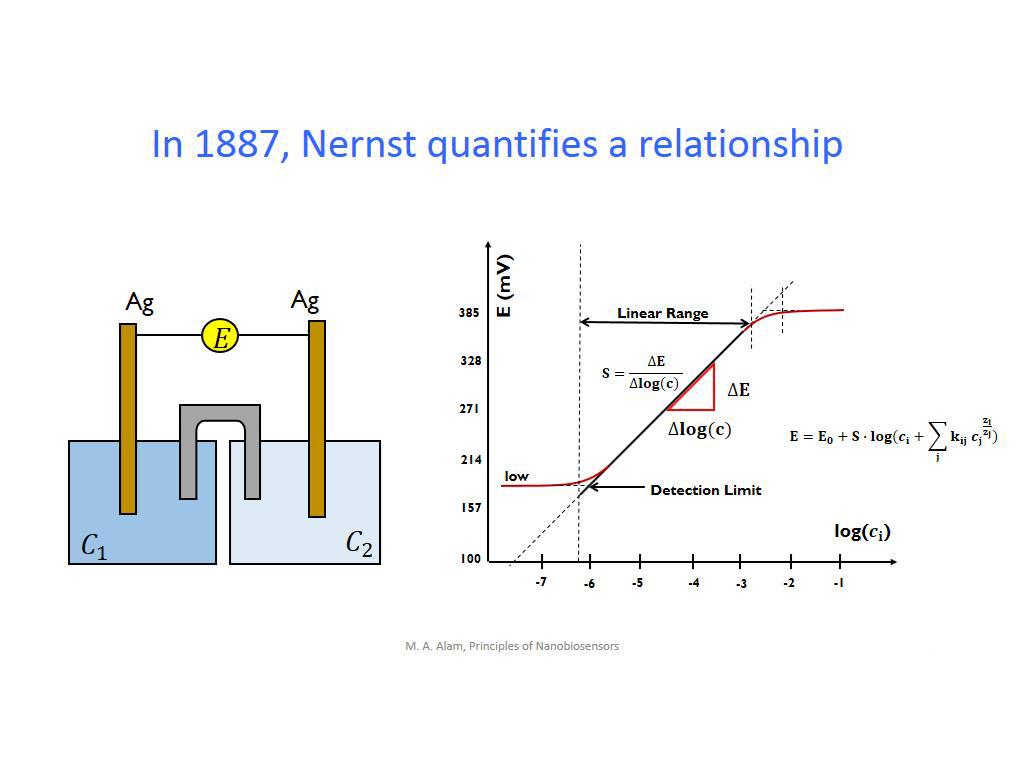 9. In 1887, Nernst quantifies a r…
521.98865532198863
00:00/00:00
9. In 1887, Nernst quantifies a r…
521.98865532198863
00:00/00:00 -
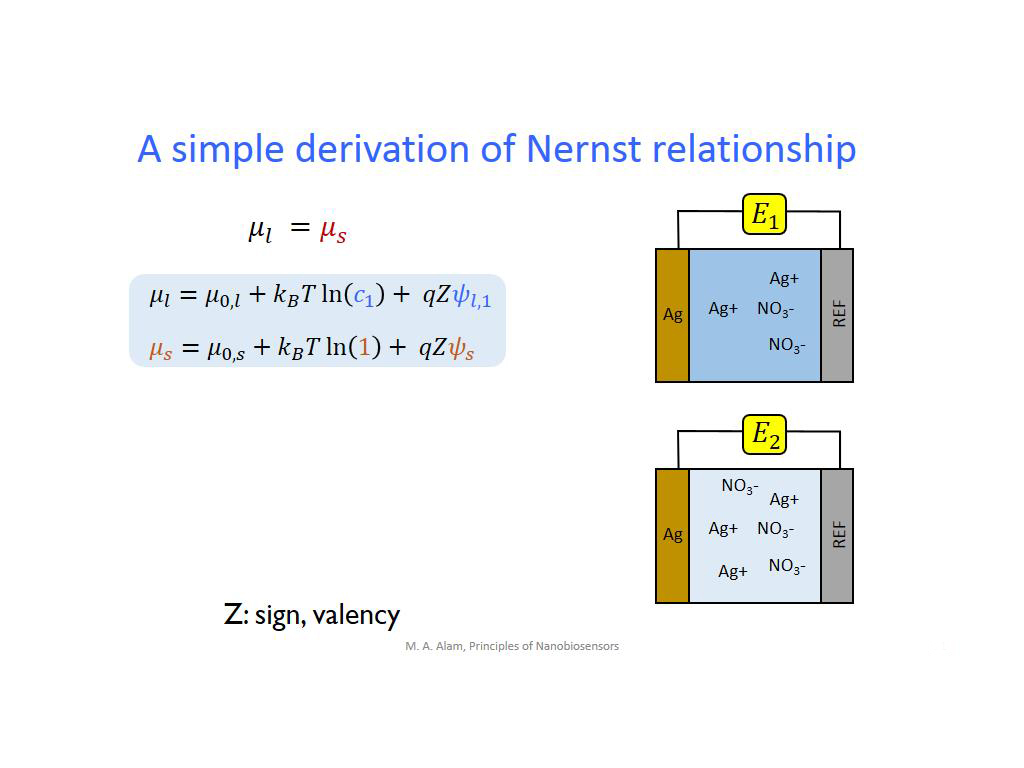
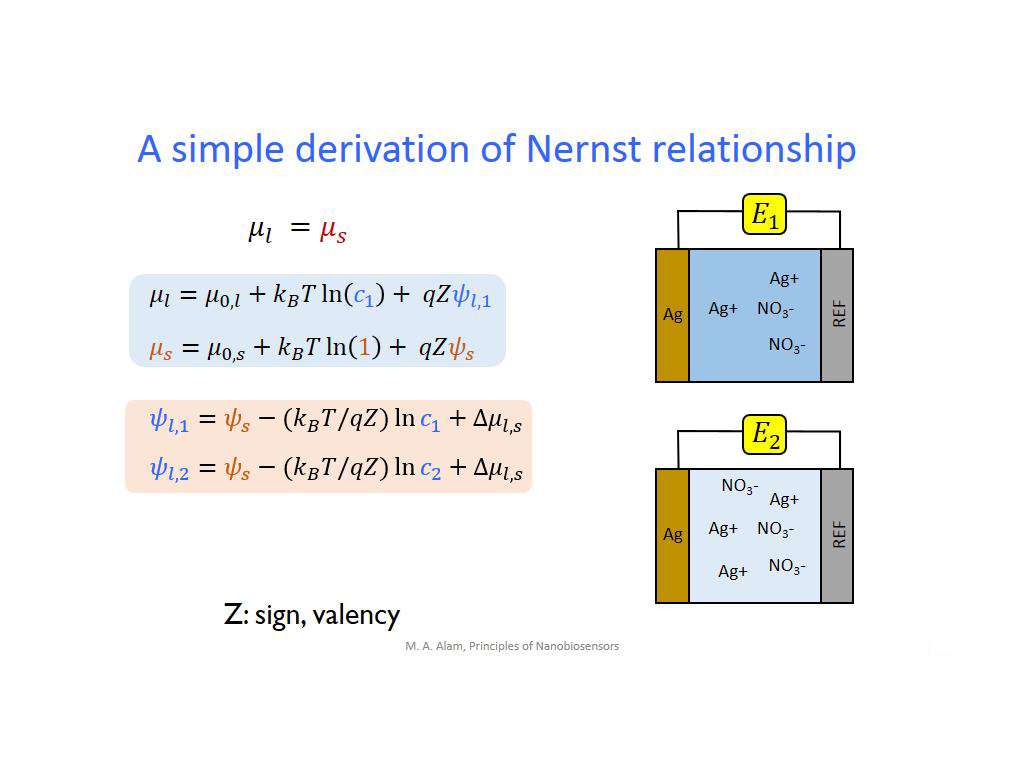
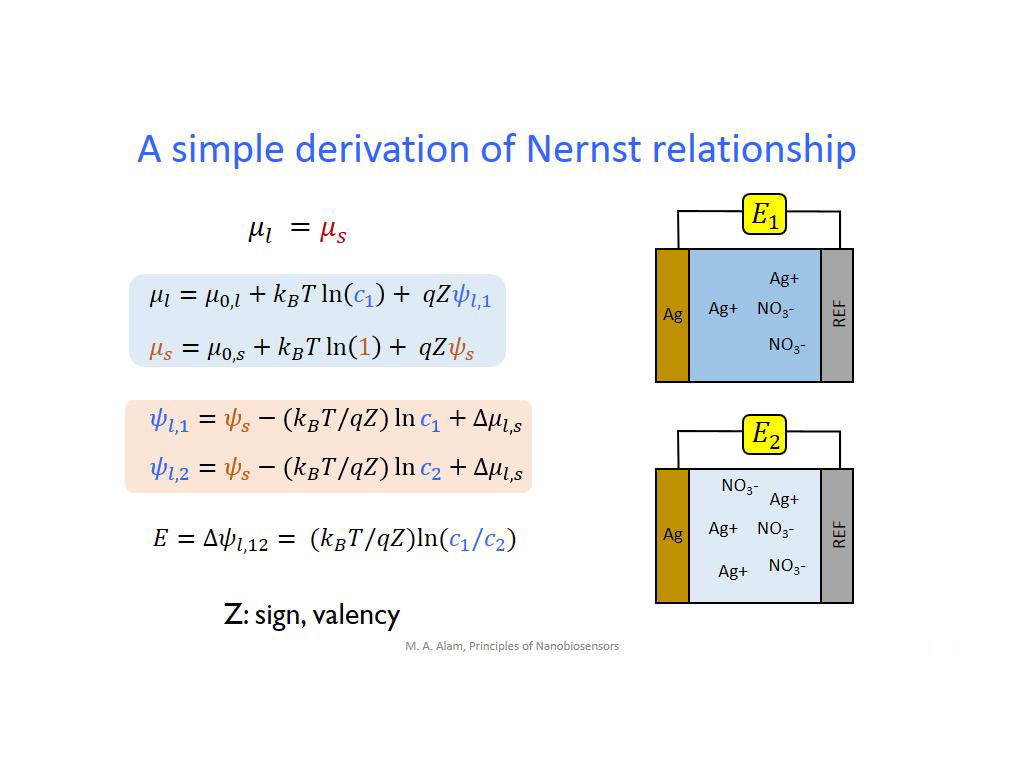 10. A simple derivation of Nernst …
752.51918585251917
00:00/00:00
10. A simple derivation of Nernst …
752.51918585251917
00:00/00:00 -
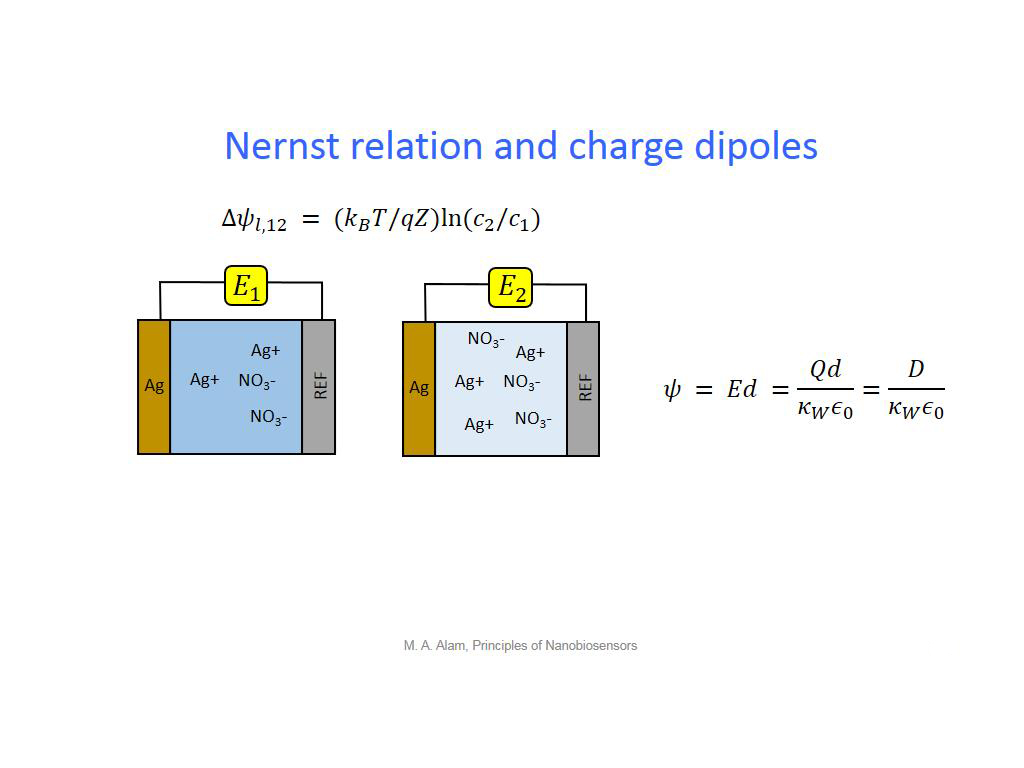
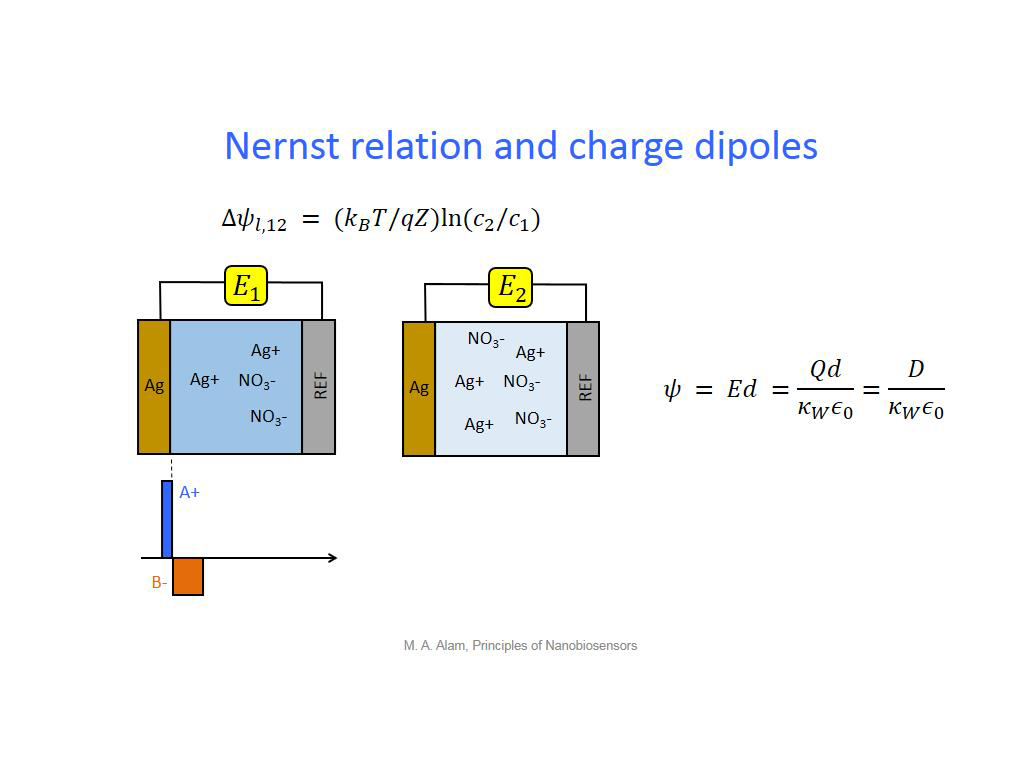
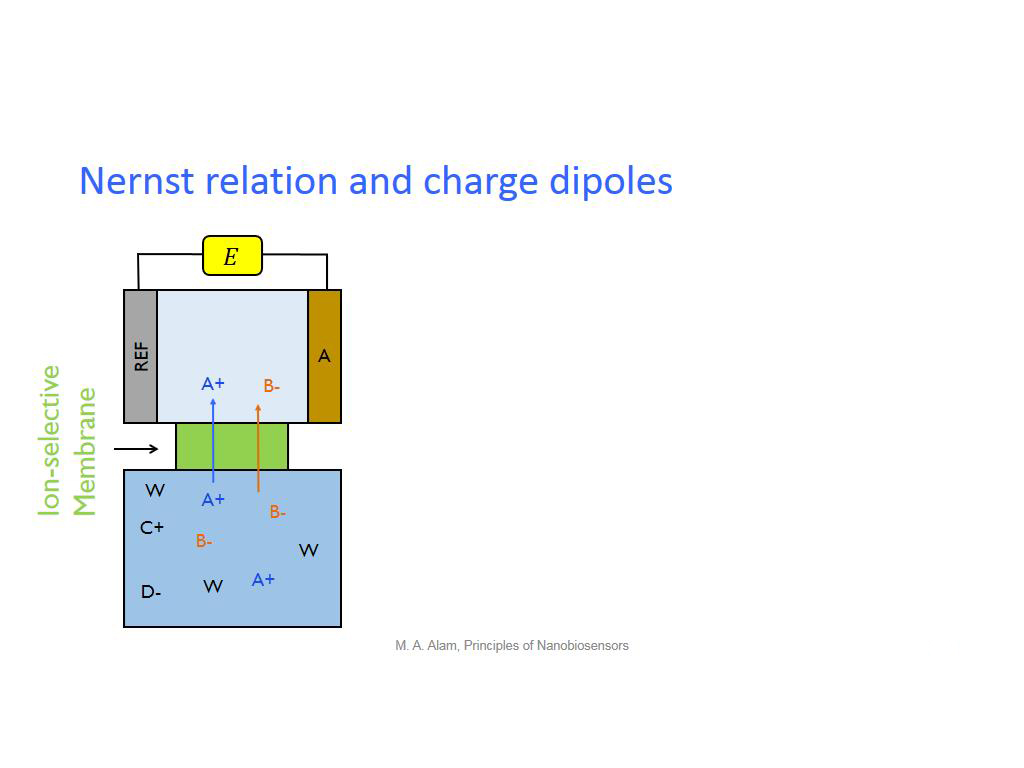
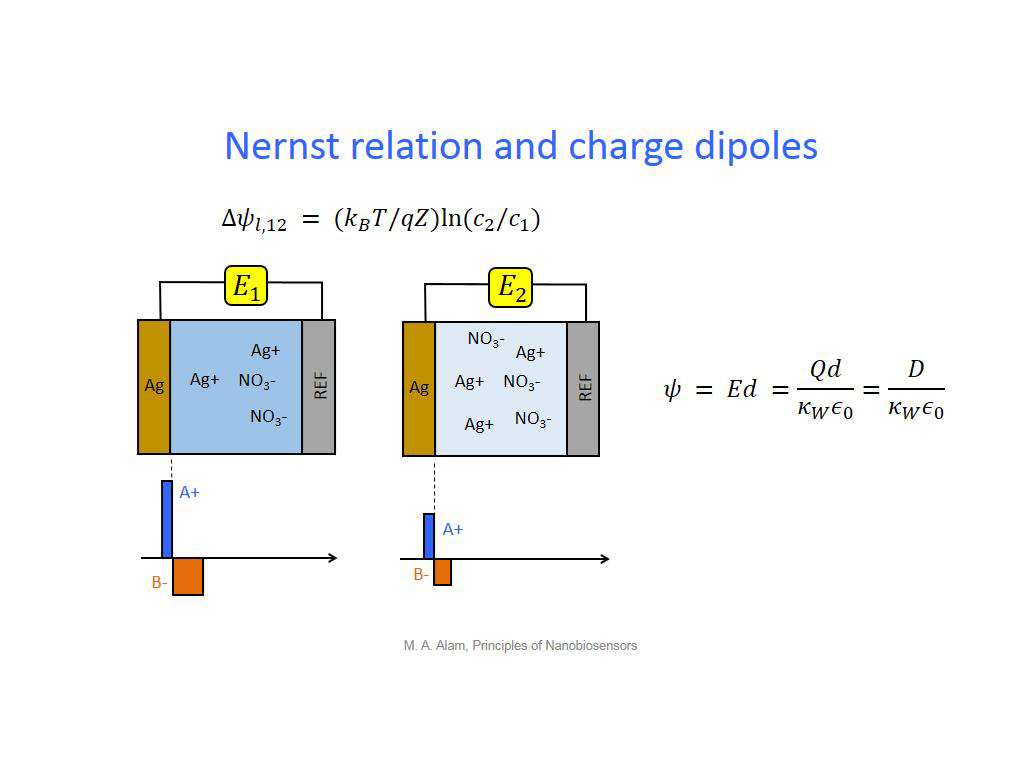 11. Nernst relation and charge dip…
877.77777777777783
00:00/00:00
11. Nernst relation and charge dip…
877.77777777777783
00:00/00:00 -
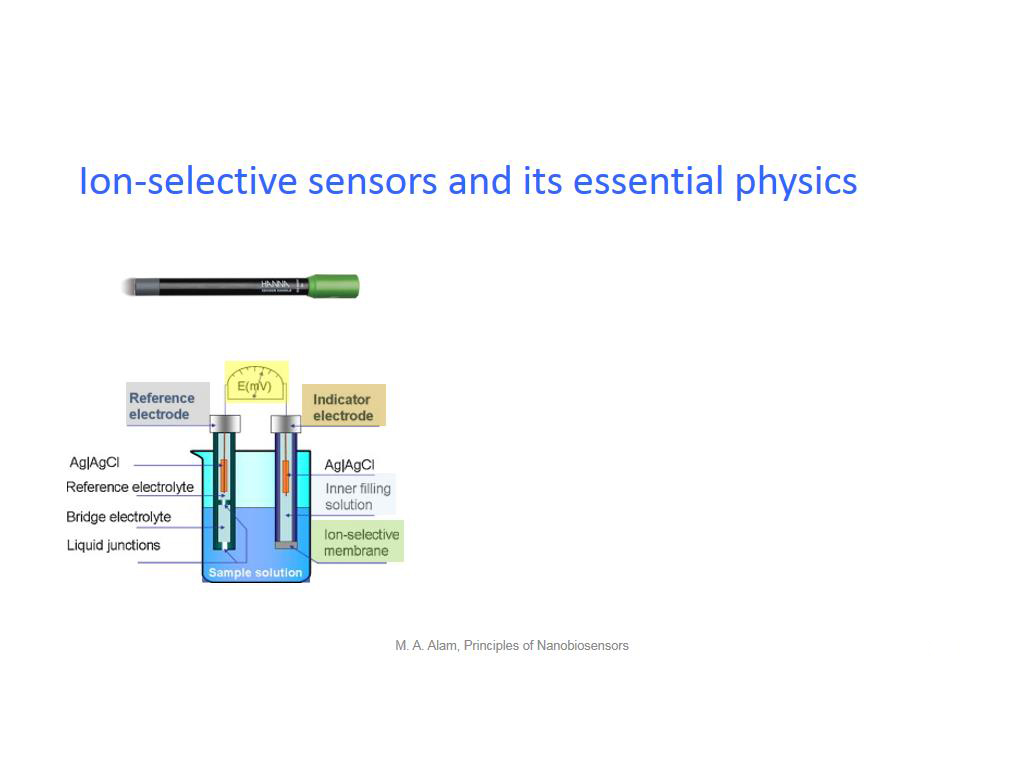
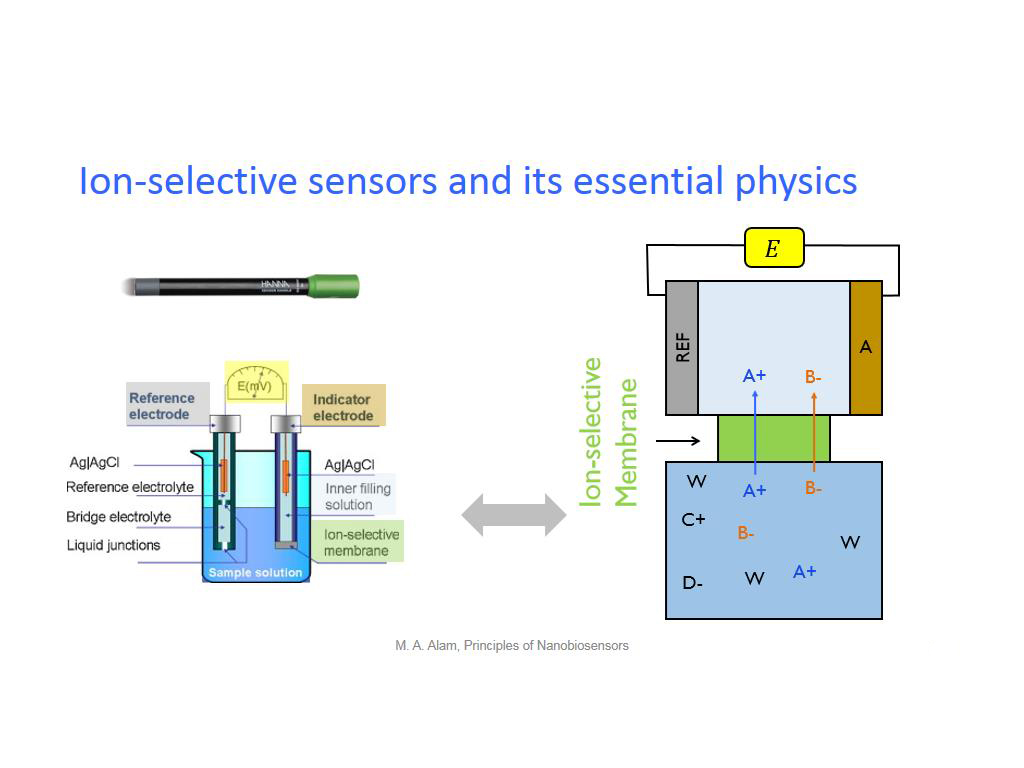 12. Ion-selective sensors and its …
964.46446446446453
00:00/00:00
12. Ion-selective sensors and its …
964.46446446446453
00:00/00:00 -
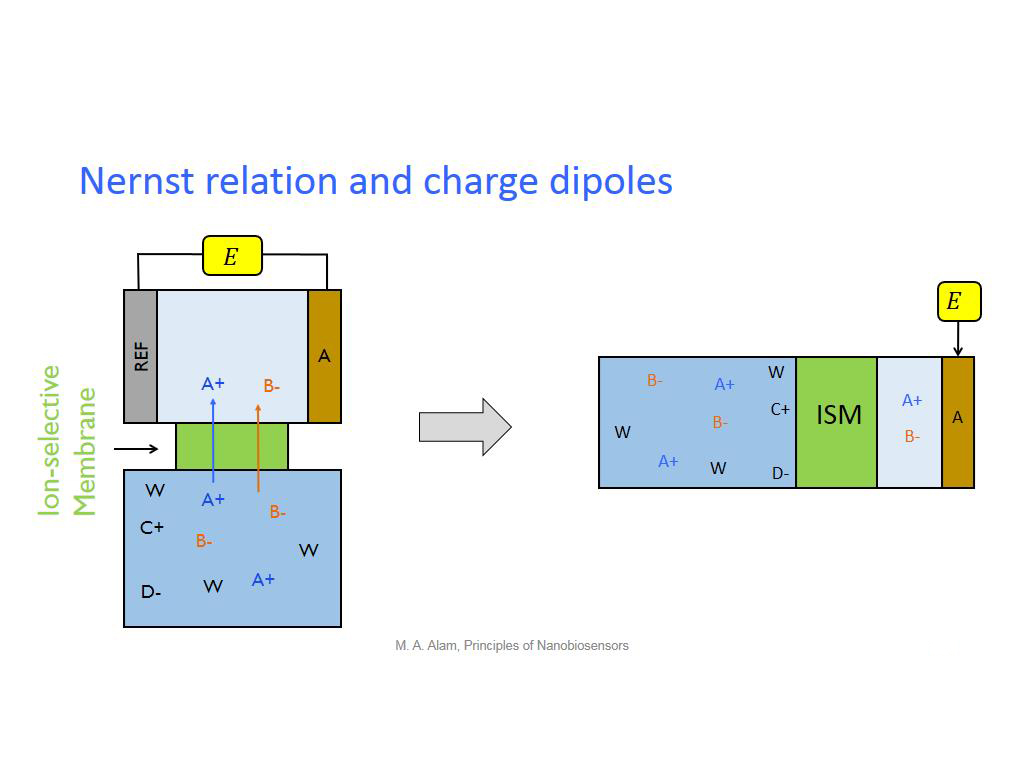 13. Nernst relation and charge dip…
1080.9476142809476
00:00/00:00
13. Nernst relation and charge dip…
1080.9476142809476
00:00/00:00 -
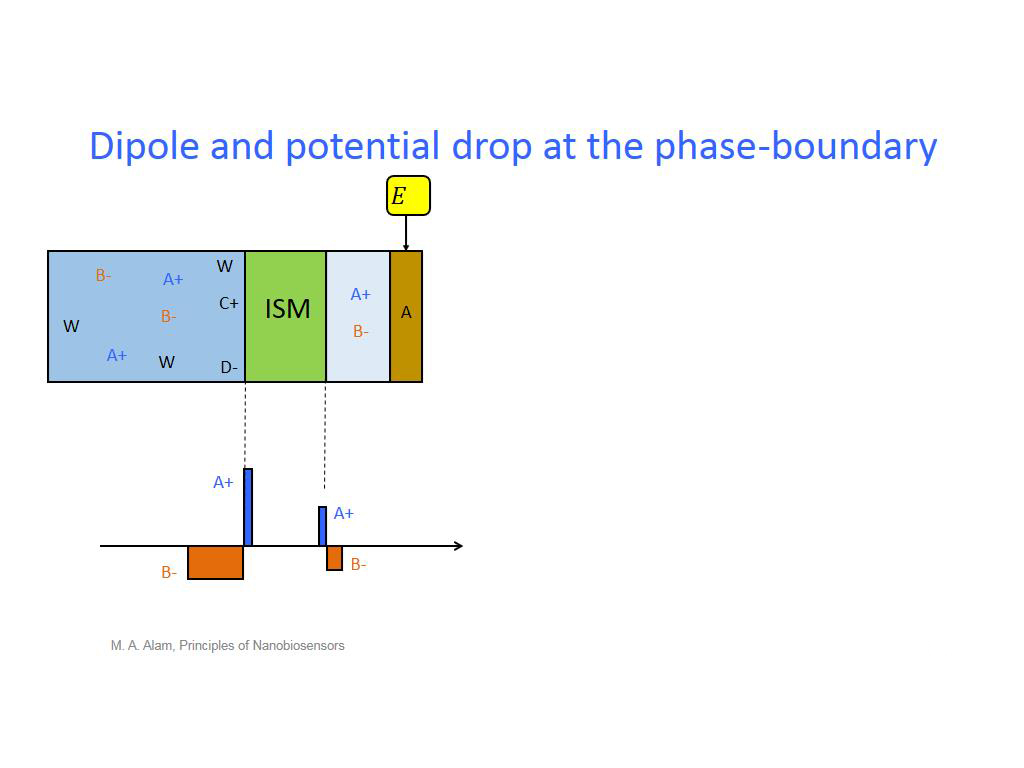
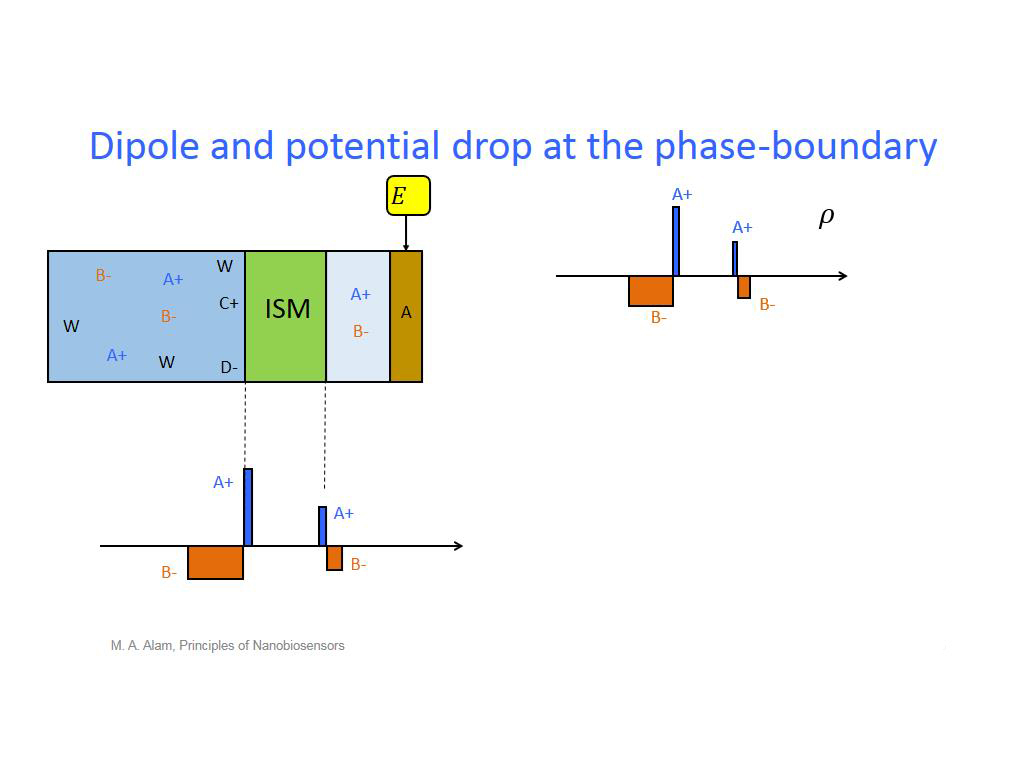
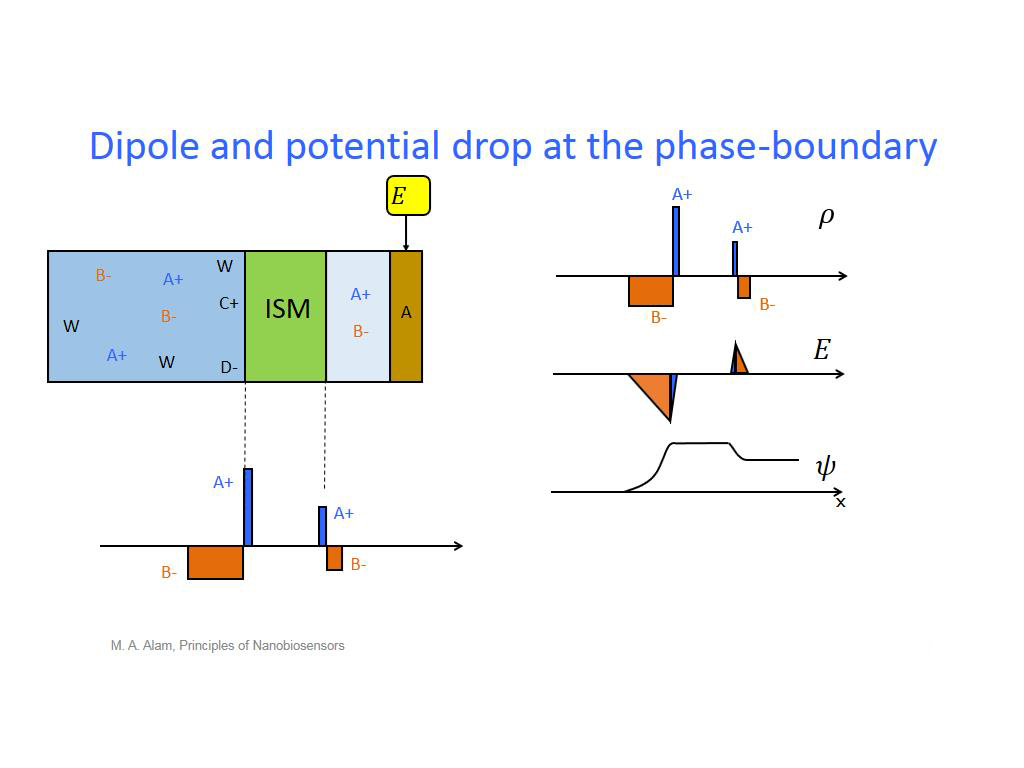
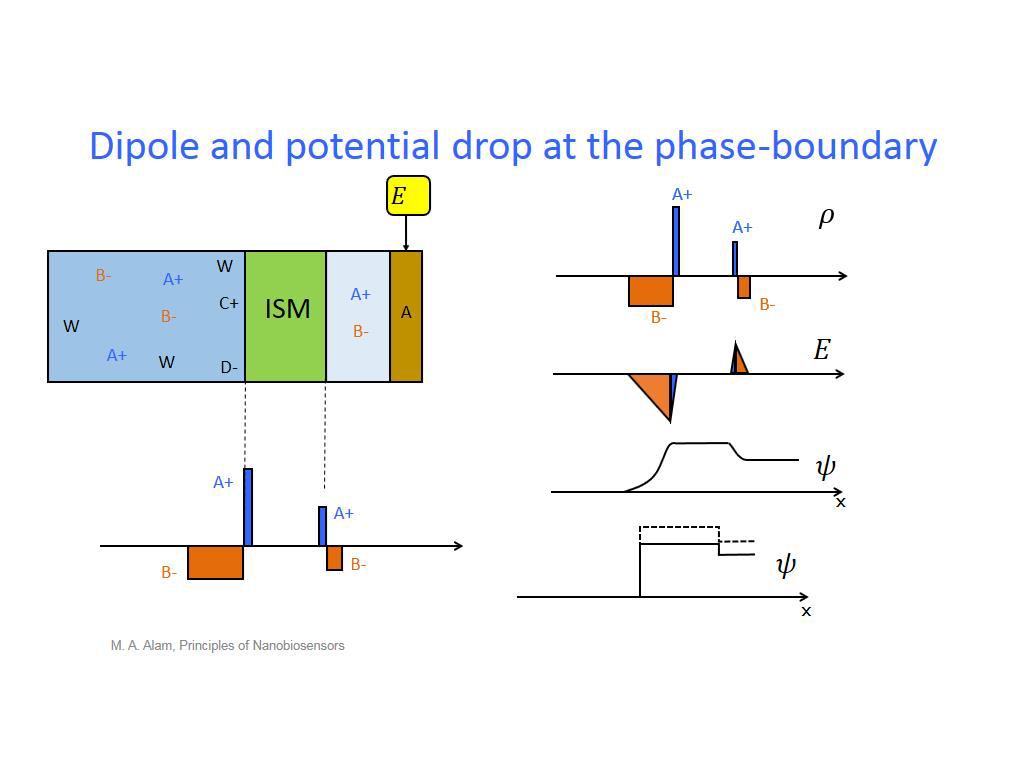 14. Dipole and potential drop at t…
1112.9796463129796
00:00/00:00
14. Dipole and potential drop at t…
1112.9796463129796
00:00/00:00 -
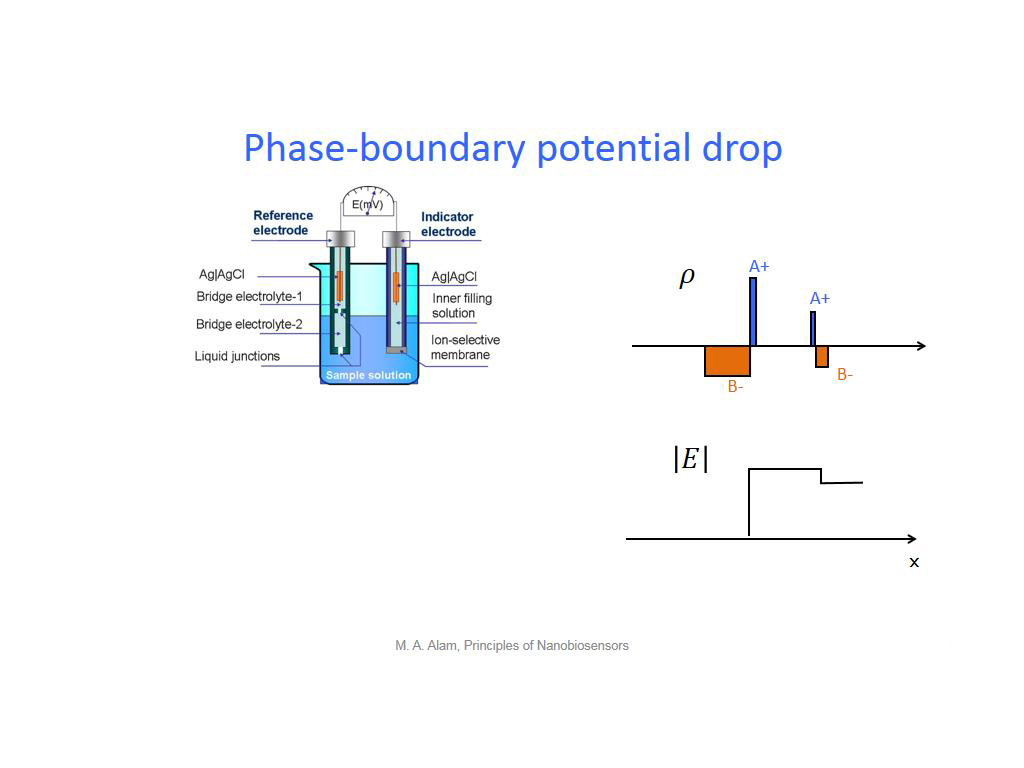
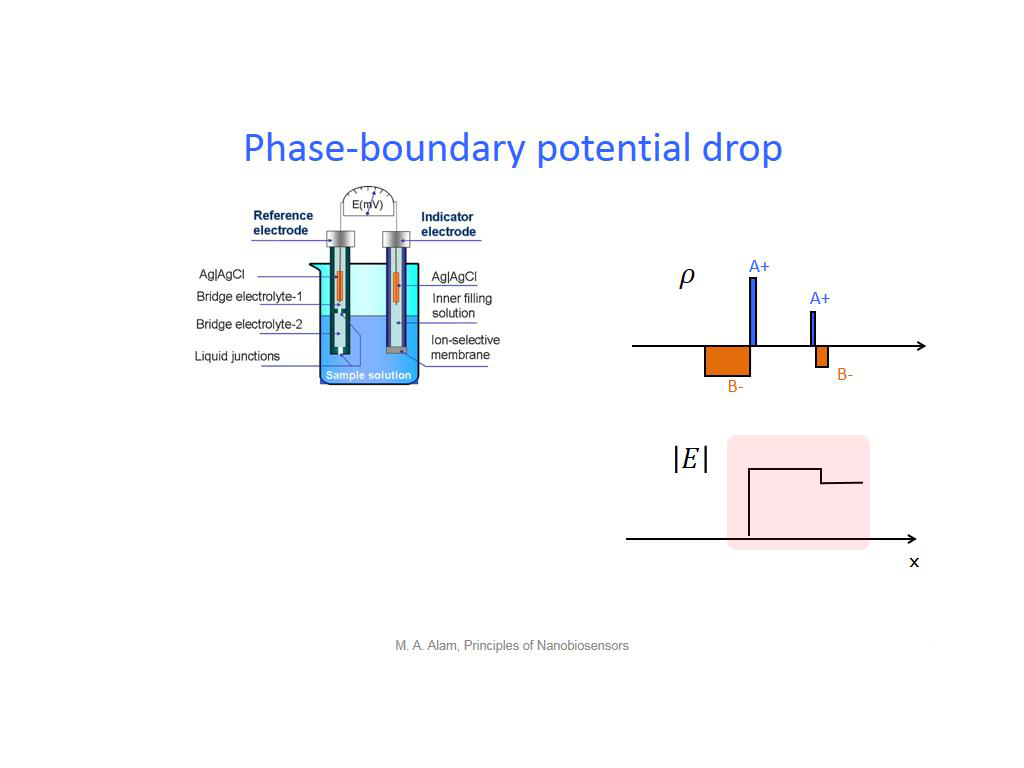
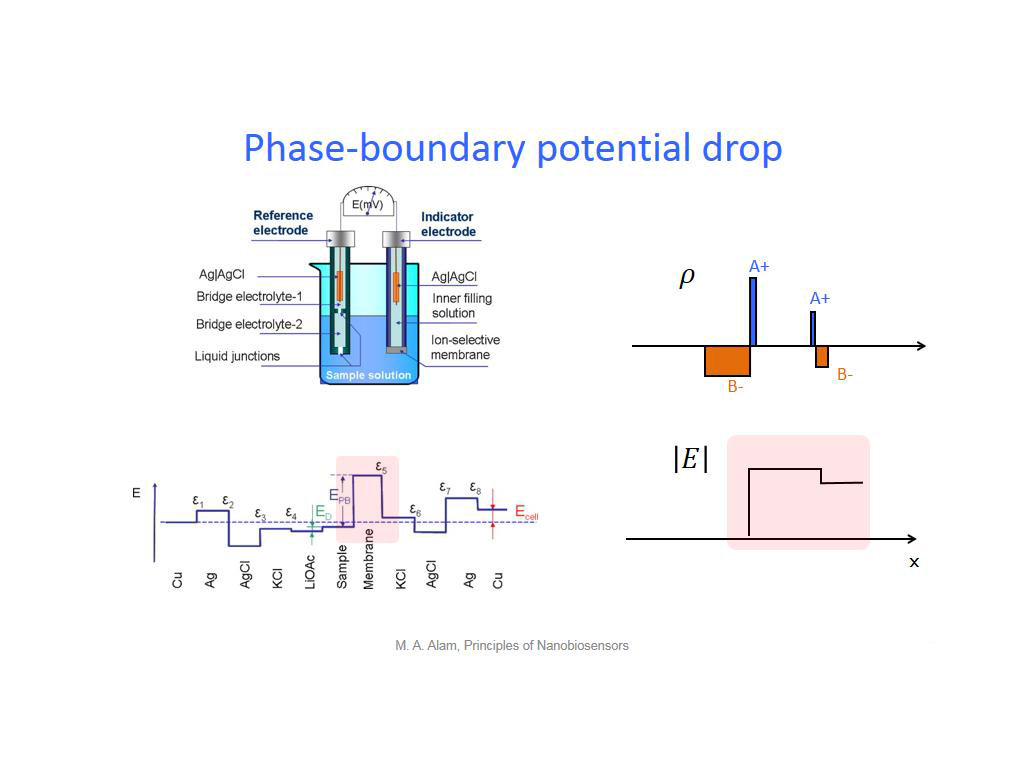
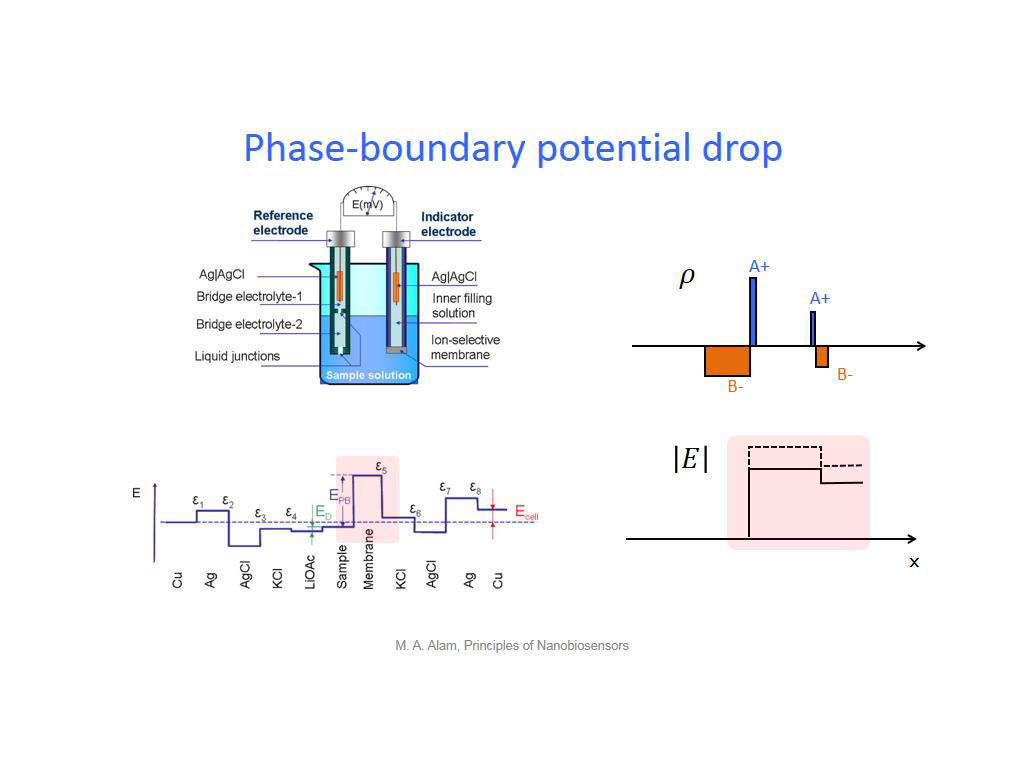 15. Phase-boundary potential drop
1257.6576576576576
00:00/00:00
15. Phase-boundary potential drop
1257.6576576576576
00:00/00:00 -
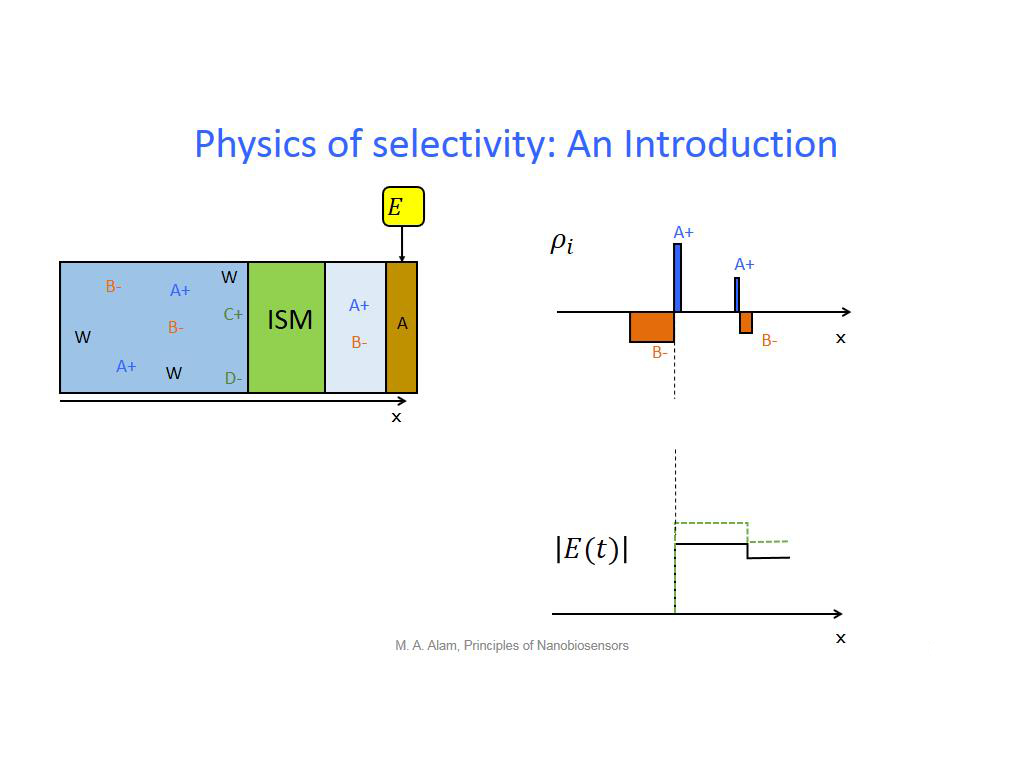
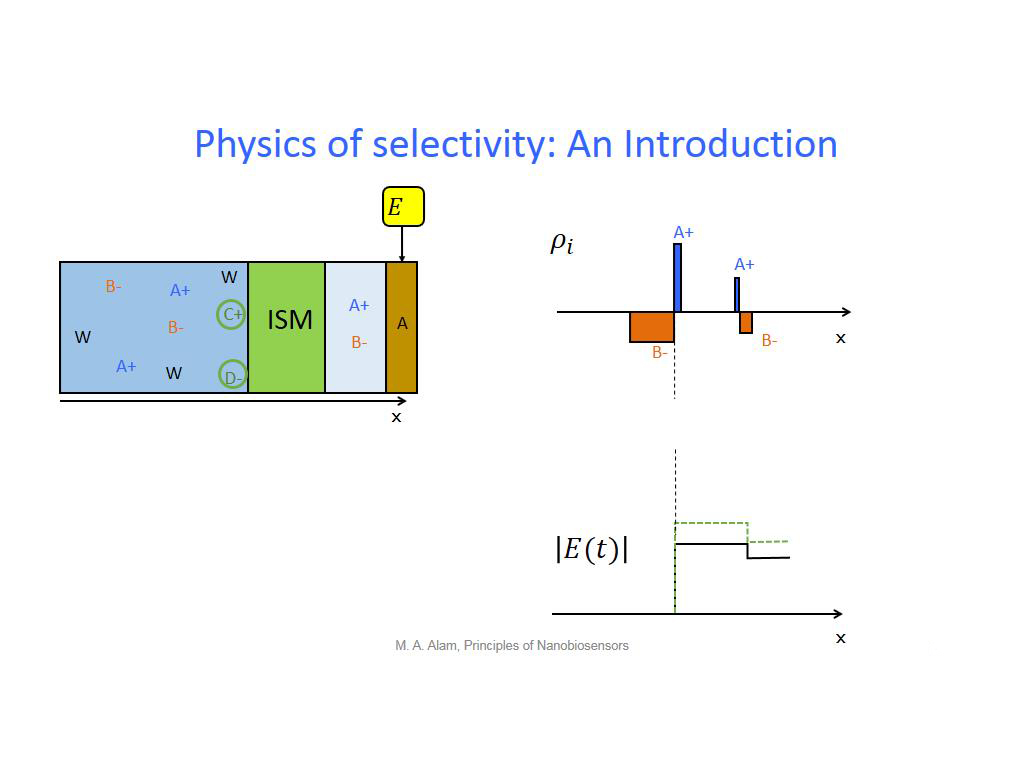
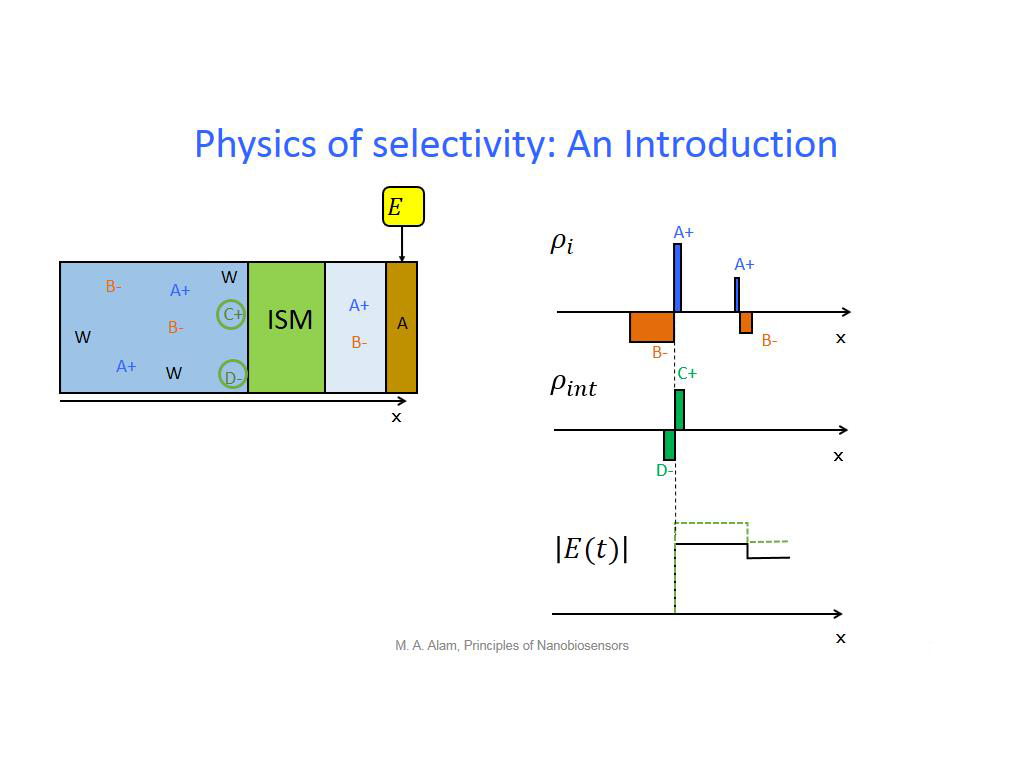
 16. Physics of selectivity: An Int…
1310.6773440106774
00:00/00:00
16. Physics of selectivity: An Int…
1310.6773440106774
00:00/00:00 -
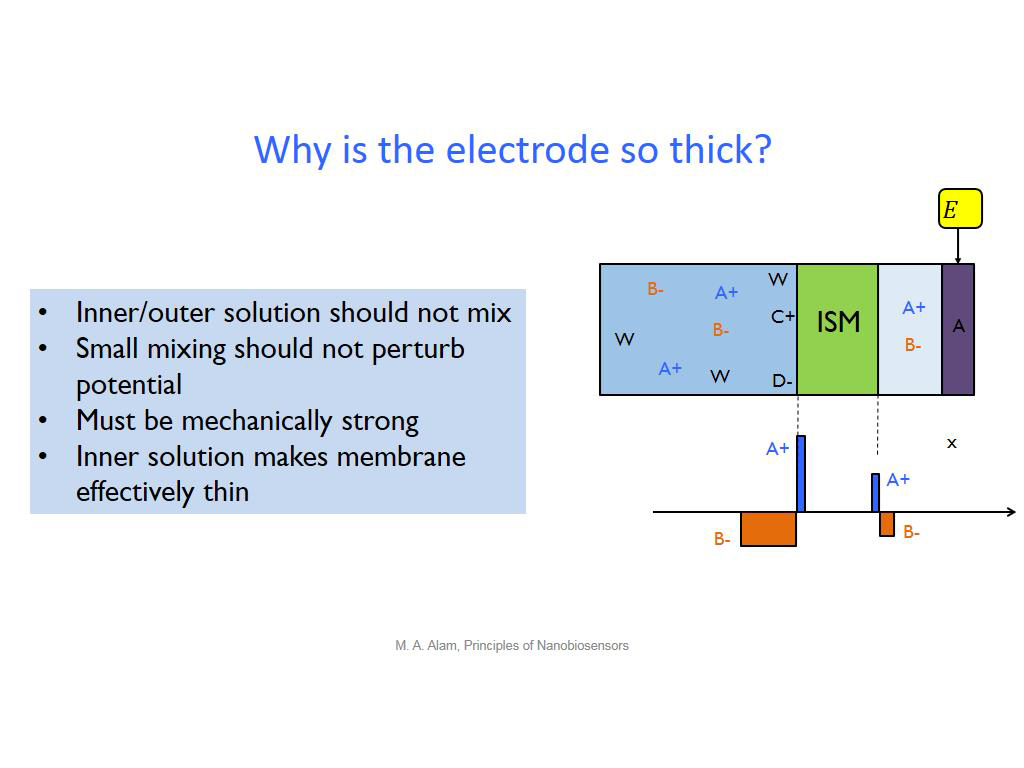
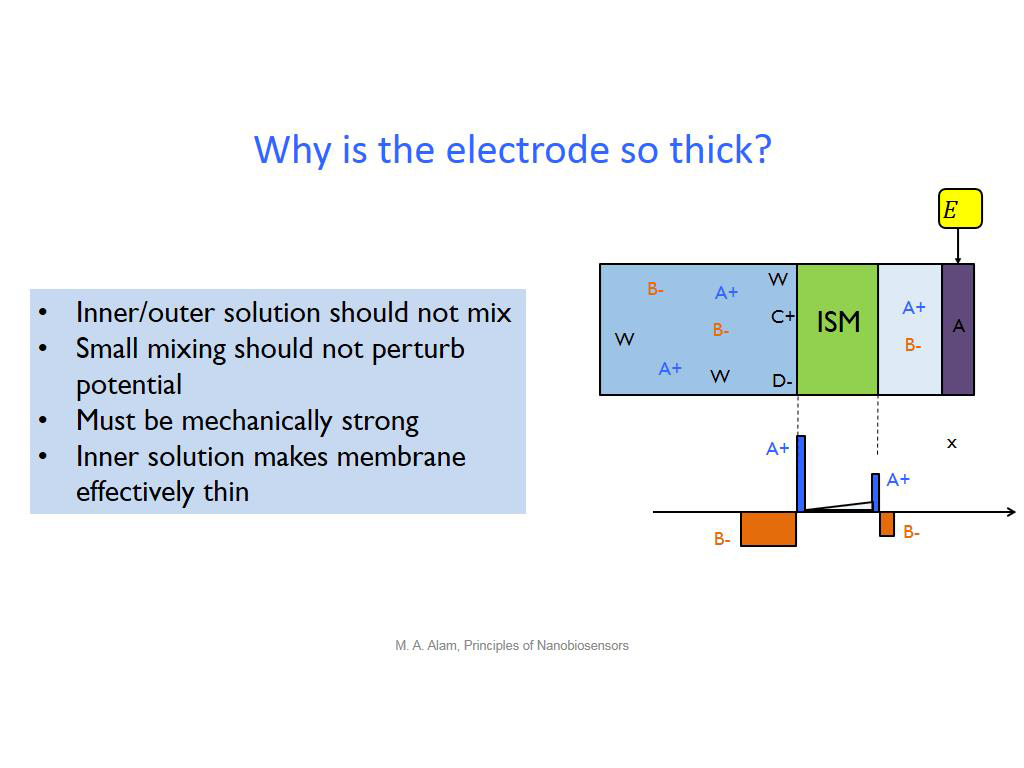
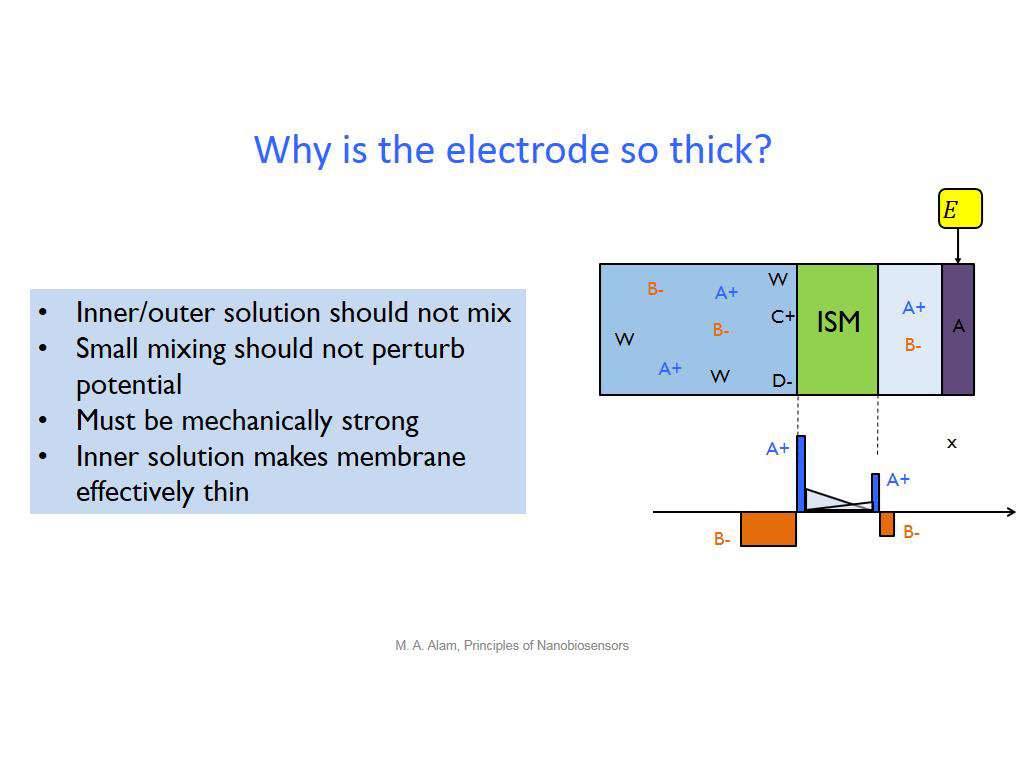 17. Why is the electrode so thick?
1379.7130463797132
00:00/00:00
17. Why is the electrode so thick?
1379.7130463797132
00:00/00:00 -
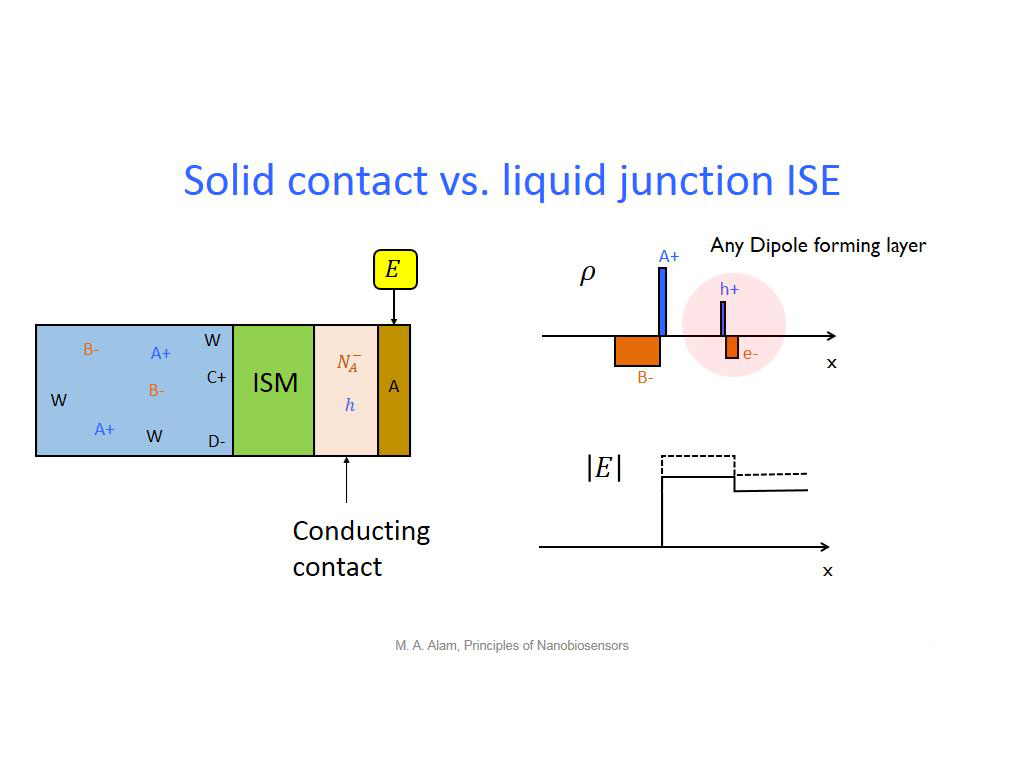 18. Solid contact vs. liquid junct…
1491.0243576910243
00:00/00:00
18. Solid contact vs. liquid junct…
1491.0243576910243
00:00/00:00 -
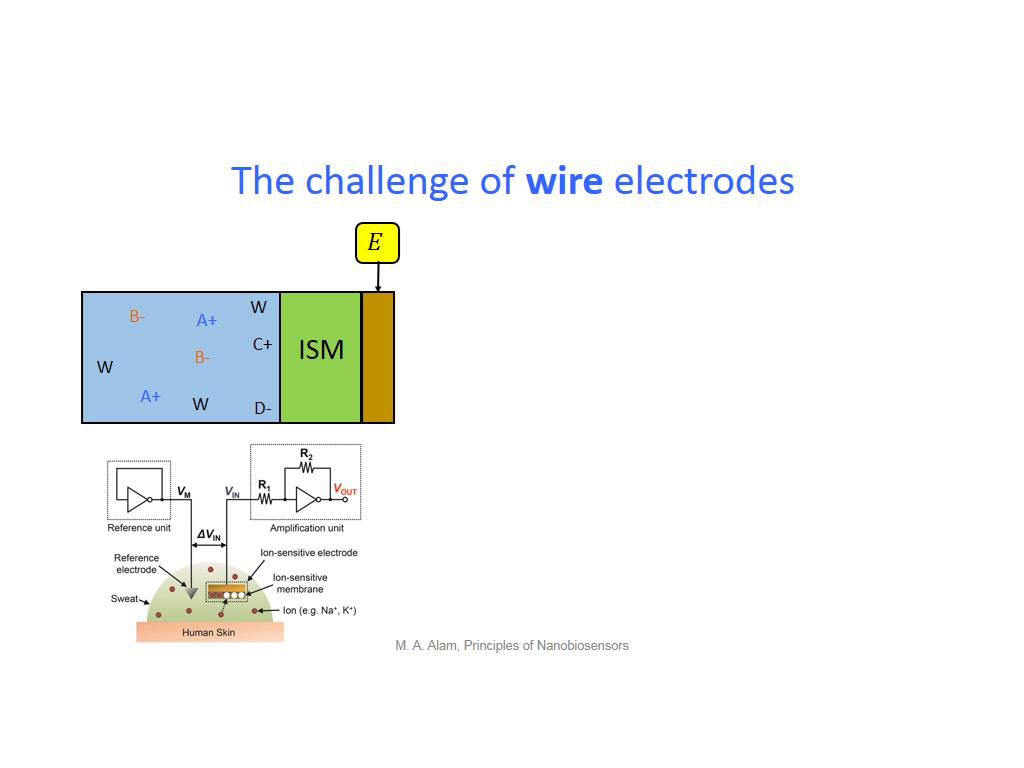
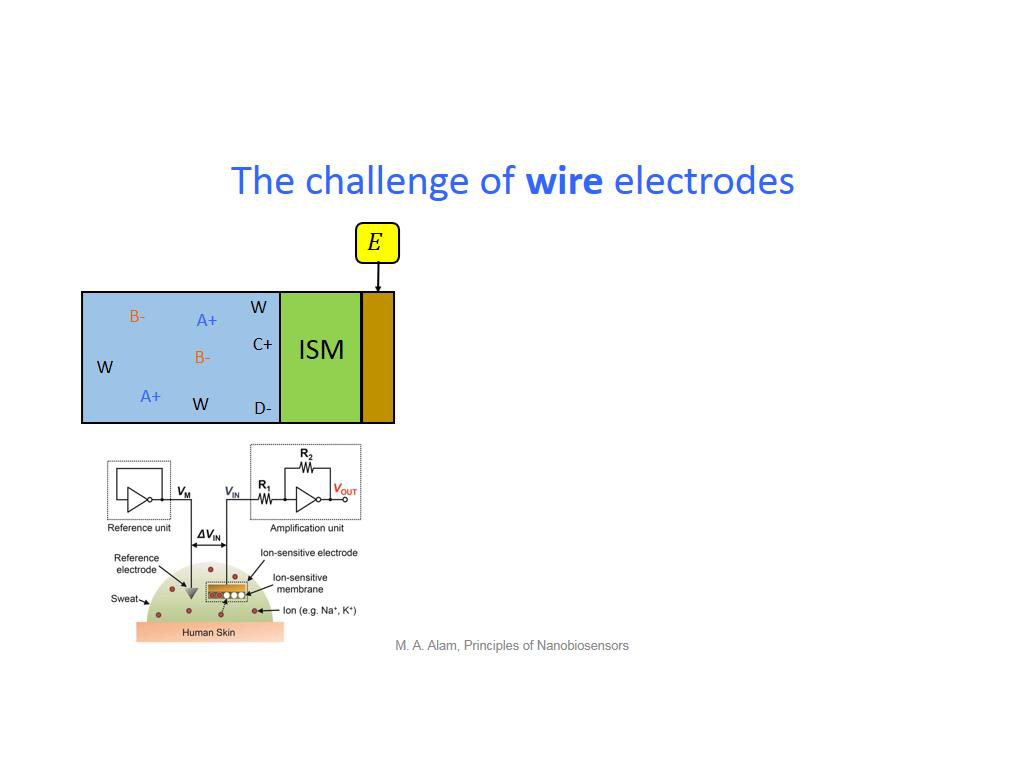
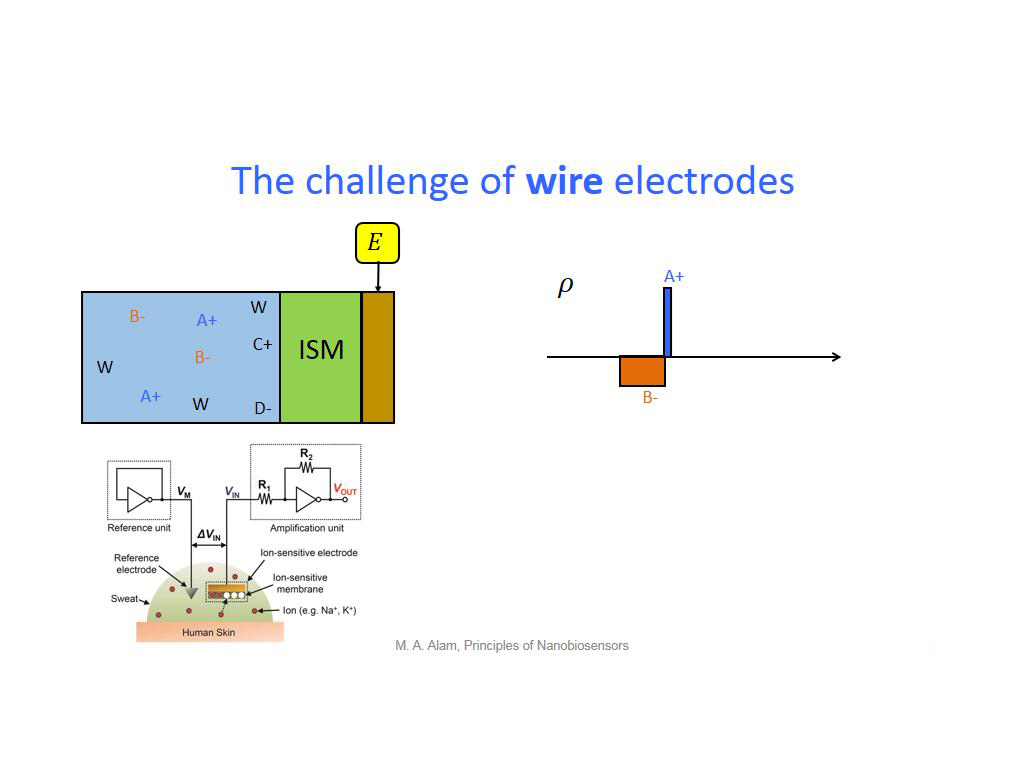
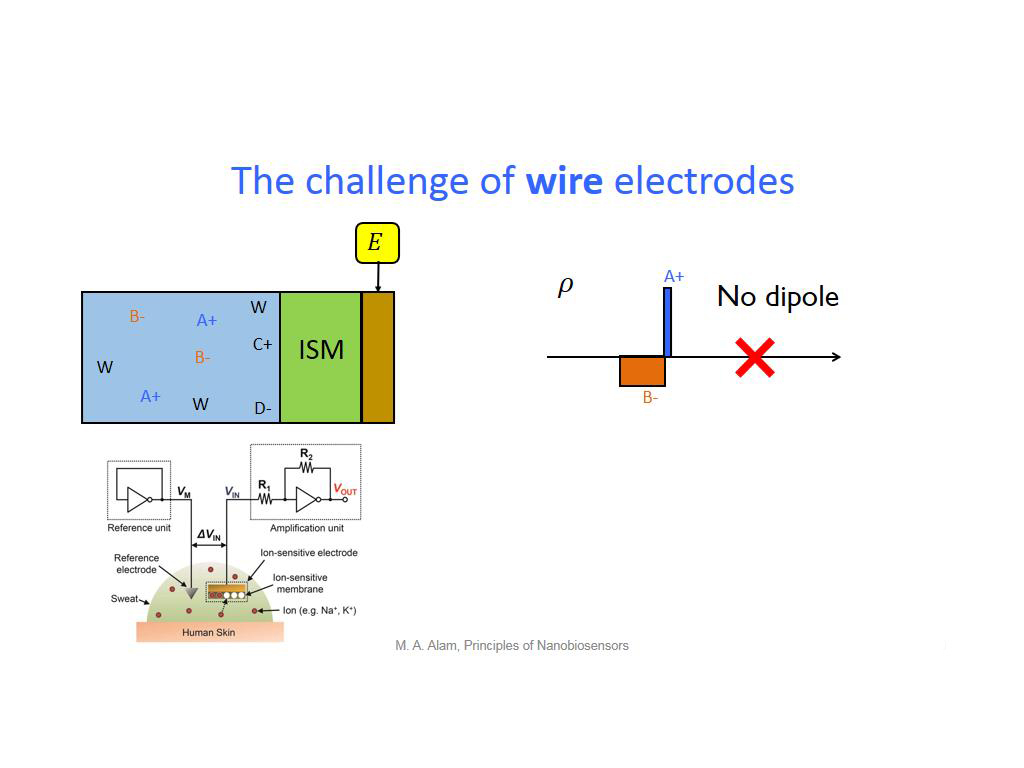
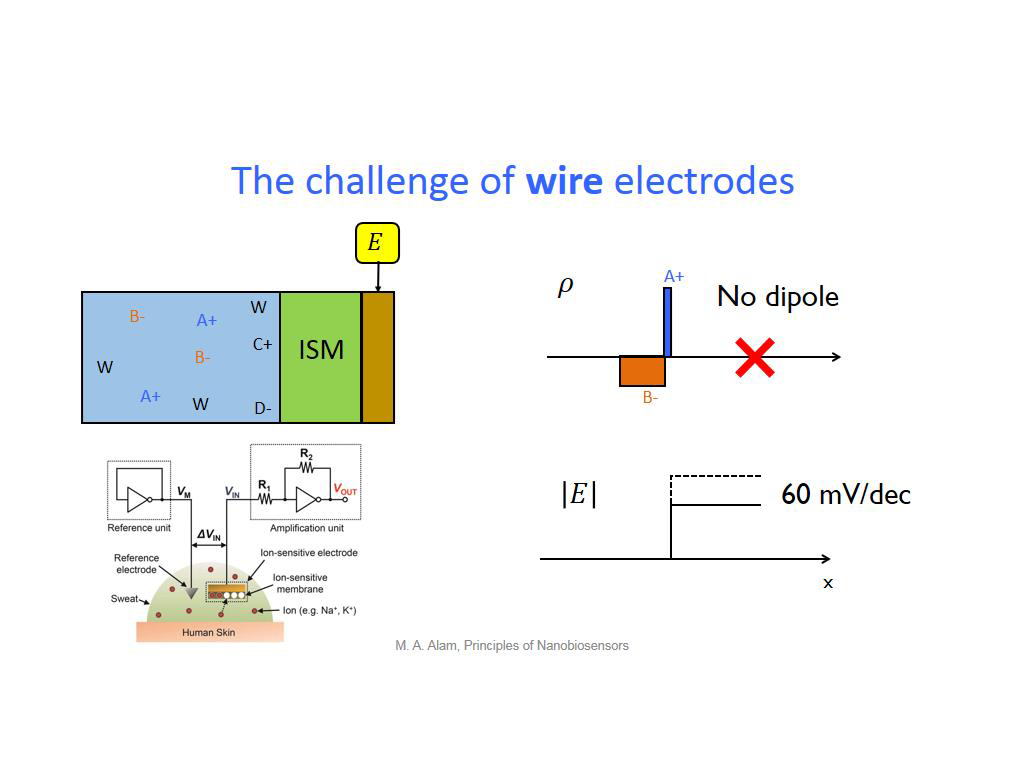 19. The challenge of wire electrod…
1544.8114781448116
00:00/00:00
19. The challenge of wire electrod…
1544.8114781448116
00:00/00:00 -
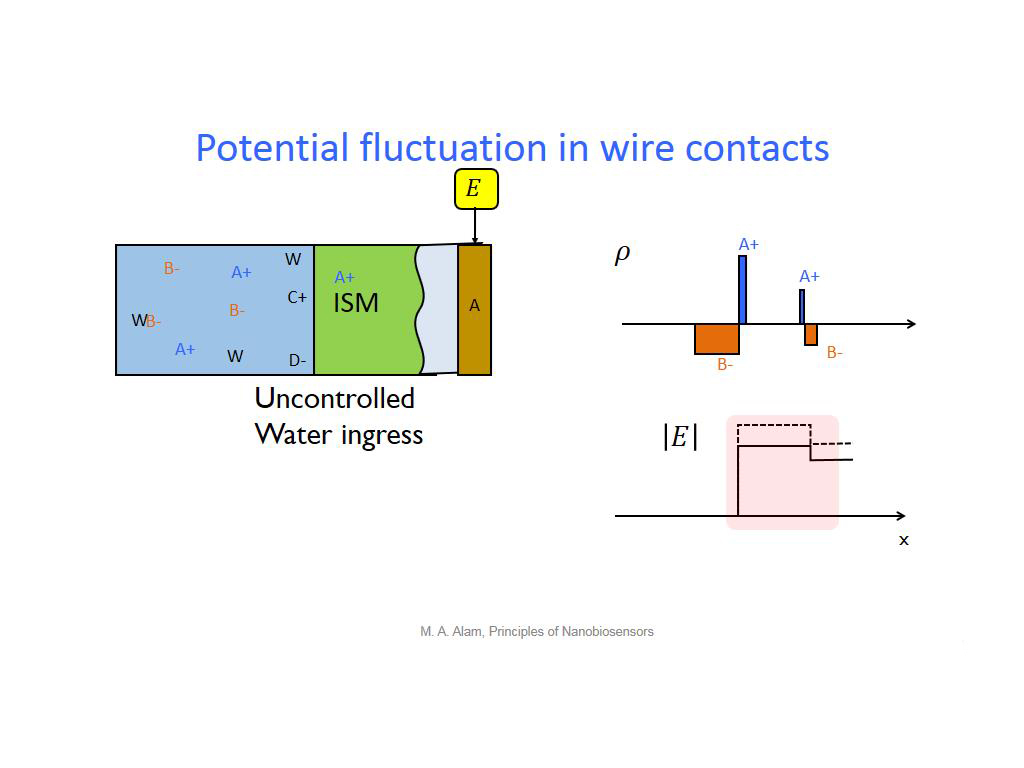
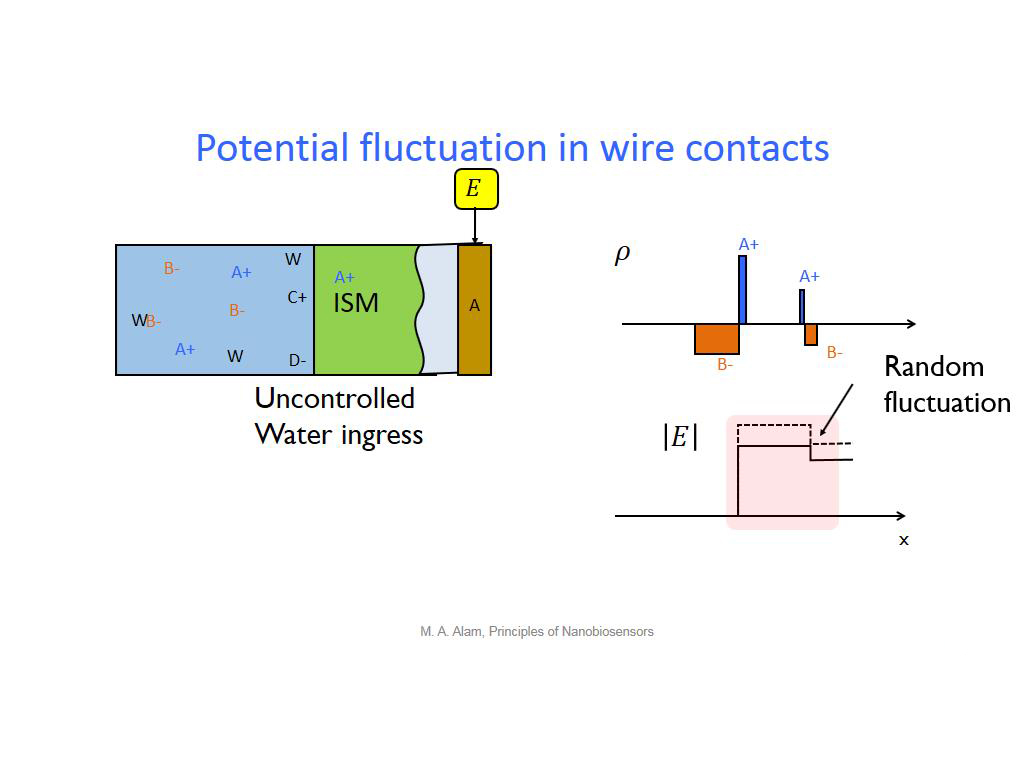
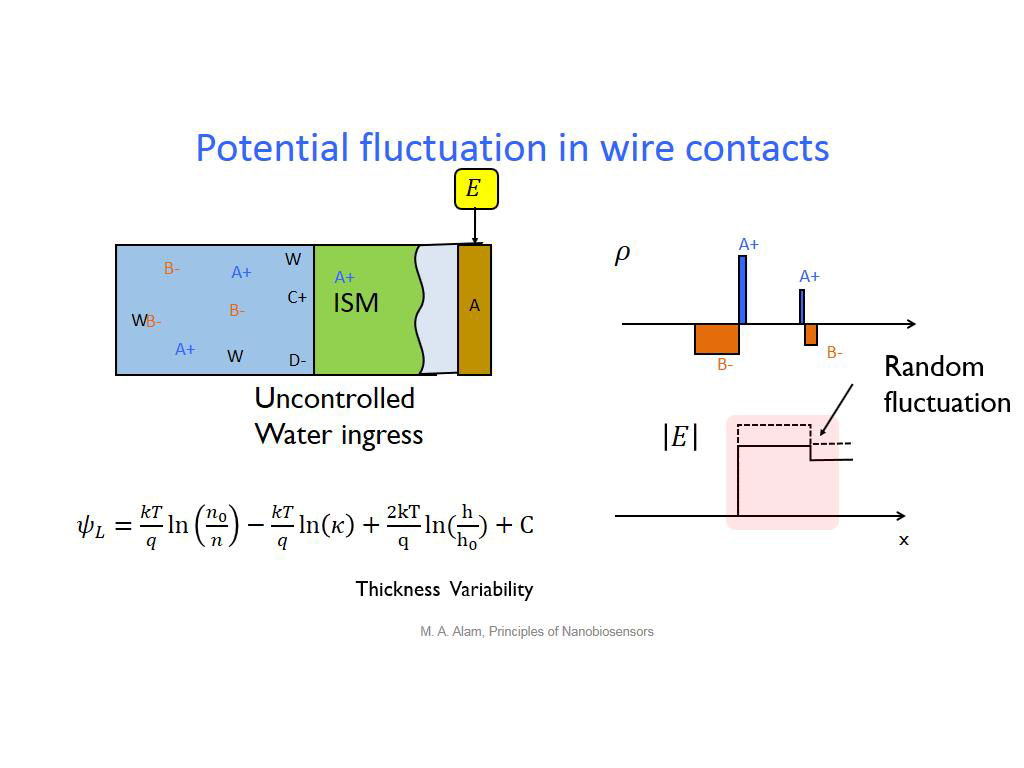 20. Potential fluctuation in wire …
1648.3149816483151
00:00/00:00
20. Potential fluctuation in wire …
1648.3149816483151
00:00/00:00 -
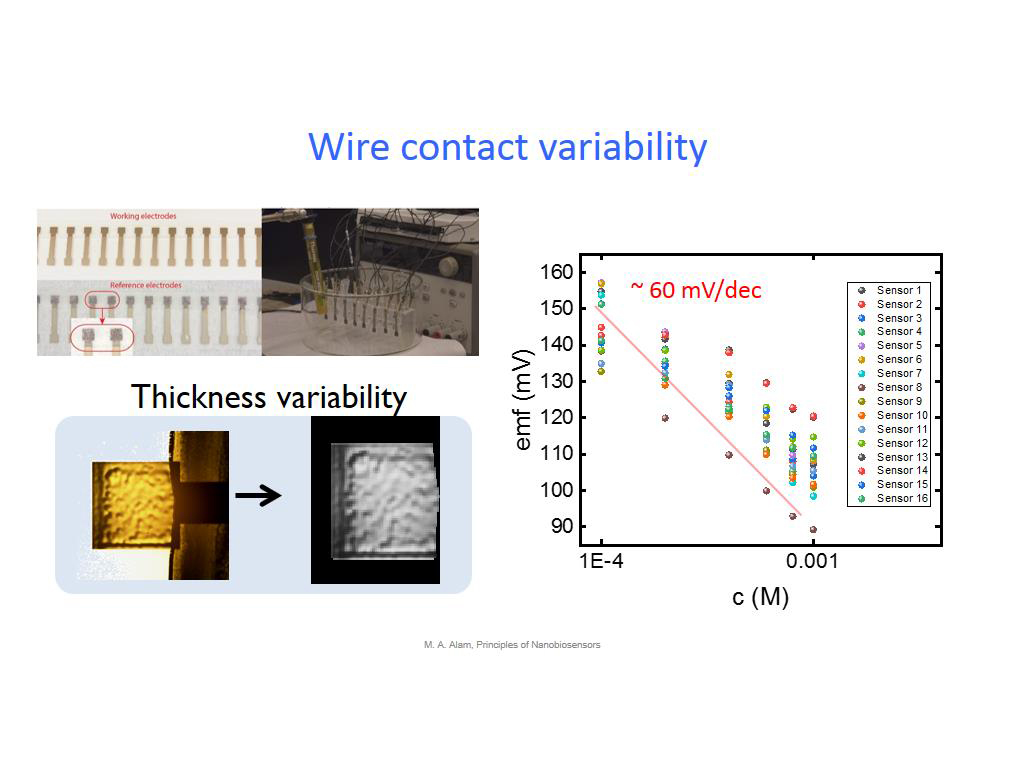 21. Wire contact variability
1734.1675008341676
00:00/00:00
21. Wire contact variability
1734.1675008341676
00:00/00:00 -
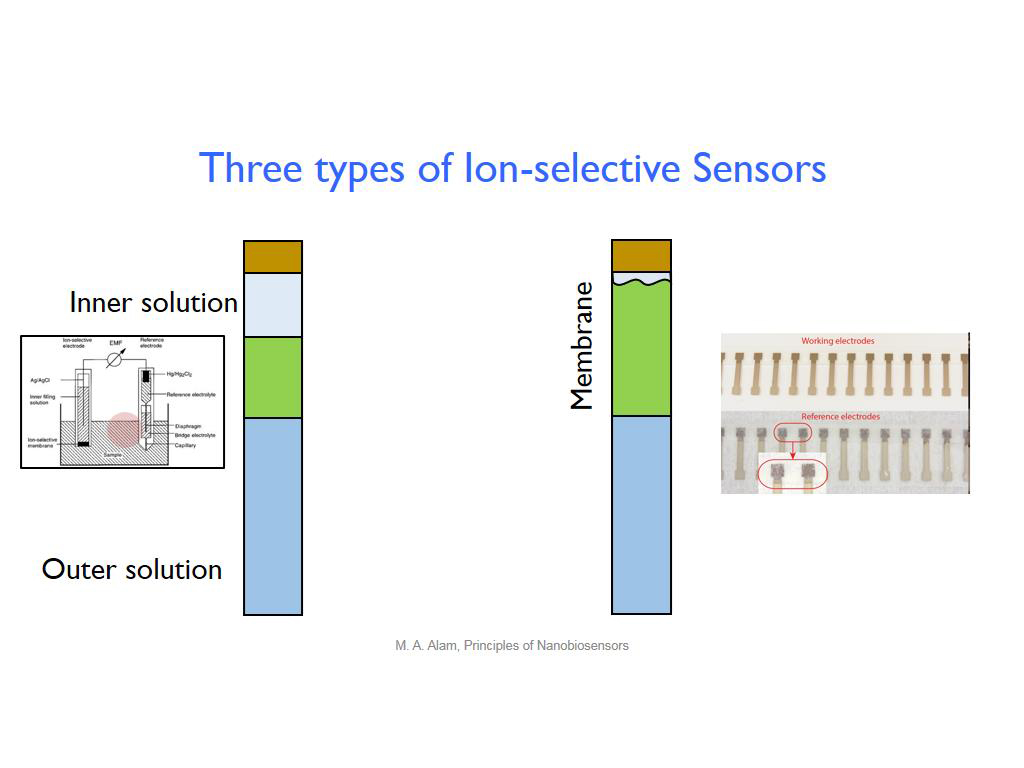
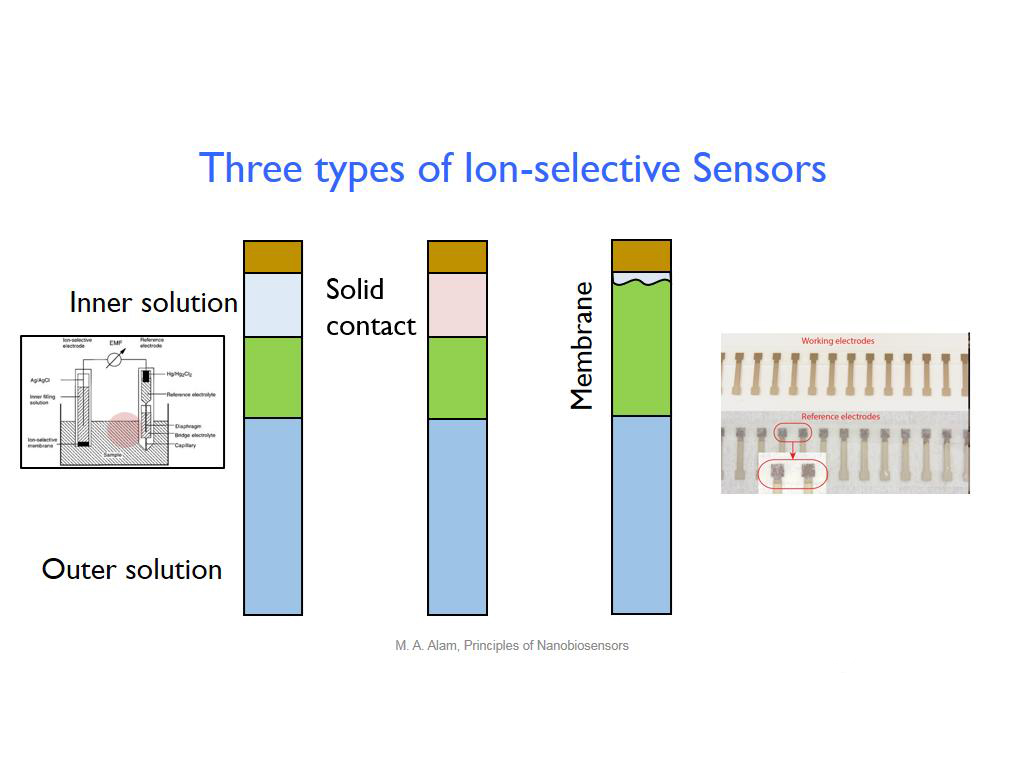 22. Three types of Ion-selective S…
1770.5705705705707
00:00/00:00
22. Three types of Ion-selective S…
1770.5705705705707
00:00/00:00 -
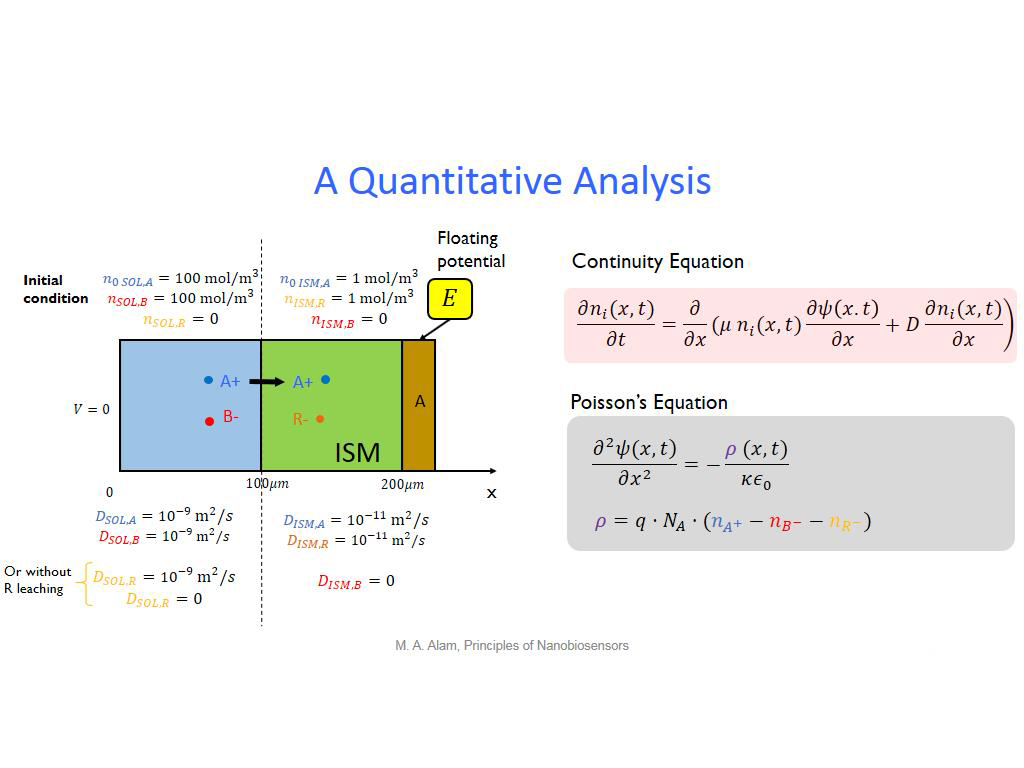 23. A Quantitative Analysis
1815.0483817150484
00:00/00:00
23. A Quantitative Analysis
1815.0483817150484
00:00/00:00 -
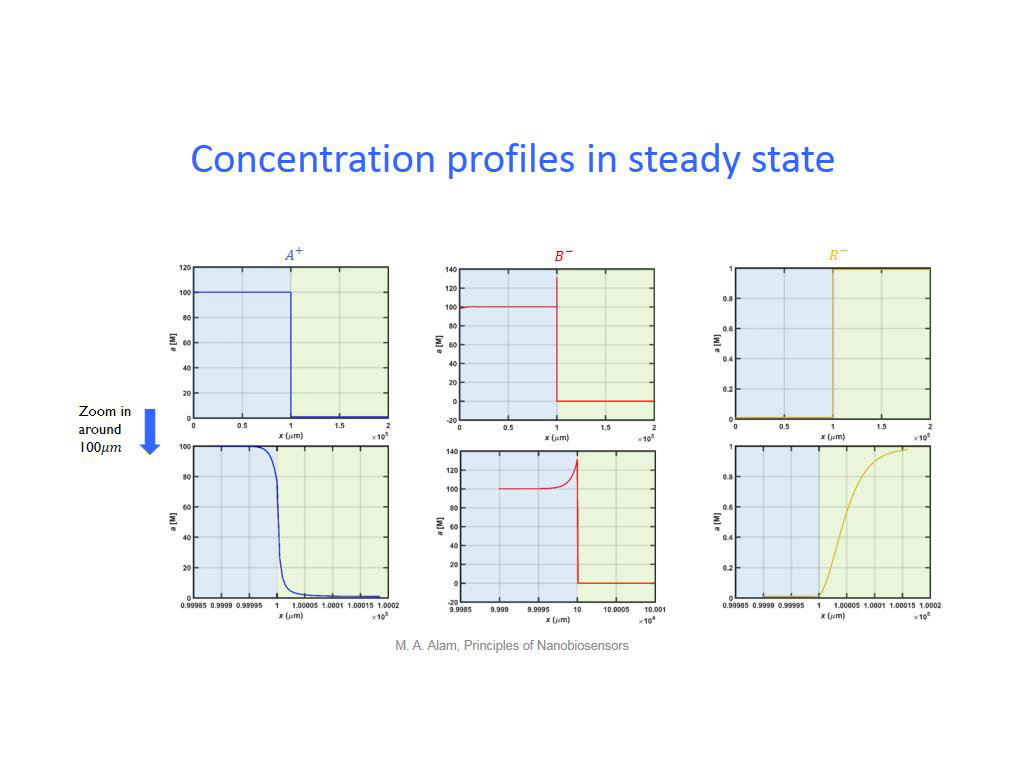 24. Concentration profiles in stea…
1848.3483483483485
00:00/00:00
24. Concentration profiles in stea…
1848.3483483483485
00:00/00:00 -
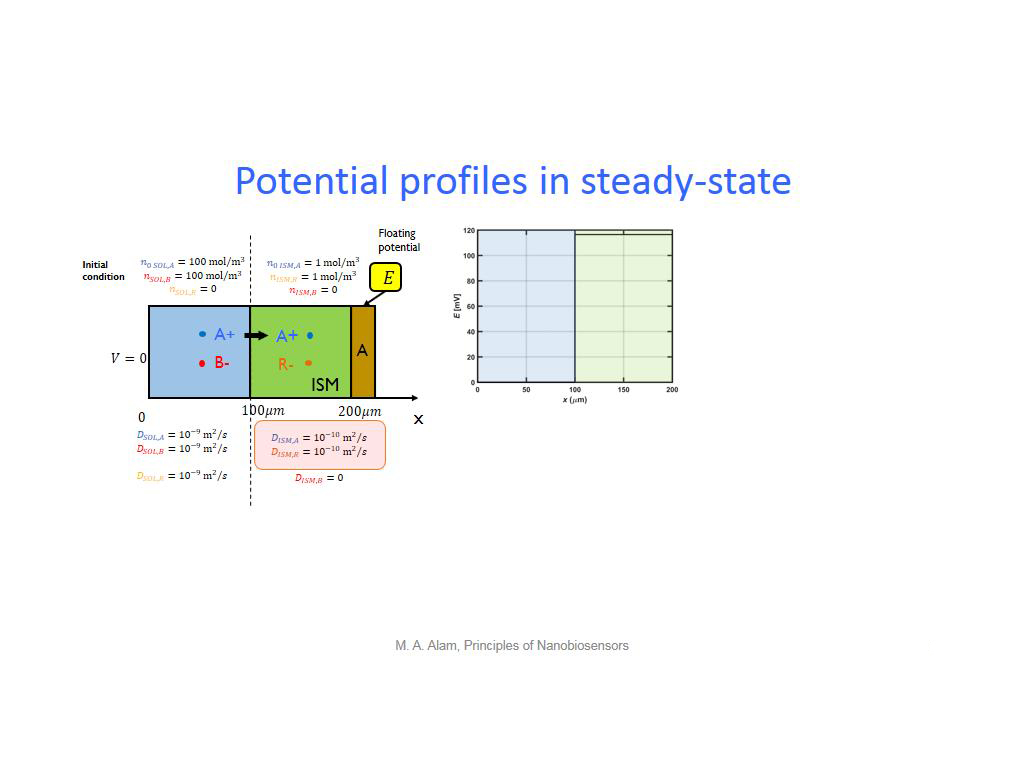
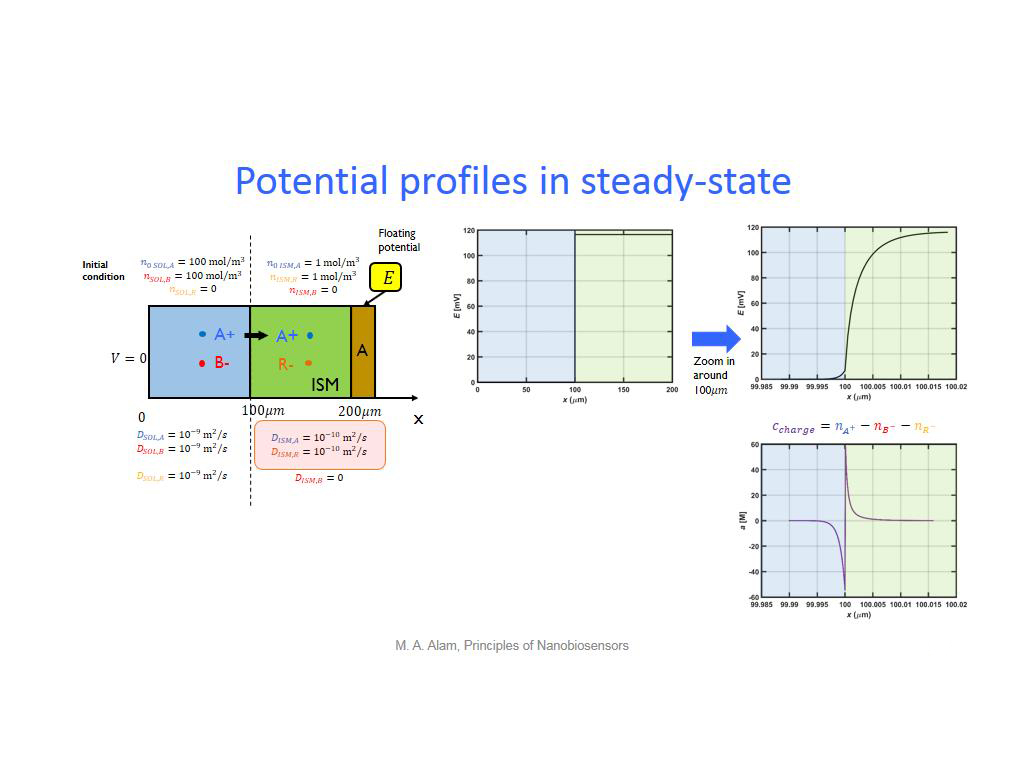 25. Potential profiles in steady-s…
1866.4998331665
00:00/00:00
25. Potential profiles in steady-s…
1866.4998331665
00:00/00:00 -
 26. Outline
1885.785785785786
00:00/00:00
26. Outline
1885.785785785786
00:00/00:00 -
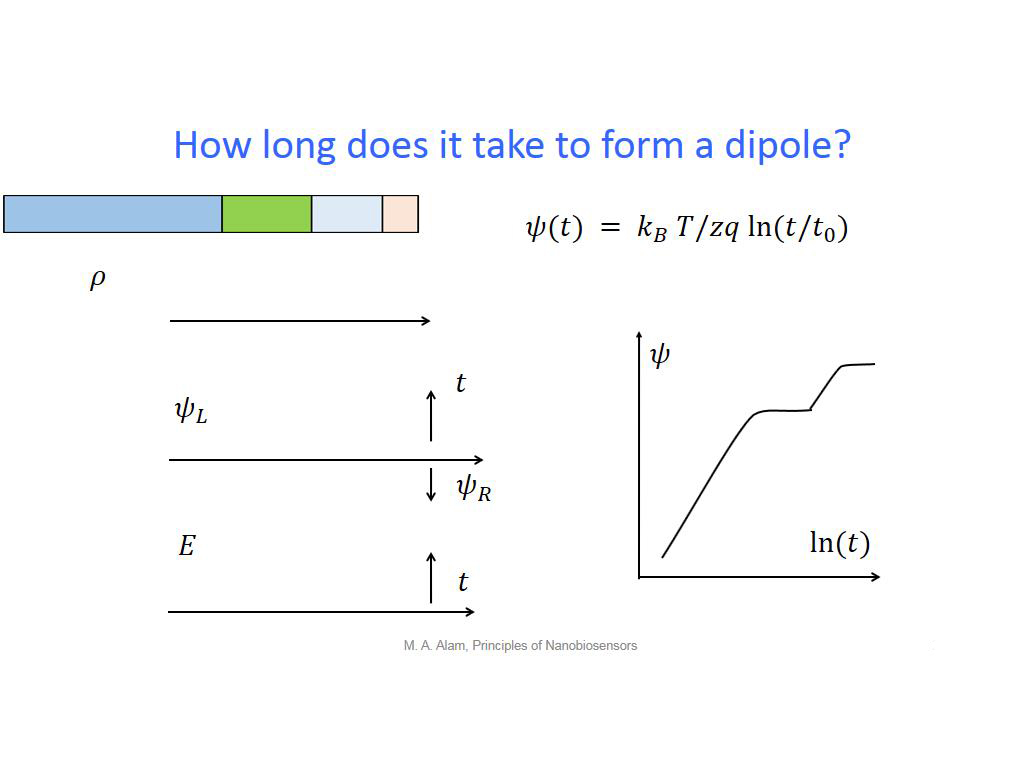
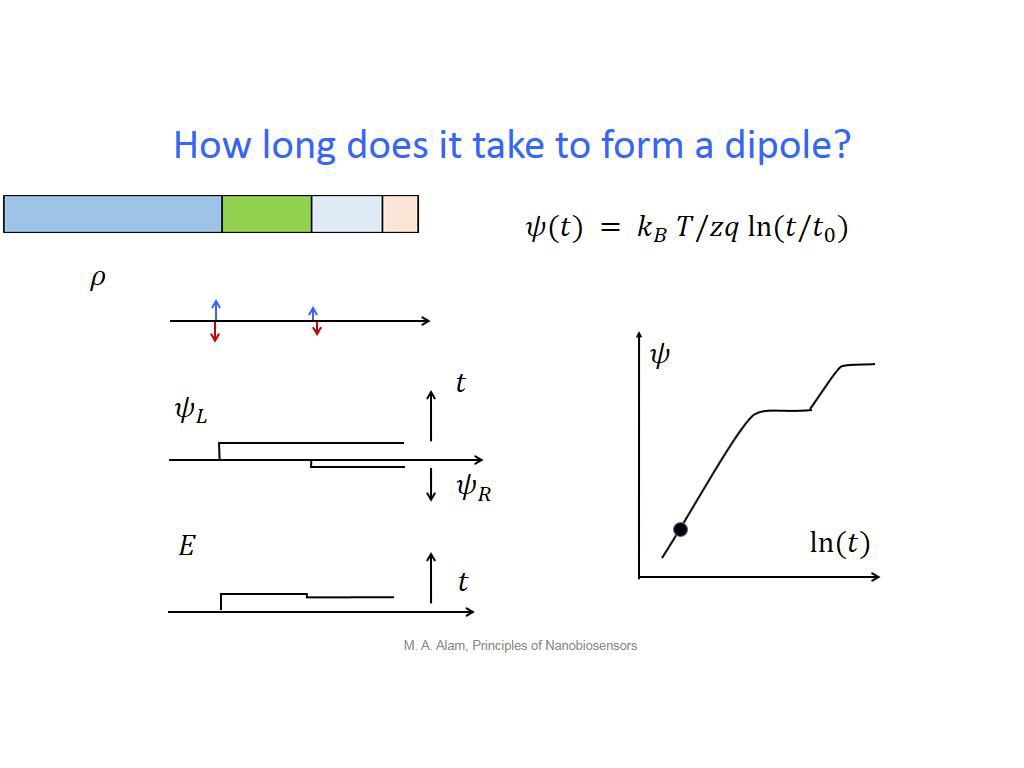
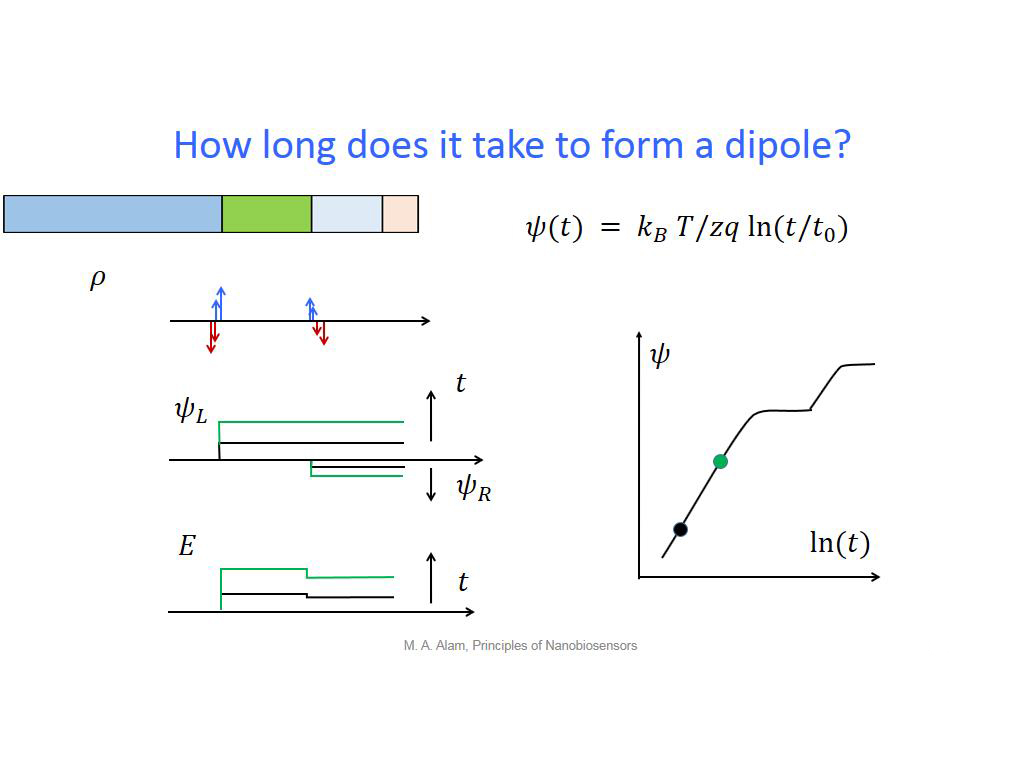
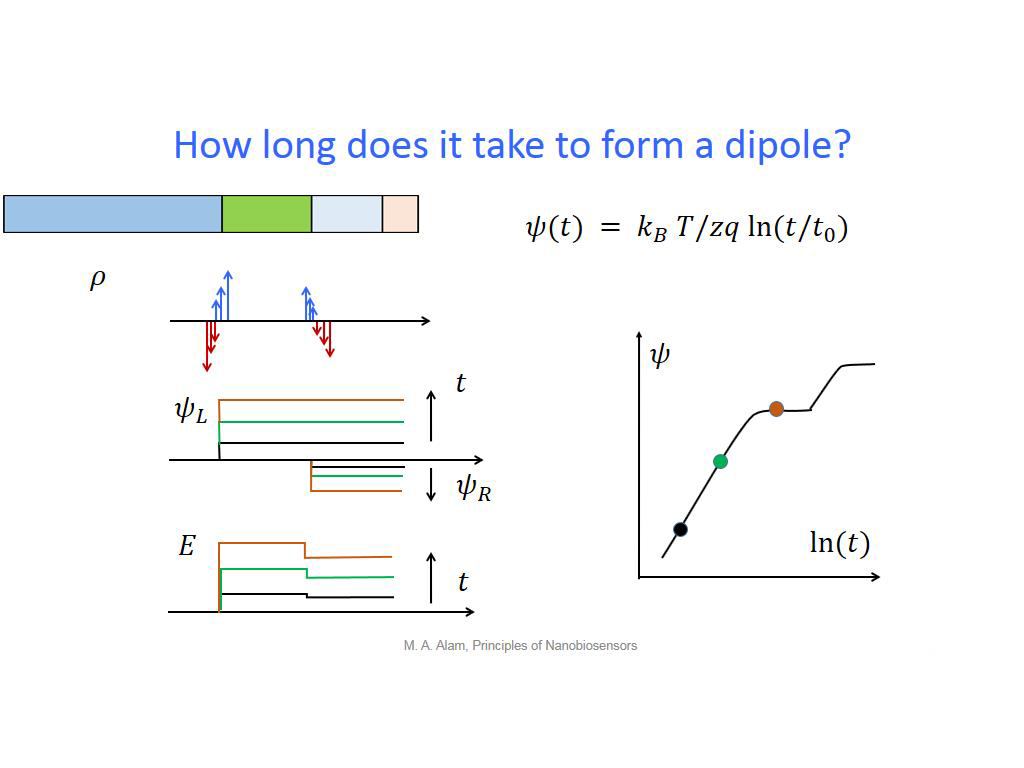 27. How long does it take to form …
1938.2382382382384
00:00/00:00
27. How long does it take to form …
1938.2382382382384
00:00/00:00 -
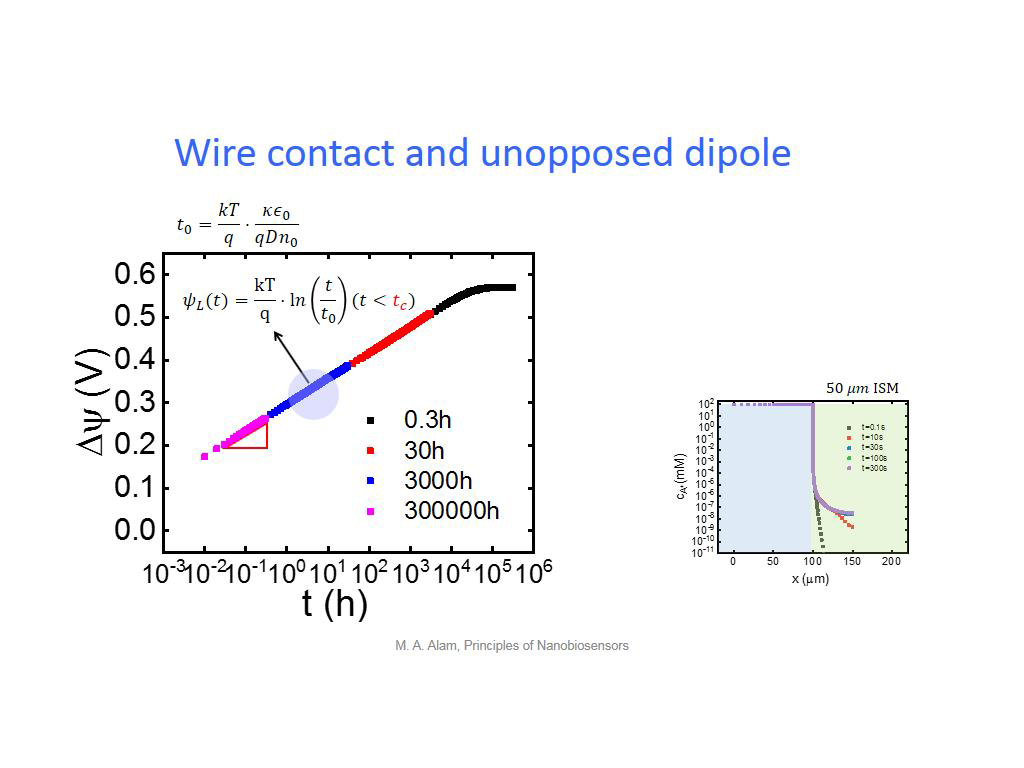
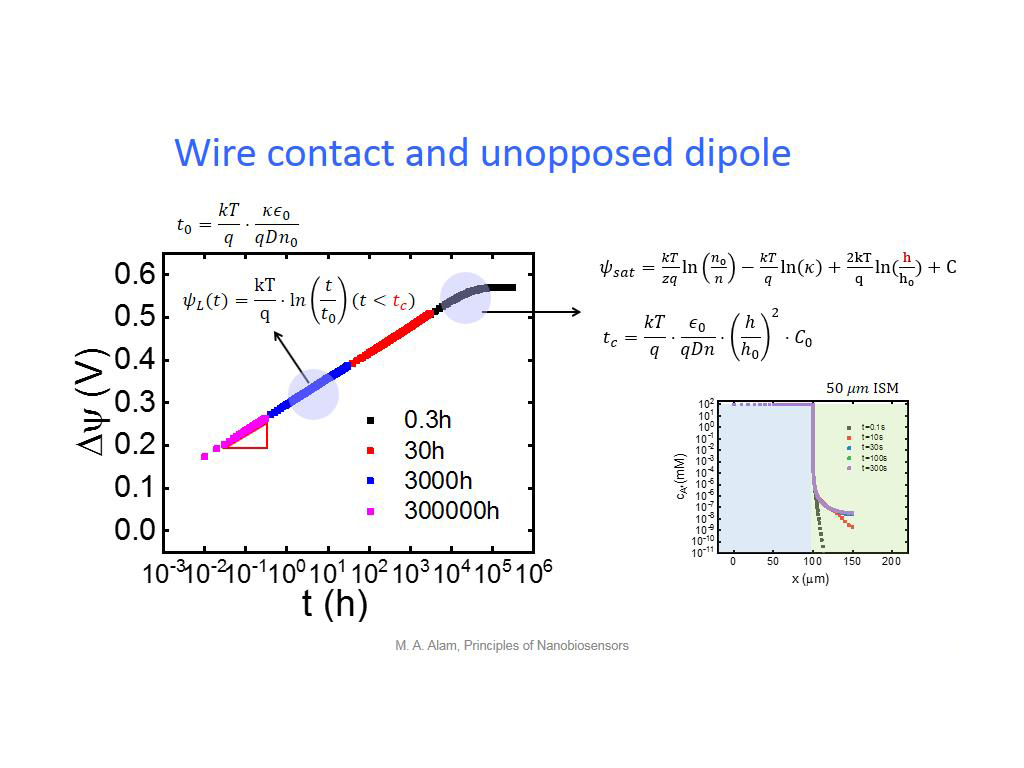
 28. Wire contact and unopposed dip…
2047.2472472472473
00:00/00:00
28. Wire contact and unopposed dip…
2047.2472472472473
00:00/00:00 -
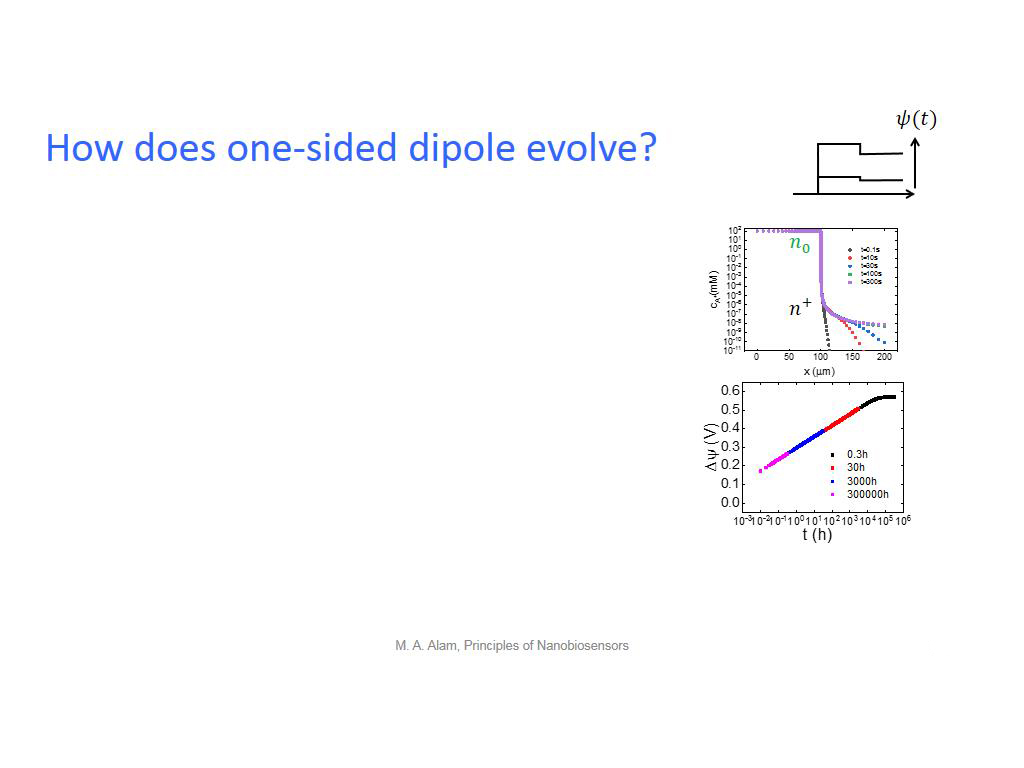
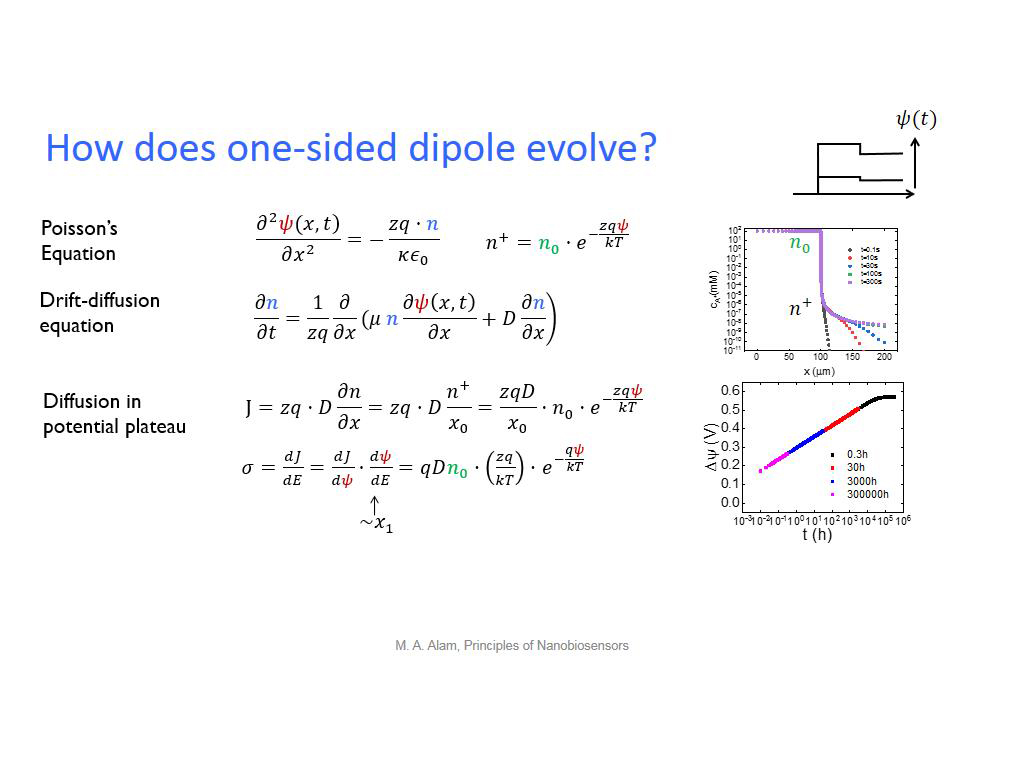
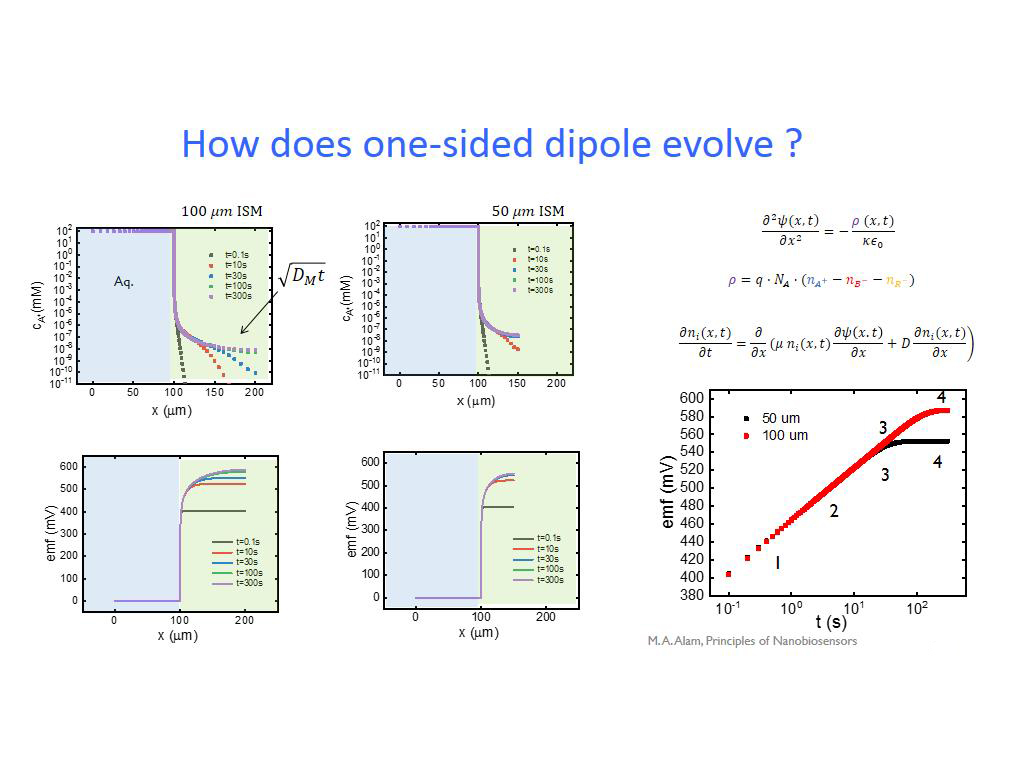
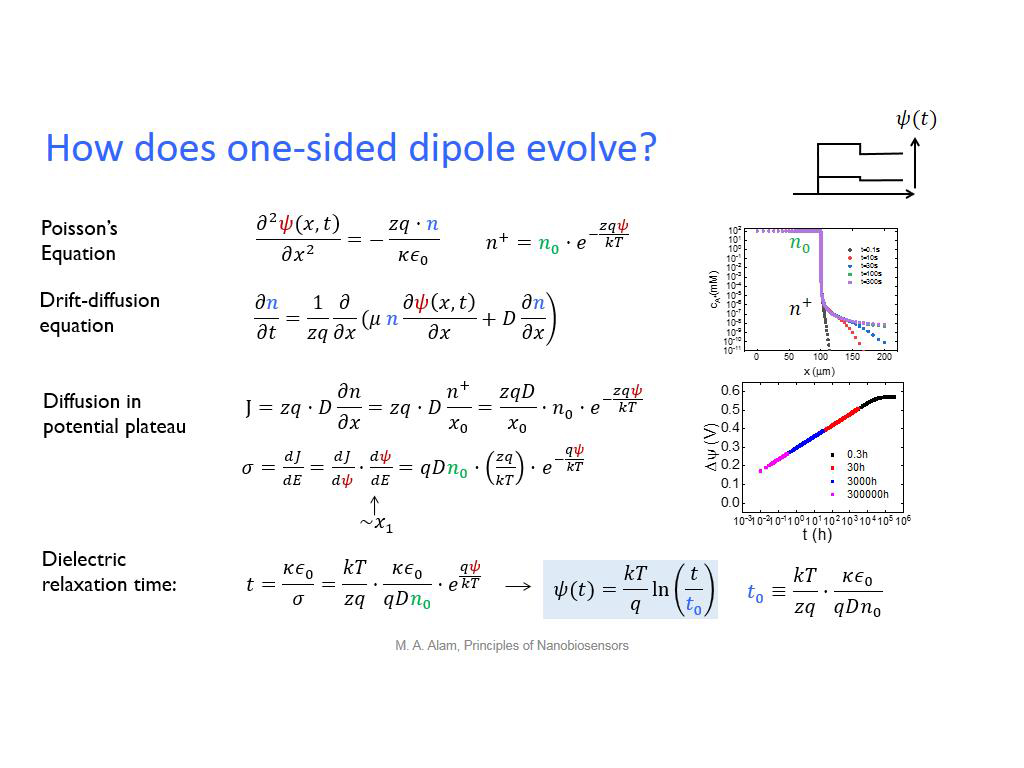 29. How does one-sided dipole evol…
2148.9823156489824
00:00/00:00
29. How does one-sided dipole evol…
2148.9823156489824
00:00/00:00 -
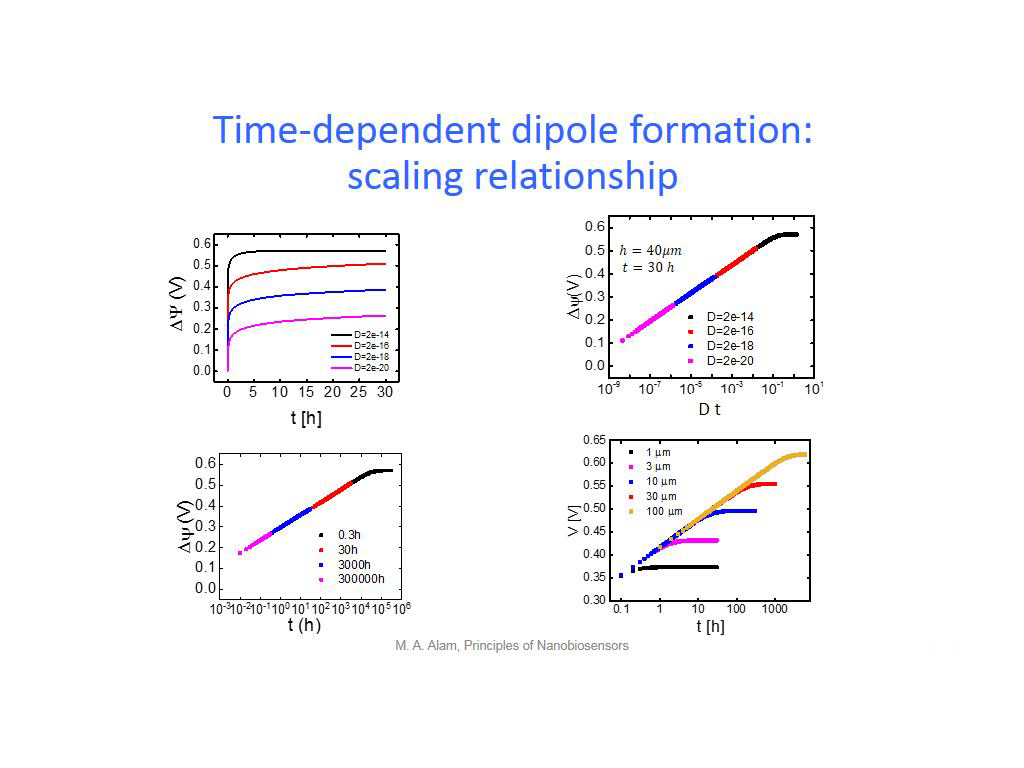
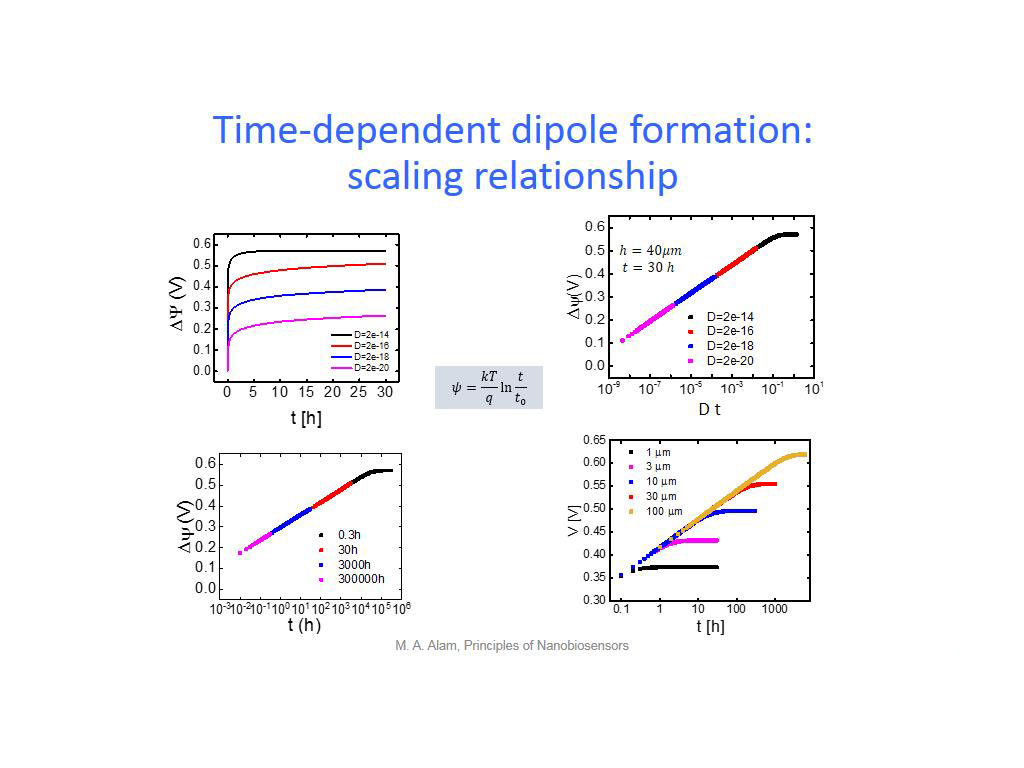
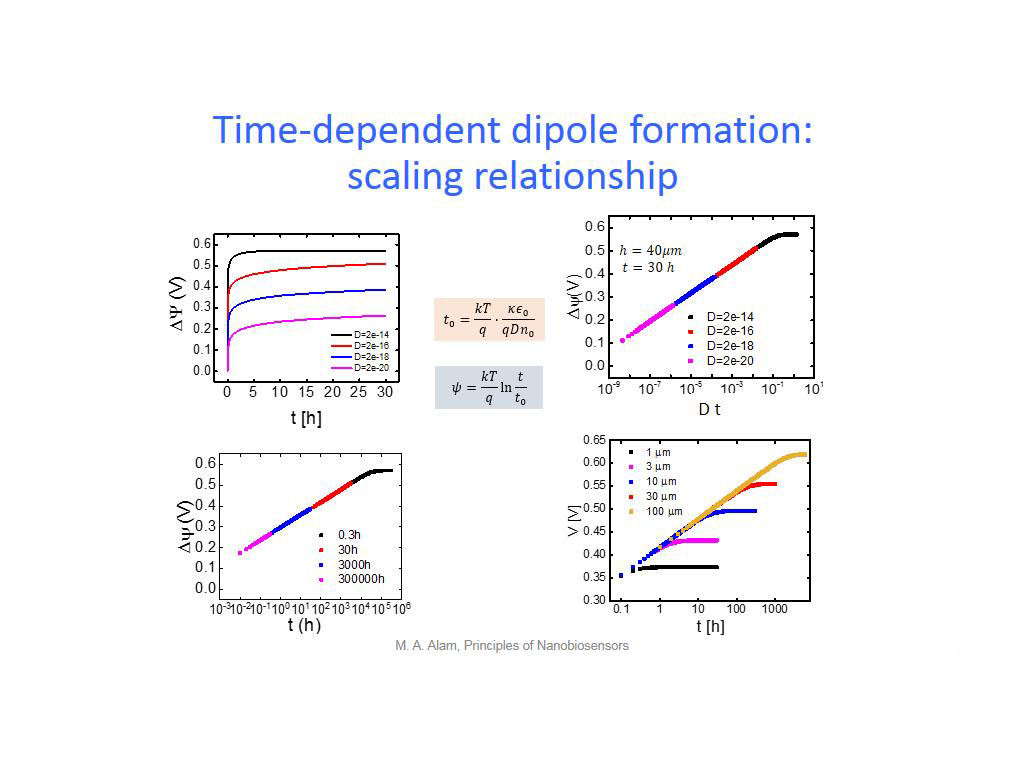
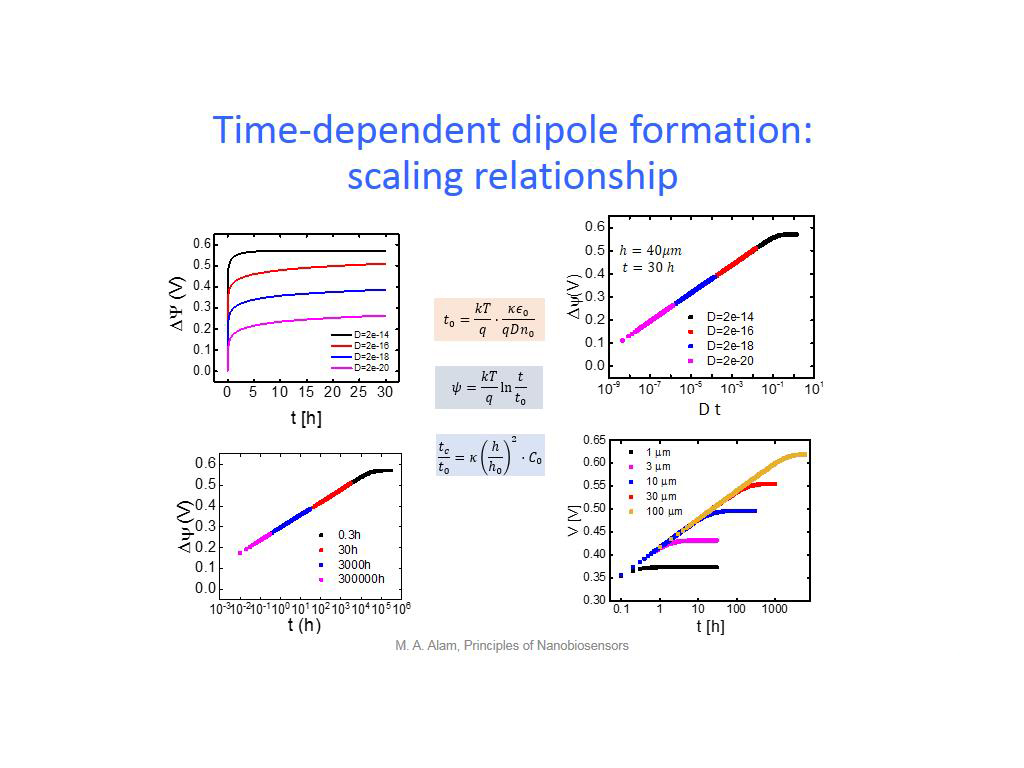 30. Time-dependent dipole formatio…
2276.7434100767437
00:00/00:00
30. Time-dependent dipole formatio…
2276.7434100767437
00:00/00:00 -
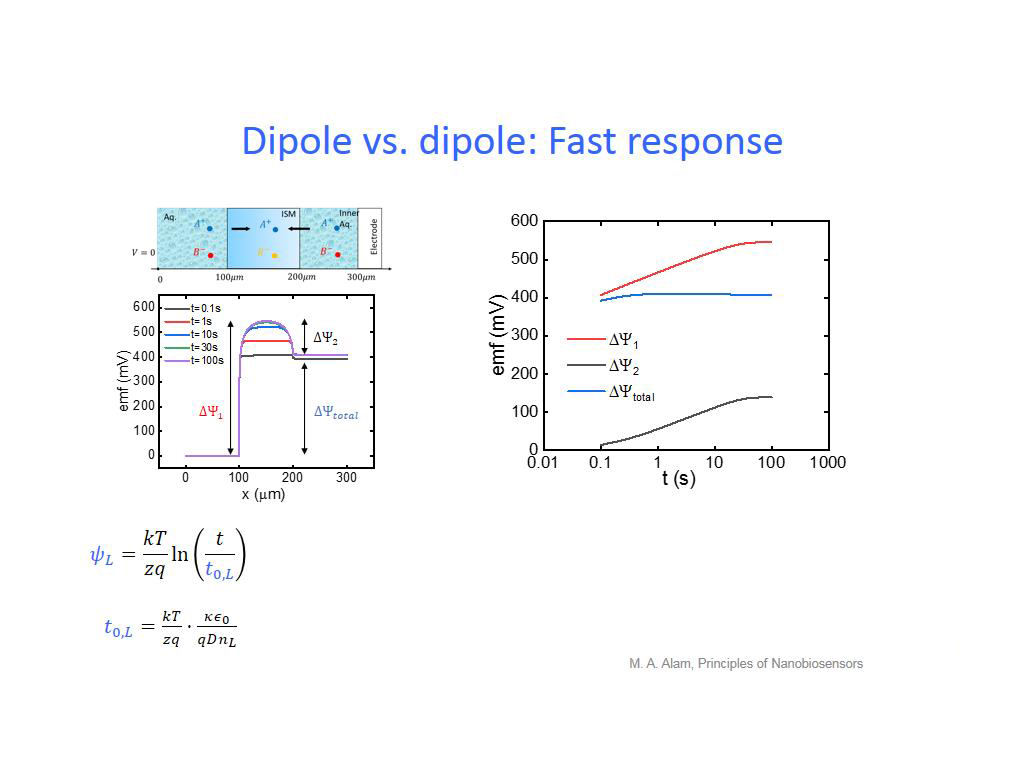
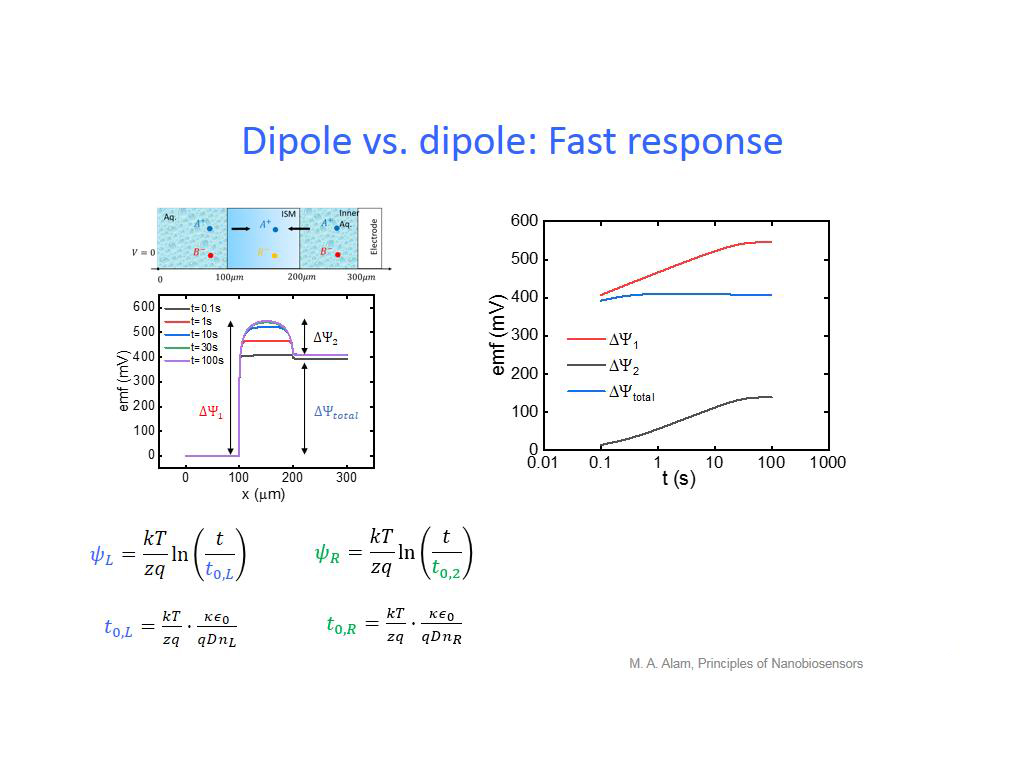
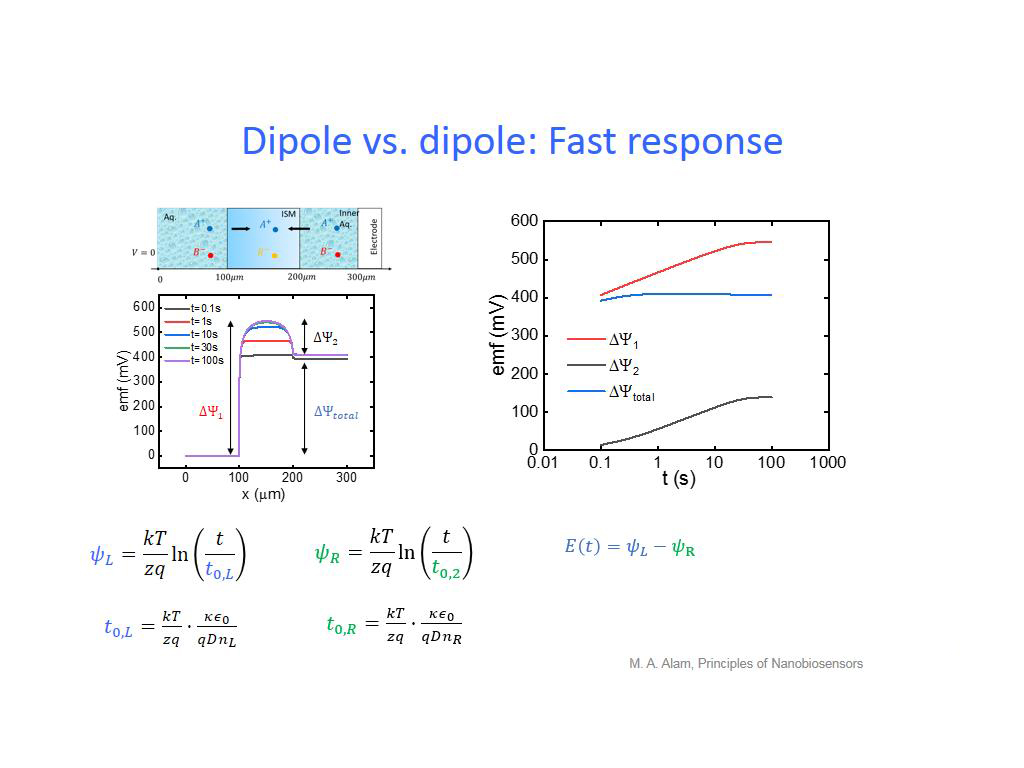
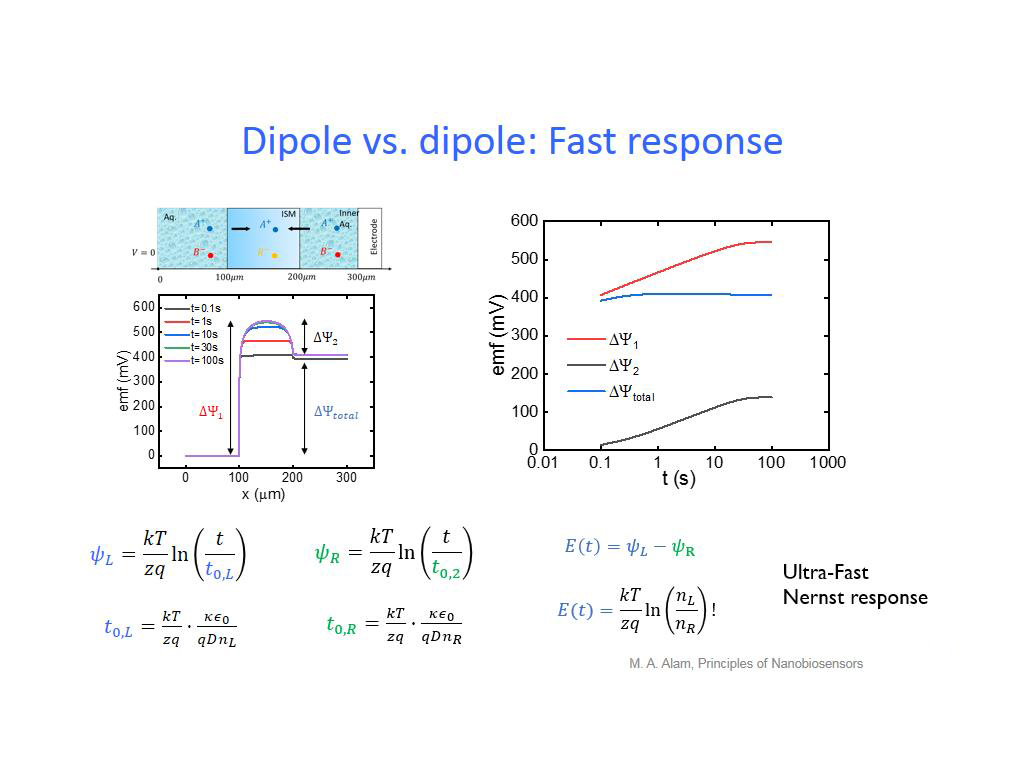 31. Dipole vs. dipole: Fast respon…
2337.5041708375043
00:00/00:00
31. Dipole vs. dipole: Fast respon…
2337.5041708375043
00:00/00:00 -
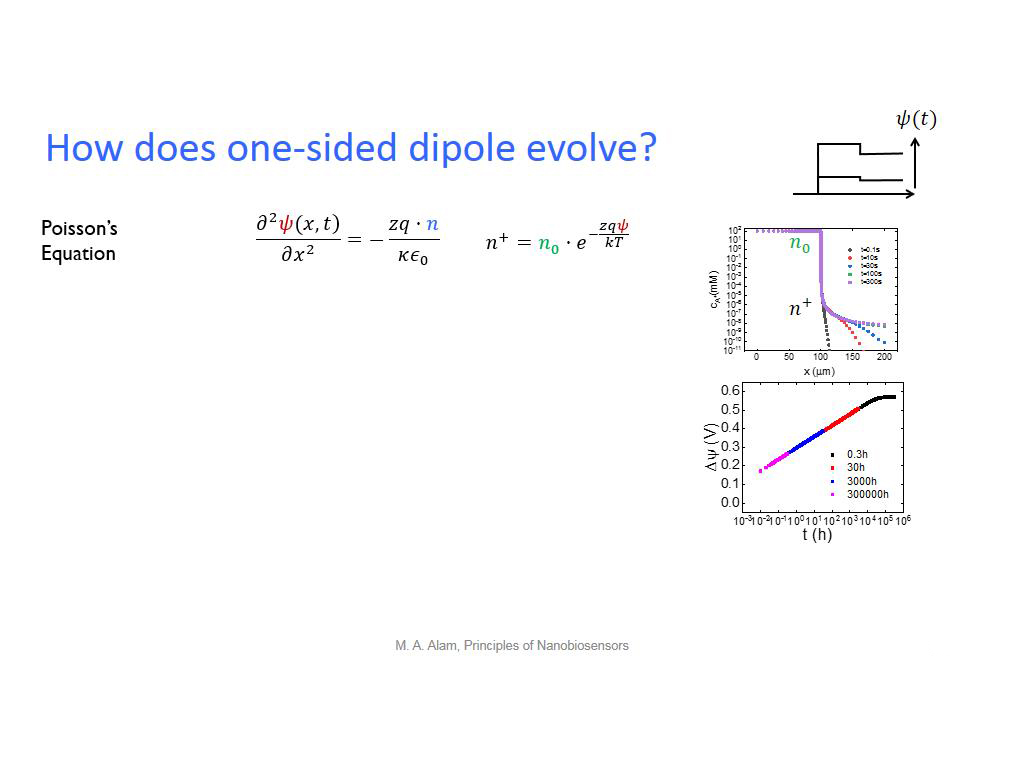
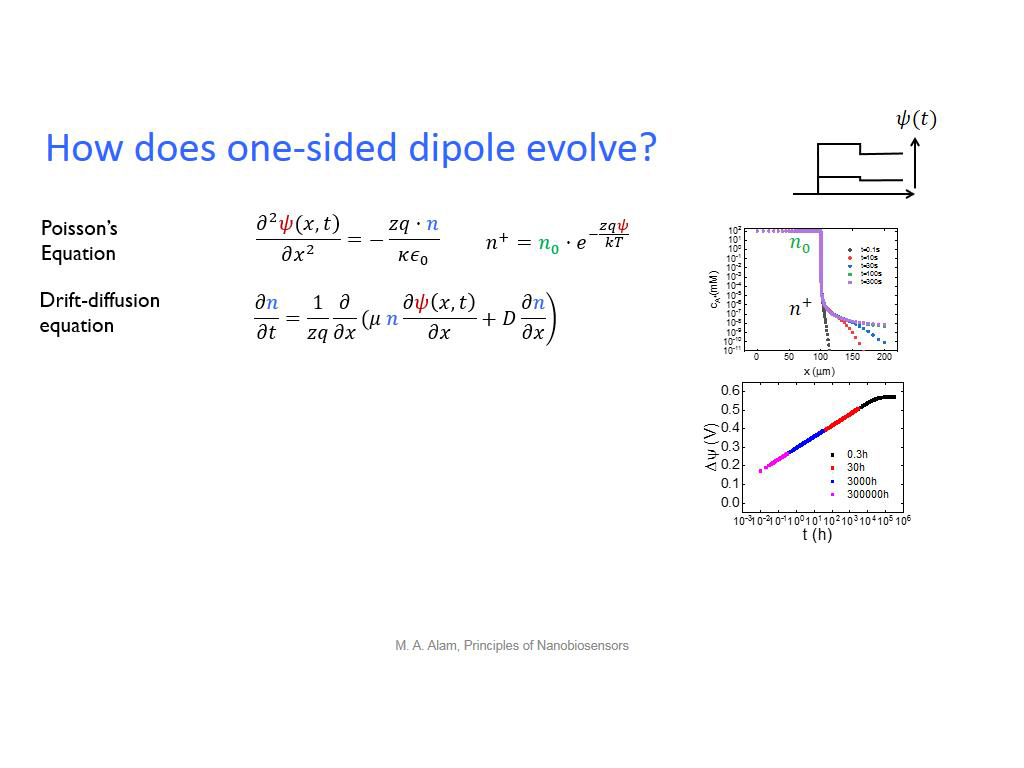
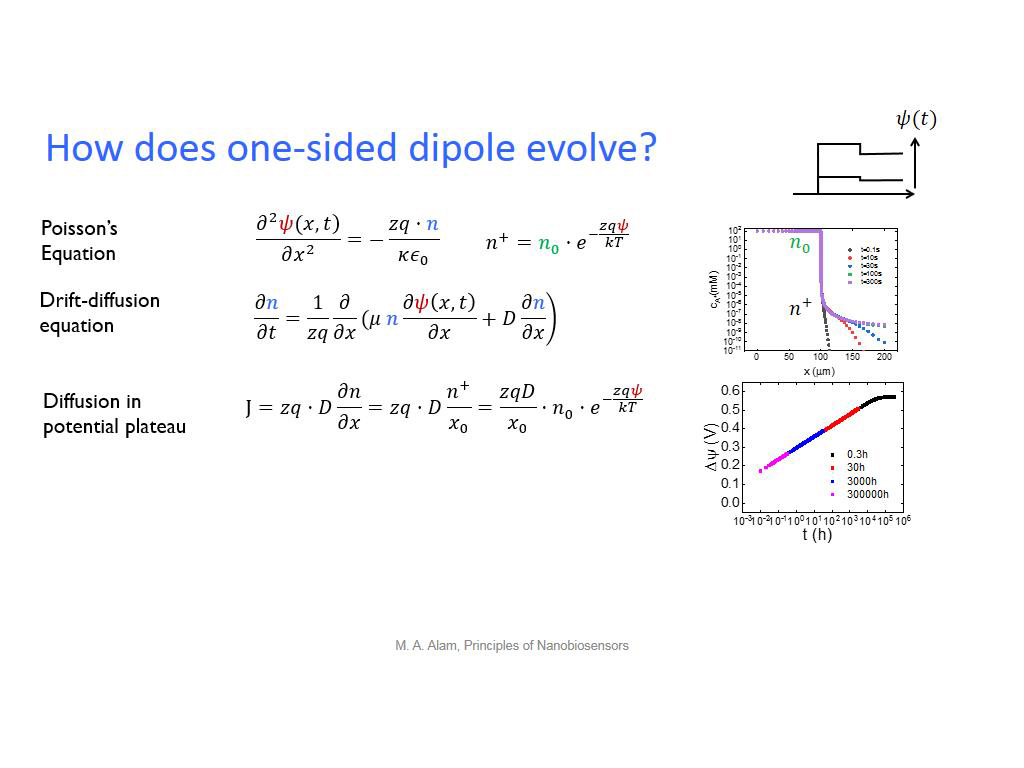
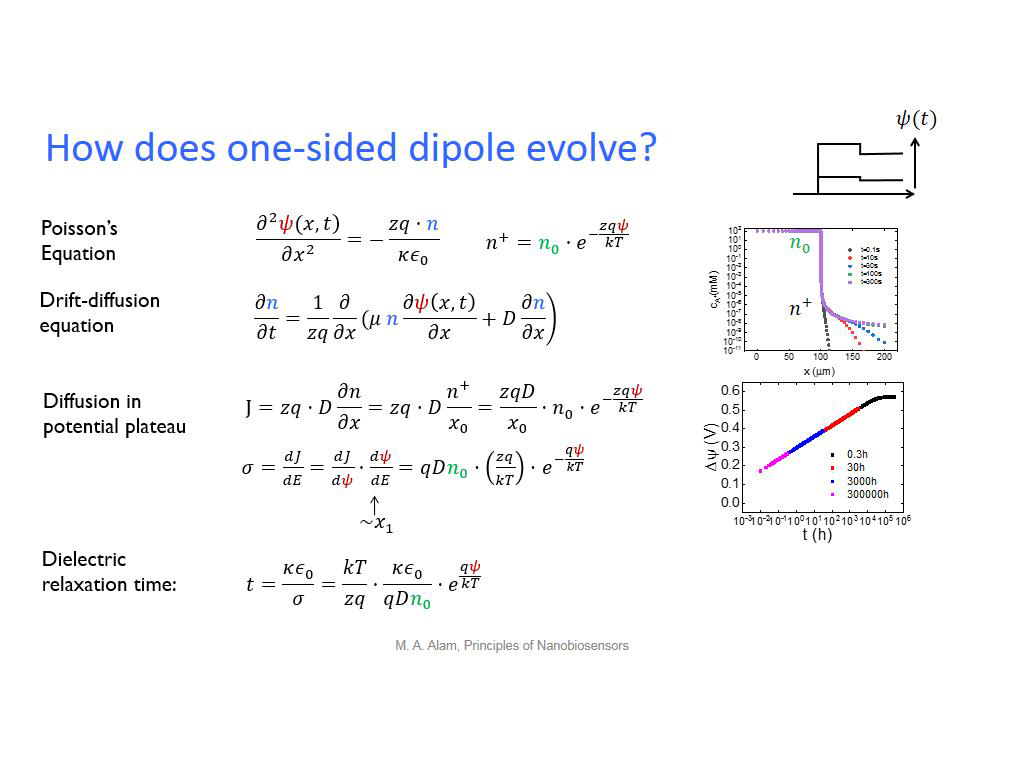
 32. How does one-sided dipole evol…
2449.94994994995
00:00/00:00
32. How does one-sided dipole evol…
2449.94994994995
00:00/00:00 -
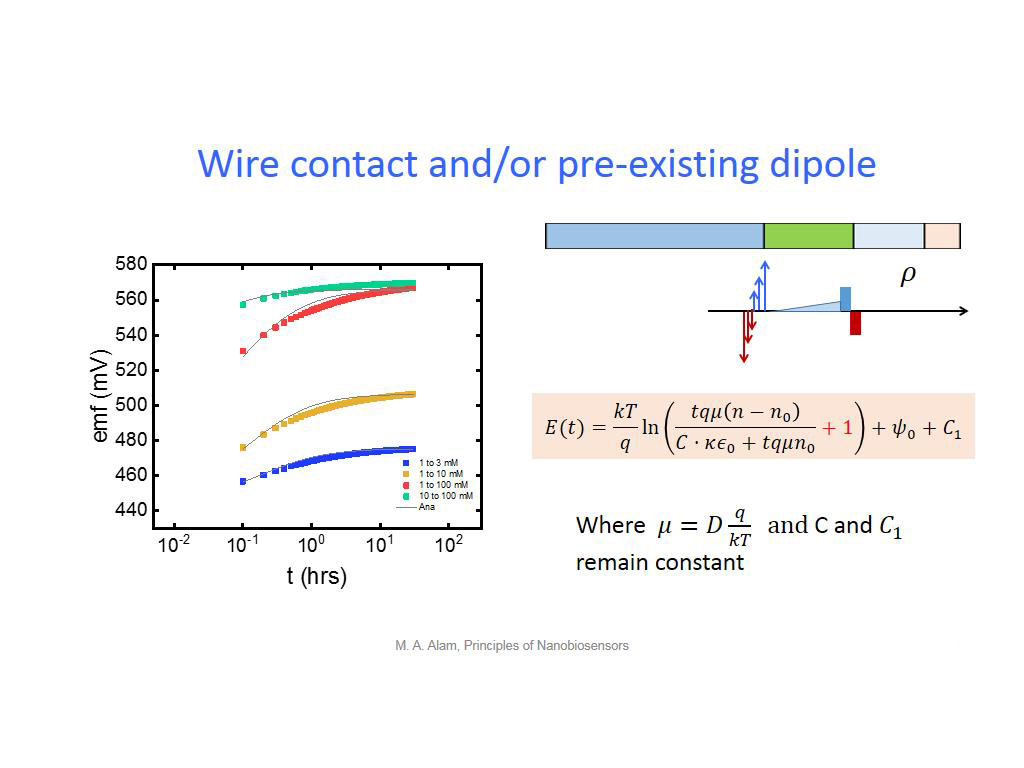 33. Wire contact and/or pre-existi…
2487.153820487154
00:00/00:00
33. Wire contact and/or pre-existi…
2487.153820487154
00:00/00:00 -
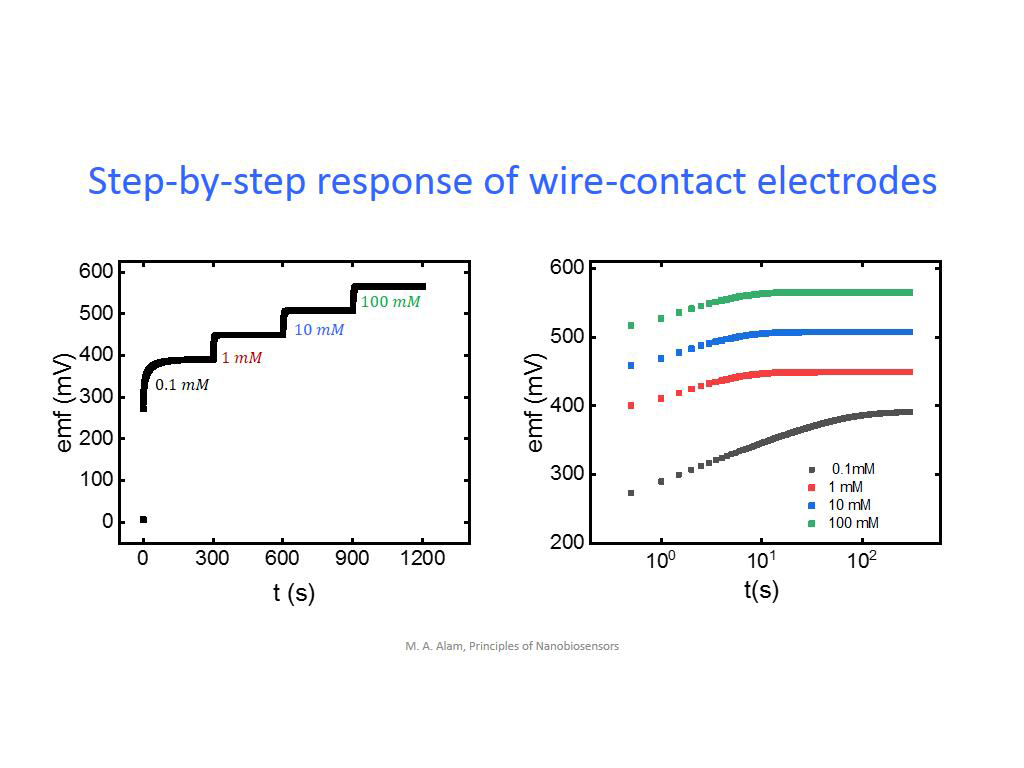 34. Step-by-step response of wire-…
2509.70970970971
00:00/00:00
34. Step-by-step response of wire-…
2509.70970970971
00:00/00:00 -
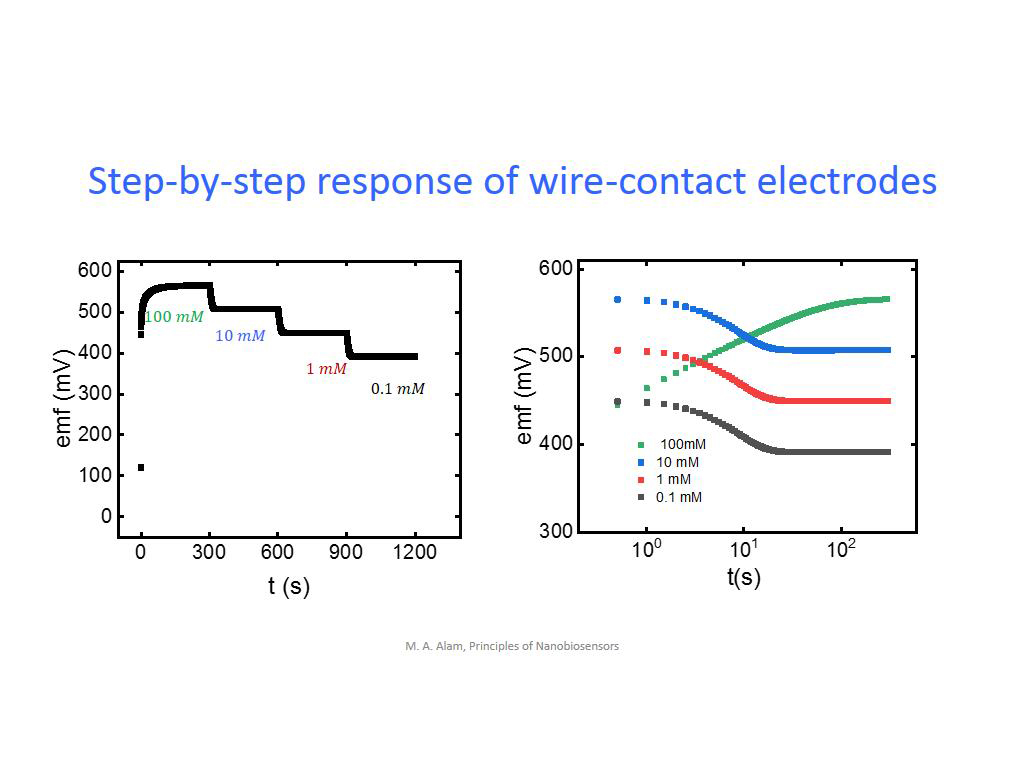 35. Step-by-step response of wire-…
2554.3543543543547
00:00/00:00
35. Step-by-step response of wire-…
2554.3543543543547
00:00/00:00 -
 36. Outline
2572.405739072406
00:00/00:00
36. Outline
2572.405739072406
00:00/00:00 -
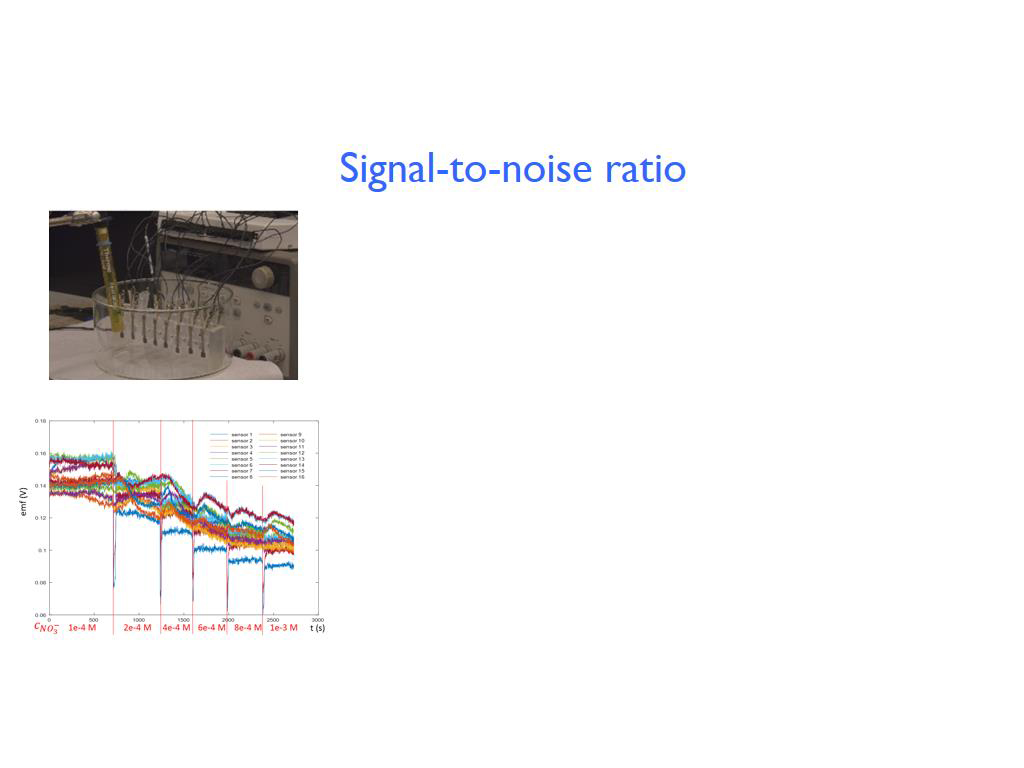
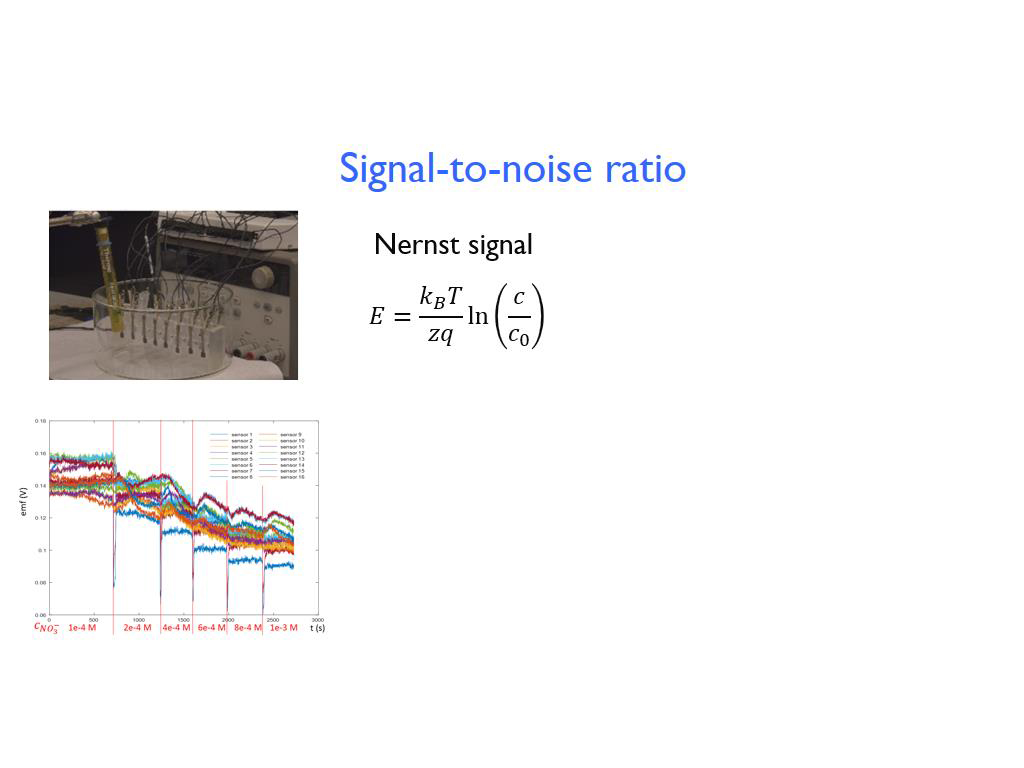
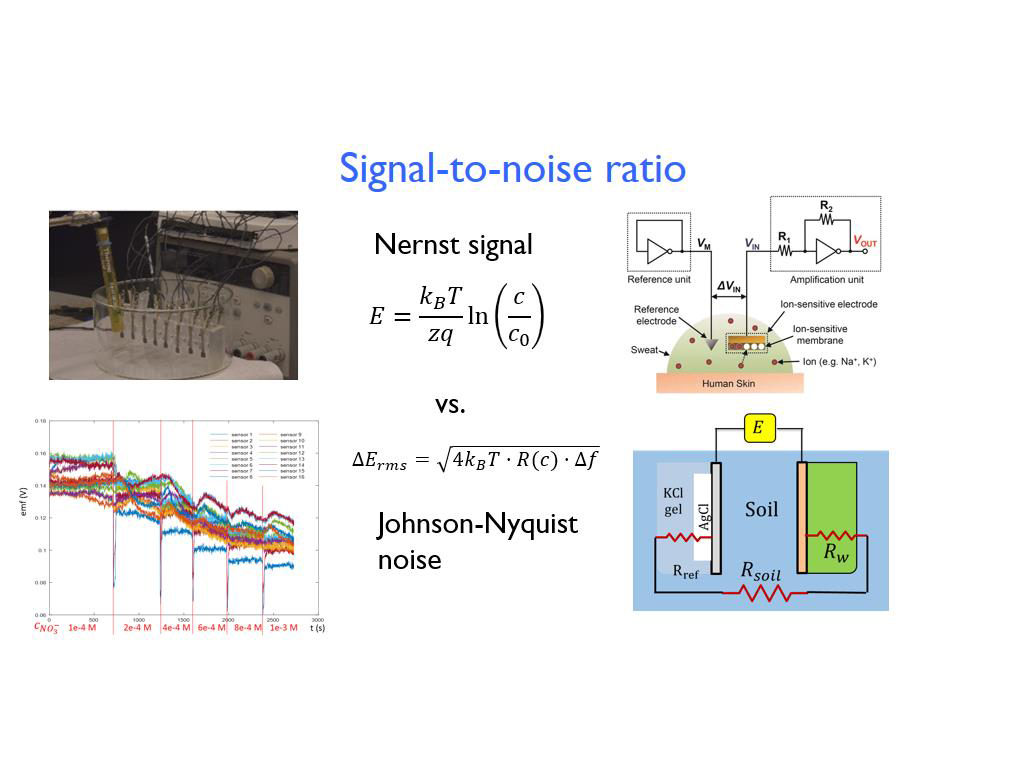 37. Signal-to-noise ratio
2607.1071071071074
00:00/00:00
37. Signal-to-noise ratio
2607.1071071071074
00:00/00:00 -
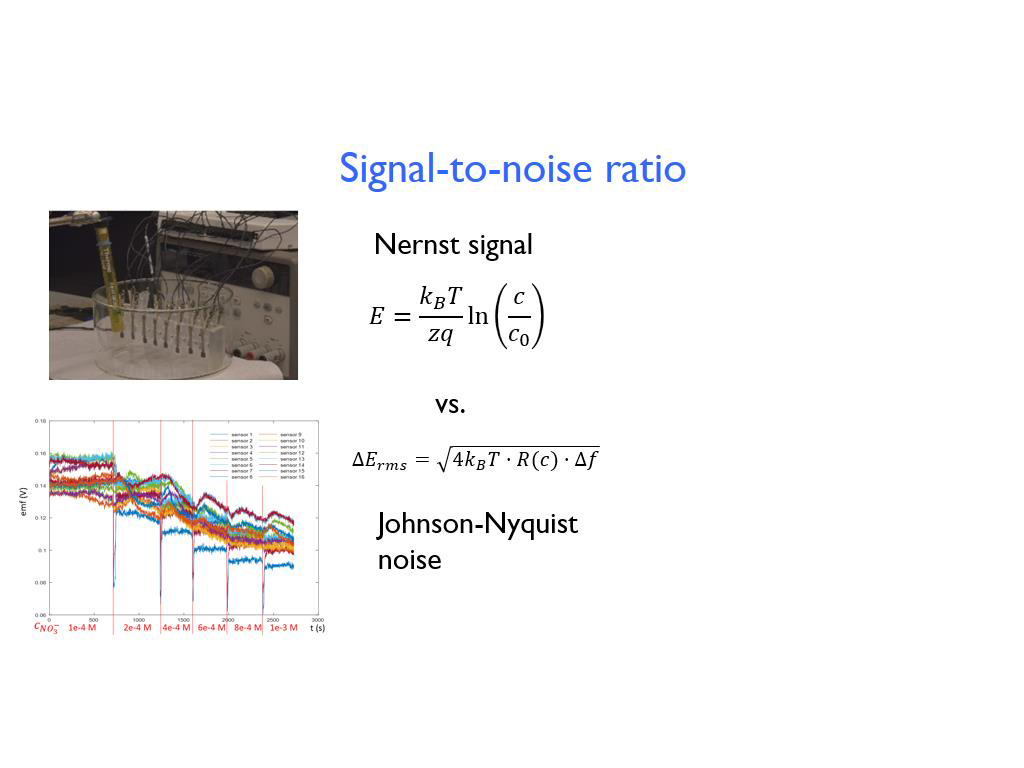
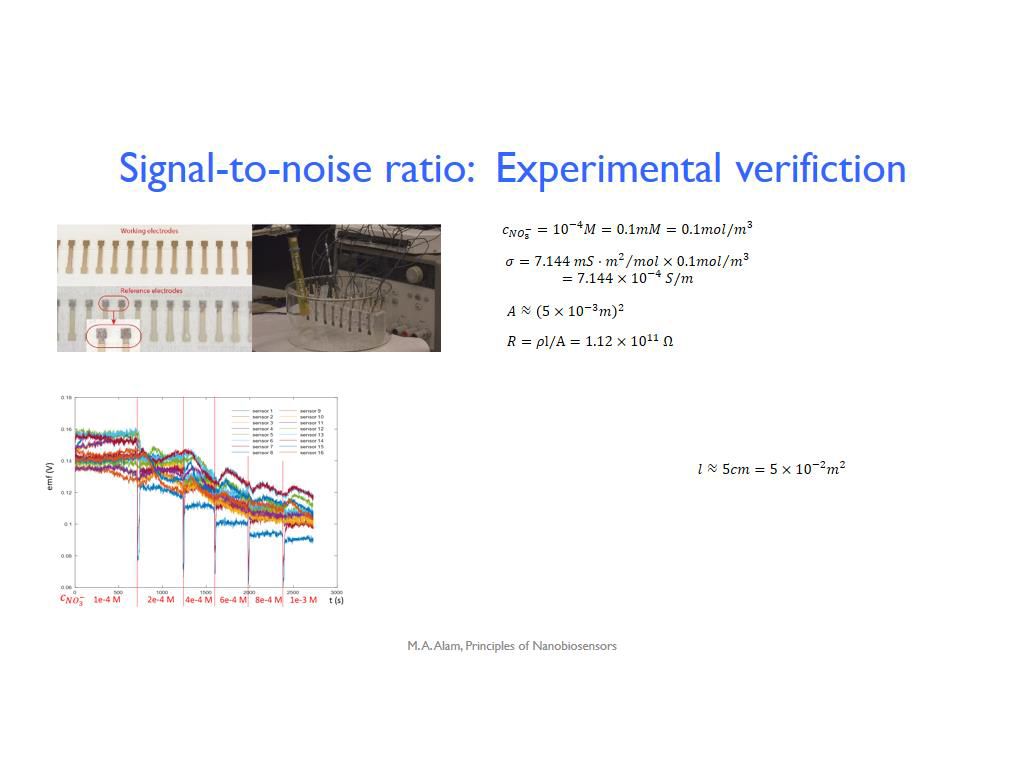
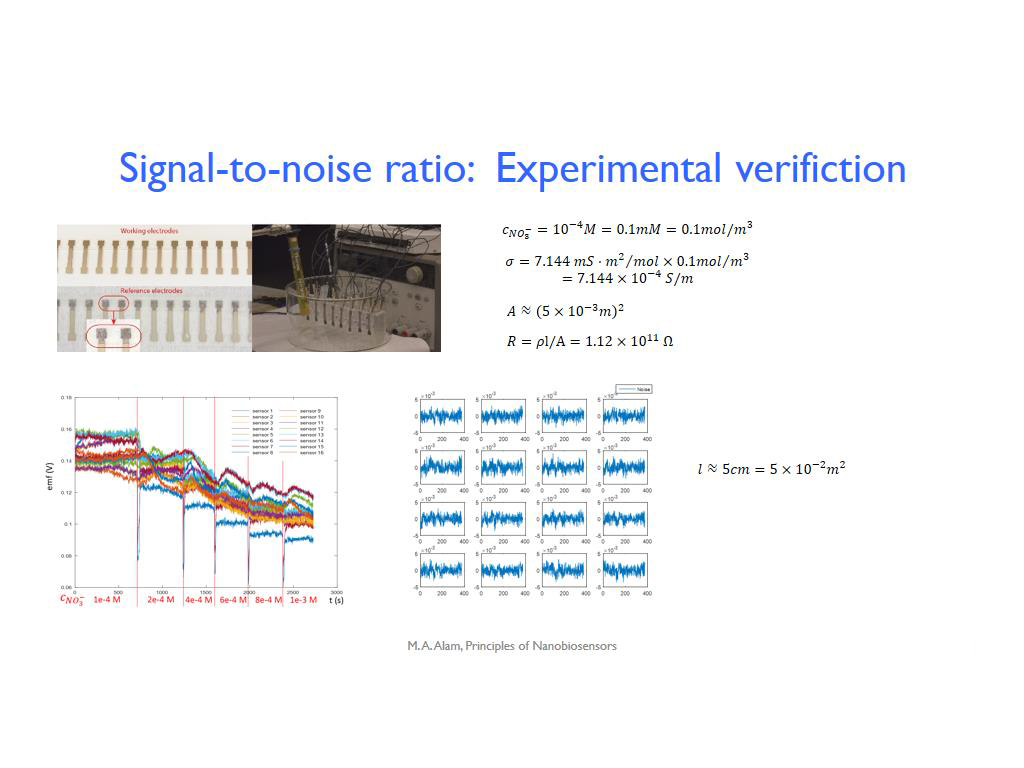
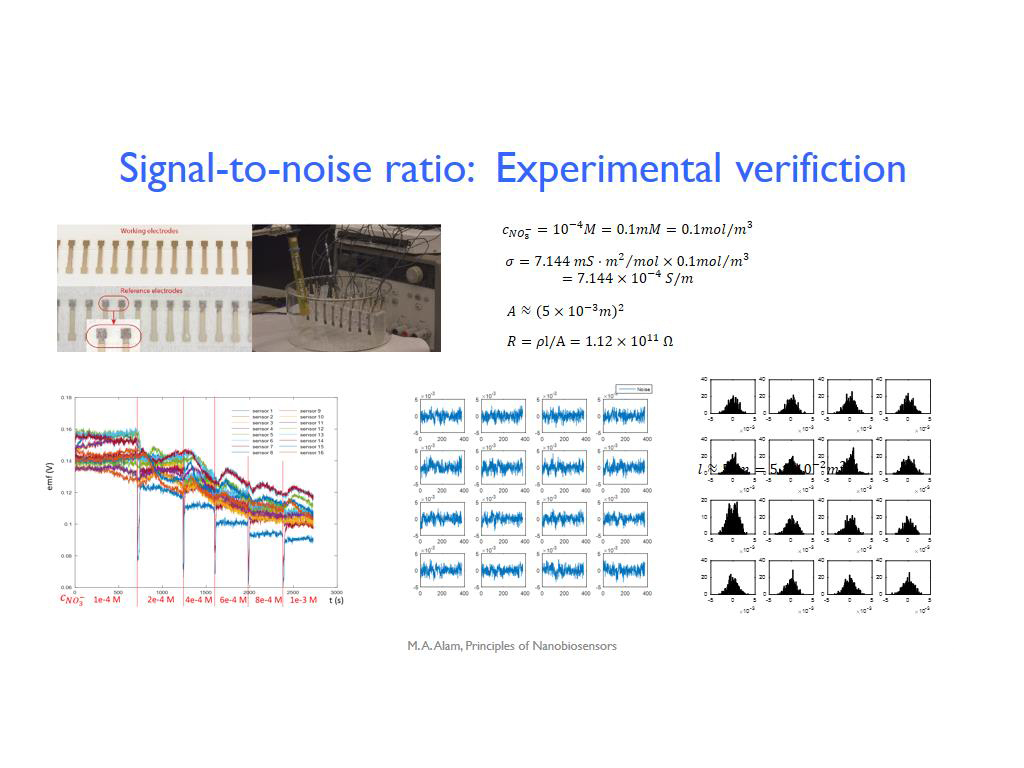
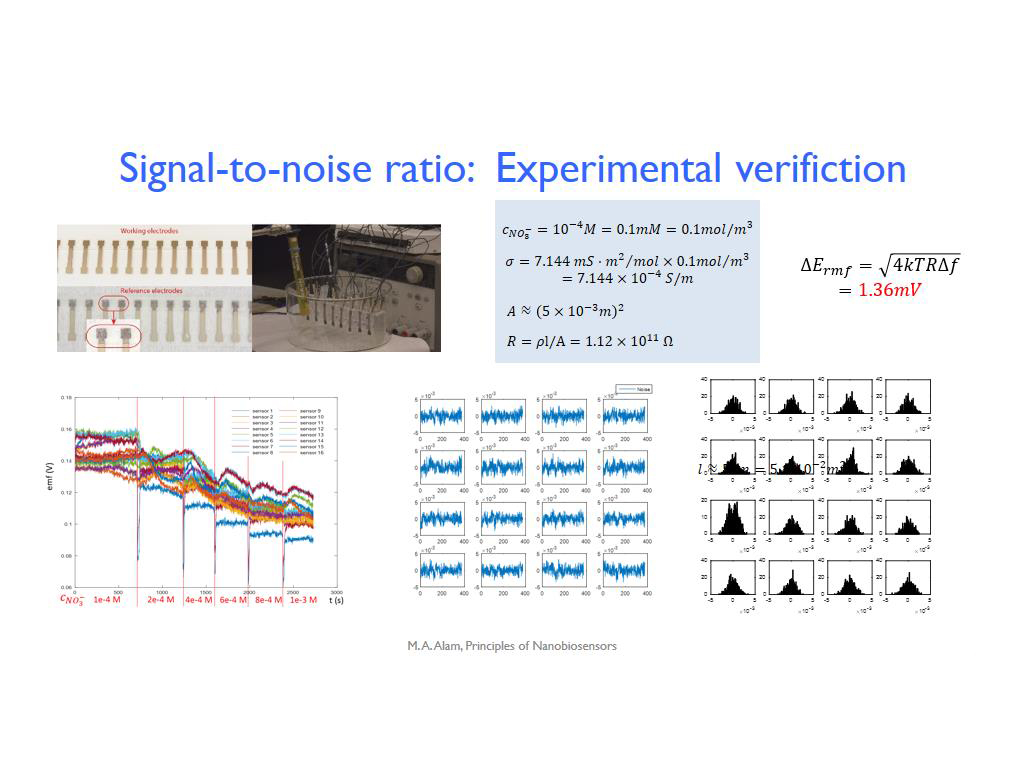 38. Signal-to-noise ratio: Experim…
2810.7774441107777
00:00/00:00
38. Signal-to-noise ratio: Experim…
2810.7774441107777
00:00/00:00 -
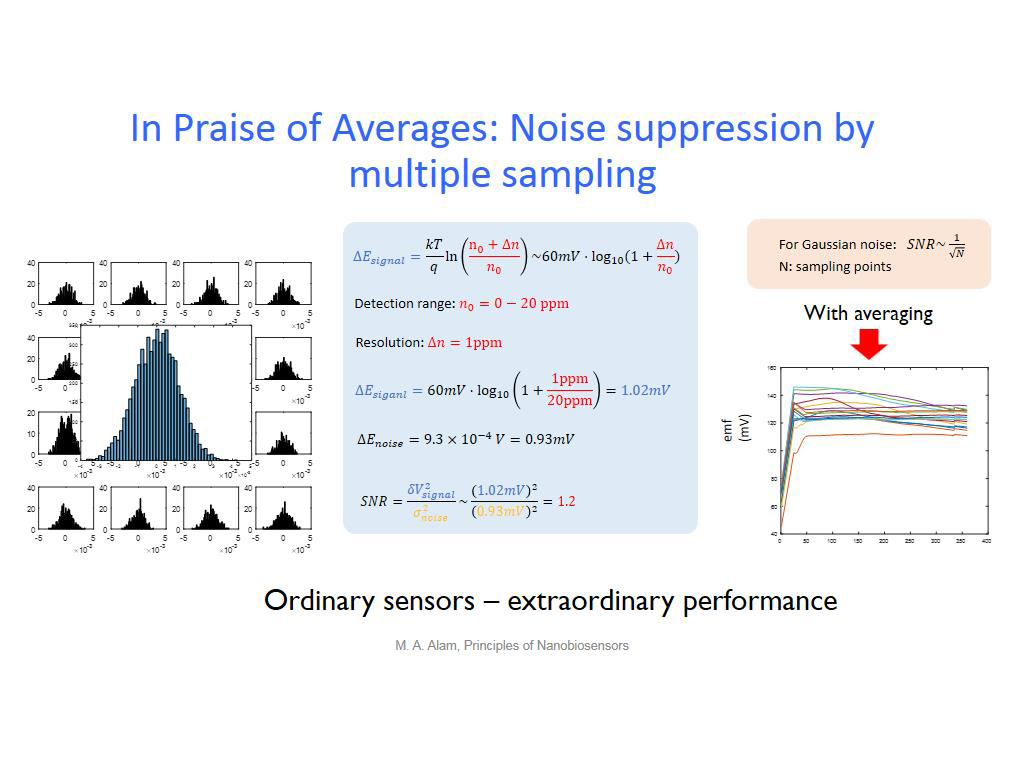 39. In Praise of Averages: Noise s…
2907.1404738071406
00:00/00:00
39. In Praise of Averages: Noise s…
2907.1404738071406
00:00/00:00 -
 40. Conclusions
3022.4891558224895
00:00/00:00
40. Conclusions
3022.4891558224895
00:00/00:00
 Muhammad Ashraful Alam is a Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering where his research and teaching focus on physics, simulation, characterization and technology of classical and emerging electronic devices. From 1995 to 2003, he was with Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, NJ, where he made important contributions to reliability physics of electronic devices, MOCVD crystal growth, and performance limits of semiconductor lasers. At Purdue, Alam’s research has broadened to include flexible electronics, solar cells, and nanobiosensors. He is a fellow of the AAAS, IEEE, and APS and received the 2006 IEEE Kiyo Tomiyasu Award for contributions to device technology.
Muhammad Ashraful Alam is a Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering where his research and teaching focus on physics, simulation, characterization and technology of classical and emerging electronic devices. From 1995 to 2003, he was with Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, NJ, where he made important contributions to reliability physics of electronic devices, MOCVD crystal growth, and performance limits of semiconductor lasers. At Purdue, Alam’s research has broadened to include flexible electronics, solar cells, and nanobiosensors. He is a fellow of the AAAS, IEEE, and APS and received the 2006 IEEE Kiyo Tomiyasu Award for contributions to device technology.